Structural controls on the emplacement of porphyry systems: the
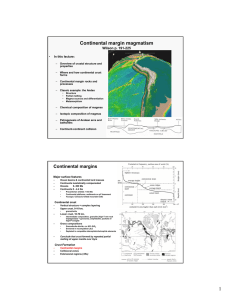
... compression, and culminated in the Early Pliocene. We have identified NW- and NE-oriented fault systems which can be followed throughout the district, oblique to the N-oriented margins of the Abanico Basin. They can be correlated with Mesozoic and Palaeozoic faults which crop out further to the west ...
... compression, and culminated in the Early Pliocene. We have identified NW- and NE-oriented fault systems which can be followed throughout the district, oblique to the N-oriented margins of the Abanico Basin. They can be correlated with Mesozoic and Palaeozoic faults which crop out further to the west ...
Slide 1
... • The Earth is constantly changing. Even the very rocks around you may have changed many times throughout their history! • The Rock Cycle explains the evolution of these igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that make up the Earth’s crust. • Many processes, such as volcanic activity, movement ...
... • The Earth is constantly changing. Even the very rocks around you may have changed many times throughout their history! • The Rock Cycle explains the evolution of these igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that make up the Earth’s crust. • Many processes, such as volcanic activity, movement ...
Movement of the Earth ’ s Crust
... form a plateau. Sometimes, magma pushes upward but does not reach the surface. The stress caused by the magma causes the rock layers above it to fold upward, forming an uplifted area. The magma cools and forms hardened rock. The uplifted area formed by rising magma is called a dome. ...
... form a plateau. Sometimes, magma pushes upward but does not reach the surface. The stress caused by the magma causes the rock layers above it to fold upward, forming an uplifted area. The magma cools and forms hardened rock. The uplifted area formed by rising magma is called a dome. ...
Detrital sediments of the ca. 3.77 Ga Nuvvuagittuq Supracrustal Belt
... amphibolites argues against a later metasomatic origin for the Amc. Oxygen isotopic analyses are underway to test this interpretation. In places, the Amc units host thin (<0.5 m thick) fuchsitic quartzites (>75wt.% SiO2; >50 ppm Cr) which share the deformational history of the belt. The quartzites h ...
... amphibolites argues against a later metasomatic origin for the Amc. Oxygen isotopic analyses are underway to test this interpretation. In places, the Amc units host thin (<0.5 m thick) fuchsitic quartzites (>75wt.% SiO2; >50 ppm Cr) which share the deformational history of the belt. The quartzites h ...
Student 1
... Southland. They exist in rocks of the Triassic-Jurassic age. They include andesites, dacites and some ignimbrite. The rocks are primarily andesites and suggest emplacement in a back arc setting near an island arc system to the east. The prominent hill near Pomahaka suggests a sill, a shallow intrusi ...
... Southland. They exist in rocks of the Triassic-Jurassic age. They include andesites, dacites and some ignimbrite. The rocks are primarily andesites and suggest emplacement in a back arc setting near an island arc system to the east. The prominent hill near Pomahaka suggests a sill, a shallow intrusi ...
How The Earth Works
... 35 minutes to birth of Christ 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
... 35 minutes to birth of Christ 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
Igneous Rocks
... Igneous Rocks Magma forms when rock in the Earth partially melts. This can occur during the following conditions: a. Pressure decreases b. Volatiles are added c. ...
... Igneous Rocks Magma forms when rock in the Earth partially melts. This can occur during the following conditions: a. Pressure decreases b. Volatiles are added c. ...
The Grenville Province
... assembled by about 1.68 billion years ago, and mostly together by about 1.45 billion years ago. Meanwhile, in the Central Metasedimentary Belt, the four sedimentary-volcanic terranes came together to make up the superterrane by about 1.25 billion years ago. Then, the final stages in the assembly of ...
... assembled by about 1.68 billion years ago, and mostly together by about 1.45 billion years ago. Meanwhile, in the Central Metasedimentary Belt, the four sedimentary-volcanic terranes came together to make up the superterrane by about 1.25 billion years ago. Then, the final stages in the assembly of ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Form from the broken bits and pieces of previously existing rocks. Quartz is the most common mineral in these sediments because quartz is a hard, tough mineral and is stable chemically at the surface of the Earth. Feldspars, the most common minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks decompose chemica ...
... Form from the broken bits and pieces of previously existing rocks. Quartz is the most common mineral in these sediments because quartz is a hard, tough mineral and is stable chemically at the surface of the Earth. Feldspars, the most common minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks decompose chemica ...
Folds and Faults - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... When a rock is subjected to increasing stress it passes through three successive stages of deformation. Elastic Deformation - the strain is reversible Ductile Deformation - the strain is irreversible Fracture - irreversible strain in which the material breaks ...
... When a rock is subjected to increasing stress it passes through three successive stages of deformation. Elastic Deformation - the strain is reversible Ductile Deformation - the strain is irreversible Fracture - irreversible strain in which the material breaks ...
CRCT Review Packet
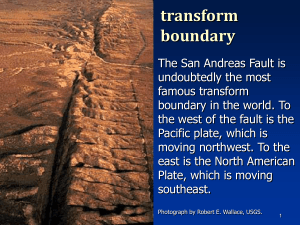
... c. The lithospheric plates are divided into two main categories: i. Oceanic crust which is ______________ dense ii. ______________ crust which is less dense 39.Complete the chart below. Type of Boundary transform Type of Fault ...
... c. The lithospheric plates are divided into two main categories: i. Oceanic crust which is ______________ dense ii. ______________ crust which is less dense 39.Complete the chart below. Type of Boundary transform Type of Fault ...
Rock Cycle 200 - FitzBrownBodleTeam
... crust meet the more dense oceanic crust will sink below the less dense continental crust 3. Where the continental crust and continental crust meet, mountains will form as the land is thrust upwards. ...
... crust meet the more dense oceanic crust will sink below the less dense continental crust 3. Where the continental crust and continental crust meet, mountains will form as the land is thrust upwards. ...
Geology Paper III
... and magnesium, c) silicon and aluminum, d) magnesiumand aluminum, e) magnesiumand silicon. ...
... and magnesium, c) silicon and aluminum, d) magnesiumand aluminum, e) magnesiumand silicon. ...
Forest River – Field Trip
... hypothesis interpreted from studies of the rocks in and around the North Shore and beyond. Paleozoic and Mesozoic History Most rocks underlying Salem, MA are over 300 million years old, and reflect a long history of volcanism and faulting related to both collision and rifting. The ancient Precambria ...
... hypothesis interpreted from studies of the rocks in and around the North Shore and beyond. Paleozoic and Mesozoic History Most rocks underlying Salem, MA are over 300 million years old, and reflect a long history of volcanism and faulting related to both collision and rifting. The ancient Precambria ...
Erosion, Transport, Deposition Key Words
... (rocks and stones) freeze-thaw action and rocks broken apart by plant roots. ...
... (rocks and stones) freeze-thaw action and rocks broken apart by plant roots. ...
Igneous Rock - East Hanover Township School District
... Earth, the larger the igneous rocks crystals will be. F) Examples of intrusive igneous rocks are granite, gabbro and diorite ...
... Earth, the larger the igneous rocks crystals will be. F) Examples of intrusive igneous rocks are granite, gabbro and diorite ...
PDF format
... E. the Marianas trench 45. Mid-ocean ridge mountain ranges are commonly associated with this type of faulting: A. normal faults B. transform faults C. thrust faults D. both A and B above E. both B and C above 46. The oceanic tectonic plate that used to exist off the entire west coast of North Americ ...
... E. the Marianas trench 45. Mid-ocean ridge mountain ranges are commonly associated with this type of faulting: A. normal faults B. transform faults C. thrust faults D. both A and B above E. both B and C above 46. The oceanic tectonic plate that used to exist off the entire west coast of North Americ ...
Rocks and The Rock Cycle
... Sedimentary Facies (facies – the character of a rock defined by its formation, composition and fossil content) ...
... Sedimentary Facies (facies – the character of a rock defined by its formation, composition and fossil content) ...
Full text
... of detrital feldspar and zircon from quartzite. The outcrop photographs show examples of soft-sediment deformation, crossbedding, and graded bedding. Chapter 24 deals with the unusual topic of fossils in metamorphic rocks. Many of these outcrop photographs illustrate fossils from the well-known loca ...
... of detrital feldspar and zircon from quartzite. The outcrop photographs show examples of soft-sediment deformation, crossbedding, and graded bedding. Chapter 24 deals with the unusual topic of fossils in metamorphic rocks. Many of these outcrop photographs illustrate fossils from the well-known loca ...
Igneous Rocks Lab - SCWIBLES - University of California, Santa Cruz
... The lava to make these rocks extrudes from, or comes out of, the earth. These rocks are called extrusive and were formed outside of the earth’s crust. They cool quickly and so have small minerals ...
... The lava to make these rocks extrudes from, or comes out of, the earth. These rocks are called extrusive and were formed outside of the earth’s crust. They cool quickly and so have small minerals ...
Chapter 10 - Continents
... How would you recognize an accreted terrane? How could you tell if it originated far away or nearby? How would you identify a region where active orogeny is taking place today? Give an example. ...
... How would you recognize an accreted terrane? How could you tell if it originated far away or nearby? How would you identify a region where active orogeny is taking place today? Give an example. ...
Metamorphic Rocks - Ms. Samuels` Science Class
... Metamorphic rocks are one of the three types of rock classifications, the other two being igneous and sedimentary. Rocks are classified by the processes under which they were formed. The differences in formation account for variations in the appearance of the rocks and, with some practice, you can l ...
... Metamorphic rocks are one of the three types of rock classifications, the other two being igneous and sedimentary. Rocks are classified by the processes under which they were formed. The differences in formation account for variations in the appearance of the rocks and, with some practice, you can l ...
Rocks - rozyckiphsscience
... – Increases with depth as the thickness of the overlying rock increases – Confining pressure: forces are applied in all directions – Produces more compact rock having greater density – Differential stress: forces that generate mountains and are unequal (produces elongated rocks---forms ...
... – Increases with depth as the thickness of the overlying rock increases – Confining pressure: forces are applied in all directions – Produces more compact rock having greater density – Differential stress: forces that generate mountains and are unequal (produces elongated rocks---forms ...
2011 ESRT created by Julie Ann Hugick (Eastchester)
... 59. What is the scale on the x-axis (eqchart)?_____________________________________________________ ...
... 59. What is the scale on the x-axis (eqchart)?_____________________________________________________ ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.