Topic 11
... - formed from particles of weathered rock - sediments can usually be seen (the rock looks and feels “dirty”) - clastic sediments can be lithified (turned into rock) in two ways: 1. compaction -- sediments accumulate, causing pressure that squeezes sediments together EX/ silt siltstone; clay shal ...
... - formed from particles of weathered rock - sediments can usually be seen (the rock looks and feels “dirty”) - clastic sediments can be lithified (turned into rock) in two ways: 1. compaction -- sediments accumulate, causing pressure that squeezes sediments together EX/ silt siltstone; clay shal ...
Chapter 8 Notes
... unexpectedly along a fault - fault zones/seismic activity - Richter Scale * measurement of ground movement * increases by a factor of 10 ...
... unexpectedly along a fault - fault zones/seismic activity - Richter Scale * measurement of ground movement * increases by a factor of 10 ...
A review sheet
... d. none of these 24. Which of the following is a common dark silicate mineral? (C) a. muscovite b. potassium feldspar c. olivine d. quartz 25. Which of the following is the most important factor that contributes to the viscosity of magma? (B) a. temperature of the magma b. amount of silica present i ...
... d. none of these 24. Which of the following is a common dark silicate mineral? (C) a. muscovite b. potassium feldspar c. olivine d. quartz 25. Which of the following is the most important factor that contributes to the viscosity of magma? (B) a. temperature of the magma b. amount of silica present i ...
Rocks and the Rock Cycle
... A. James Hutton (1795) began concept of uniformitarianism, which states that: 1. The same geologic processes have always been at work. 2. These processes formed the Earth as it is today over a long period of time. B. Rock (def'n) - a group of minerals bound together in some way. C. Igneous rocks for ...
... A. James Hutton (1795) began concept of uniformitarianism, which states that: 1. The same geologic processes have always been at work. 2. These processes formed the Earth as it is today over a long period of time. B. Rock (def'n) - a group of minerals bound together in some way. C. Igneous rocks for ...
mountain building chapter 11 - NVHSEarthScienceKDudenhausen
... ______________– when the hanging wall block moves down relative to the footwall block, caused by tensional forces ______________– the hanging wall block moves up relative to the footwall, caused by compressional forces ______________– reverse faults with dips less than 45o ...
... ______________– when the hanging wall block moves down relative to the footwall block, caused by tensional forces ______________– the hanging wall block moves up relative to the footwall, caused by compressional forces ______________– reverse faults with dips less than 45o ...
Plate Boundaries - Learn Earth Science
... • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
... • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
Plate Boundaries
... • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
... • Alfred Wegner, 1915 • The continents were once a super-continent called Pangea • the continents are plowing through the ocean floors---most people didn’t believe this ...
Name
... A. two plates carrying oceanic crust collideB. two plates carrying continental crust collideC. a plate made of oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust5. Explain what force caused the movement of the continents from one super-continent to their present positions. ...
... A. two plates carrying oceanic crust collideB. two plates carrying continental crust collideC. a plate made of oceanic crust collides with a plate carrying continental crust5. Explain what force caused the movement of the continents from one super-continent to their present positions. ...
Museum of Natural History field trip - e
... The most abundant elements in Earth’s crust are three: O, Si, Al. The most abundant elements in Earth as a whole (which includes the composition of the mantle and core), and the other stony planets, are four : _____, _____, _____, ______. The most abundant elements in the giant gas planets are two: ...
... The most abundant elements in Earth’s crust are three: O, Si, Al. The most abundant elements in Earth as a whole (which includes the composition of the mantle and core), and the other stony planets, are four : _____, _____, _____, ______. The most abundant elements in the giant gas planets are two: ...
Geology of the Precambrian Sangre De Cristo Range of New Mexico
... -It was a prolonged thermotectonic episode resulting from collision, subduction, and continued convergence. -This occurred along the paleosuture known as the Cheyenne Belt along the Archean Wyoming ...
... -It was a prolonged thermotectonic episode resulting from collision, subduction, and continued convergence. -This occurred along the paleosuture known as the Cheyenne Belt along the Archean Wyoming ...
2.0 The Rock Cycle describes how rocks form and change over time
... Scientists classify rocks into categories which have shared characteristics. Geology Tools and Techniques Remote Sensing – satellite mapping of the Earth’s surface Geophysical prospecting – sensitive instruments like the magnetometer detect minerals hidden deep beneath the surface of the Earth. Geoc ...
... Scientists classify rocks into categories which have shared characteristics. Geology Tools and Techniques Remote Sensing – satellite mapping of the Earth’s surface Geophysical prospecting – sensitive instruments like the magnetometer detect minerals hidden deep beneath the surface of the Earth. Geoc ...
Drive from UW to Snoqualmie Pass
... ago in a series of about 40 floods that had devastating effects on eastern Washington. For a short time, the floods carried flows greater than all present rivers of the world combined. They cut channels in the loess (wind-deposited glacially-derived sediment) down to the basalt bedrock to form the c ...
... ago in a series of about 40 floods that had devastating effects on eastern Washington. For a short time, the floods carried flows greater than all present rivers of the world combined. They cut channels in the loess (wind-deposited glacially-derived sediment) down to the basalt bedrock to form the c ...
MineralsRocksCycle
... compacted and cemented sediments • Weathering physically and chemically breaks rocks into small pieces called sediments • Sediments are moved by wind, water, ice, and gravity • Eventually, they are dropped and form layers that are cemented together ...
... compacted and cemented sediments • Weathering physically and chemically breaks rocks into small pieces called sediments • Sediments are moved by wind, water, ice, and gravity • Eventually, they are dropped and form layers that are cemented together ...
File
... 8) Most earthquakes along the _________________________________________________. 9) There are approximately ____________________ earthquakes in Canada each year, but only a few of these are strong enough to be felt by people. 10) A _______________________ is an opening of Earth’s crust. 11) Volcani ...
... 8) Most earthquakes along the _________________________________________________. 9) There are approximately ____________________ earthquakes in Canada each year, but only a few of these are strong enough to be felt by people. 10) A _______________________ is an opening of Earth’s crust. 11) Volcani ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... – Burial Metamorphism – e.g. Burial of sediments deeper than 10 km – non-foliated – Dynamothermal Metamorphism – Directed pressure in Plate Tectonic Processes - foliated ...
... – Burial Metamorphism – e.g. Burial of sediments deeper than 10 km – non-foliated – Dynamothermal Metamorphism – Directed pressure in Plate Tectonic Processes - foliated ...
Metamorphic Rocks - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... - aureole = zone of contact between pluton and adjacent material - usually 1 - 100 meters wide that is changed (metamorphosed) Page 161 Fig. 7.9 e.g. limestone changes to marble (marble quarries from which marble ‘mined’ aren’t huge since they represent the contact area of a pluton and sedimentary r ...
... - aureole = zone of contact between pluton and adjacent material - usually 1 - 100 meters wide that is changed (metamorphosed) Page 161 Fig. 7.9 e.g. limestone changes to marble (marble quarries from which marble ‘mined’ aren’t huge since they represent the contact area of a pluton and sedimentary r ...
Test # 2 Study Guide Weathering What is Weathering? - in
... - characterized by a conchoidal fracture ...
... - characterized by a conchoidal fracture ...
Magma Emplacement Room Problem How to Accommodate Plutons
... • Variable time intervals (and cooling histories) between intrusions ...
... • Variable time intervals (and cooling histories) between intrusions ...
Review questions exam I
... 2. How do interactions between the solid earth system and the hydrological system led to sedimentary rocks? 3. Explain why silicates are the most abundant mineral class and why there is such a diversity in silicate mineral structure types. 4. Describe how magma forms at a convergent plate boundary a ...
... 2. How do interactions between the solid earth system and the hydrological system led to sedimentary rocks? 3. Explain why silicates are the most abundant mineral class and why there is such a diversity in silicate mineral structure types. 4. Describe how magma forms at a convergent plate boundary a ...
Chapter 11 Study GuideName: Section 11.1 – Rock Deformation
... 29. Is the following sentence true or false? At a convergent boundary between two plates carrying continental crust, a collision between the continental fragments will result in the formation of folded mountains. ________________________ 30. ________________________ mountains are formed along ocean ...
... 29. Is the following sentence true or false? At a convergent boundary between two plates carrying continental crust, a collision between the continental fragments will result in the formation of folded mountains. ________________________ 30. ________________________ mountains are formed along ocean ...
No Slide Title
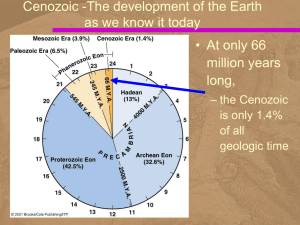
... Cenozoic -The development of the Earth as we know it today • At only 66 million years long, – the Cenozoic is only 1.4% of all geologic time ...
... Cenozoic -The development of the Earth as we know it today • At only 66 million years long, – the Cenozoic is only 1.4% of all geologic time ...
Granitoid Rocks
... Associated volcanics are common and have same origin, but are typically eroded away ...
... Associated volcanics are common and have same origin, but are typically eroded away ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.