Glossary
... The innermost part of the Earth and consisting of a solid central region and surrounded by a liquid zone. The predominant elements are iron and nickel. A circular depression usually found at the top of a volcanic vent from which erupts magma and gases. ...
... The innermost part of the Earth and consisting of a solid central region and surrounded by a liquid zone. The predominant elements are iron and nickel. A circular depression usually found at the top of a volcanic vent from which erupts magma and gases. ...
Rock Cycle - SchoolSpeak
... How the cycle works: • Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic rocks undergo weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction & cementation to form sedimentary rock. ...
... How the cycle works: • Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic rocks undergo weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction & cementation to form sedimentary rock. ...
The Isotopic Datings by U-Pb in Zircons of Granitoides of Gashi
... the granitic massif of Fierza are dated by U-Pb method in zircons. The isotopic dating is realized in the Istem, CC 066 Laboratory of the Montpellie II University, France. Based on these data we conclude that there are two kinds of granitoide rocks. Juniku granites is dated 329.6±2.1 Ma (Carbon, Mis ...
... the granitic massif of Fierza are dated by U-Pb method in zircons. The isotopic dating is realized in the Istem, CC 066 Laboratory of the Montpellie II University, France. Based on these data we conclude that there are two kinds of granitoide rocks. Juniku granites is dated 329.6±2.1 Ma (Carbon, Mis ...
Unit 1 Major land forms and water forms DEFINITIONS
... plateau. An extensive, relatively flat upland area. plate tectonics. The theory that Earth's crust consists of eight large and several small plates. The movement of some plates causes earthquakes and volcanoes. This occurs when one plate plunges below another. At oceanic ridges, plates divide and ma ...
... plateau. An extensive, relatively flat upland area. plate tectonics. The theory that Earth's crust consists of eight large and several small plates. The movement of some plates causes earthquakes and volcanoes. This occurs when one plate plunges below another. At oceanic ridges, plates divide and ma ...
GEOHAZARD, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS OF
... from Northern Luzon to Sothern Mindanao called the Philippine Fault line. The Philippine trench in the east and the Cotabato trench in southwest encompassing the island of Mindanao on sea and a Mindanao fault is present on land trending southeast to northwest. In Sulop, Davao del Sur, a thrust fault ...
... from Northern Luzon to Sothern Mindanao called the Philippine Fault line. The Philippine trench in the east and the Cotabato trench in southwest encompassing the island of Mindanao on sea and a Mindanao fault is present on land trending southeast to northwest. In Sulop, Davao del Sur, a thrust fault ...
Name GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Igneous Rocks
... on the basis of their mineral content (or other components if minerals are not present) and texture. The system of classification and the textural terminology are different, however, for the three groups (igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary) of rocks. It is therefore important to determine the rock gr ...
... on the basis of their mineral content (or other components if minerals are not present) and texture. The system of classification and the textural terminology are different, however, for the three groups (igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary) of rocks. It is therefore important to determine the rock gr ...
07_Metamorphic-Rocks_Lab7_10thEd_FW2017
... easily or at the fastest rate generally occur along plate margins. Wherever there is a high geothermal gradient such as near intrusions, in the crust along an arc or with rapid burial rocks encounter new thermal conditions. This is also the most likely place to experience rapid pressure increase or ...
... easily or at the fastest rate generally occur along plate margins. Wherever there is a high geothermal gradient such as near intrusions, in the crust along an arc or with rapid burial rocks encounter new thermal conditions. This is also the most likely place to experience rapid pressure increase or ...
EESC1163 Environmental Resources and Issues Final Exam_July
... a) Plate tectonic processes control the rock-forming processes prevalent at plate boundaries. b) Plate tectonic processes are directly responsible for weathering. c) Plate tectonic processes are responsible for the internal heat that causes metamorphism and melting. d) Plate tectonic processes ...
... a) Plate tectonic processes control the rock-forming processes prevalent at plate boundaries. b) Plate tectonic processes are directly responsible for weathering. c) Plate tectonic processes are responsible for the internal heat that causes metamorphism and melting. d) Plate tectonic processes ...
Slide 1
... Earthquake = the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy. Focus = point inside Earth where the earthquake starts. Epicenter = location on the surface directly above the focus. Epicenter and Focus http://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/animations/earthquakes/index.html ...
... Earthquake = the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy. Focus = point inside Earth where the earthquake starts. Epicenter = location on the surface directly above the focus. Epicenter and Focus http://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/animations/earthquakes/index.html ...
Bedrock v7 - University of Michigan
... thickness of about 15,000 feet beneath Midland. The oldest formations reach the surface around the margins of the Michigan Basin and are buried at great depth in the central part of the basin, whereas the younger formations are near the surface in the center of the basin. Beneath these Michigan Basi ...
... thickness of about 15,000 feet beneath Midland. The oldest formations reach the surface around the margins of the Michigan Basin and are buried at great depth in the central part of the basin, whereas the younger formations are near the surface in the center of the basin. Beneath these Michigan Basi ...
Picture Review Name
... 83. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 84. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 85. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 86. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 87. What is the relationship between o ...
... 83. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 84. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 85. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 86. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 87. What is the relationship between o ...
Igneous Rocks - School District of Grafton
... Veins: streaks of valuable metal within a mineral. Created when a metal-rich fluid, such as goldquartz, goes through fractional crystallization, the mineral (quartz) has a lower crystallization temp and thus solidifies before the gold. The gold remains liquid and settles between the quartz ...
... Veins: streaks of valuable metal within a mineral. Created when a metal-rich fluid, such as goldquartz, goes through fractional crystallization, the mineral (quartz) has a lower crystallization temp and thus solidifies before the gold. The gold remains liquid and settles between the quartz ...
rocks-sec 2 igneous
... In certain places within the Earth, the temperature and pressure are just right for rocks to melt and form magma. ...
... In certain places within the Earth, the temperature and pressure are just right for rocks to melt and form magma. ...
Structural Geology
... • Faults are fractures along which displacement has occurred. • Joints are fractures where there has been no displacement. ...
... • Faults are fractures along which displacement has occurred. • Joints are fractures where there has been no displacement. ...
Chapter 11
... Strike-slip fault: A fault where the rocks on opposite sides of the fault plane move horizontally. ...
... Strike-slip fault: A fault where the rocks on opposite sides of the fault plane move horizontally. ...
Plate Tectonics
... Earth’s Interior Crust- Earth’s “outer skin” 3-40 miles thick. Made of solid rock. Thickest on continents (continental crust), thinnest below ocean (oceanic crust) Mantle- largest layer, plastic-like and able to flow Outer core- liquid iron and nickel. Inner core- solid iron and nickel because of e ...
... Earth’s Interior Crust- Earth’s “outer skin” 3-40 miles thick. Made of solid rock. Thickest on continents (continental crust), thinnest below ocean (oceanic crust) Mantle- largest layer, plastic-like and able to flow Outer core- liquid iron and nickel. Inner core- solid iron and nickel because of e ...
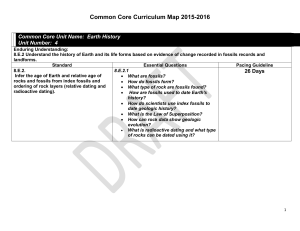
Earth History Unit Number: 4
... time scale to show how Earth has changed over time? What evidence supports the fact that Earth's constant changing has lead to major geologic events such as Ice Ages, volcanic activity and continental ...
... time scale to show how Earth has changed over time? What evidence supports the fact that Earth's constant changing has lead to major geologic events such as Ice Ages, volcanic activity and continental ...
DE pg 101
... Usually organic, because made of pebbles. may be formed from Cemented by clay, mud, & shells of sea animals. sand. Chalk is soft limestone Pebbles are smooth & round, because they are Coal: weathered by water. Made from dead plants Also called puddingstone. Breccia – sharp/angular Sand ...
... Usually organic, because made of pebbles. may be formed from Cemented by clay, mud, & shells of sea animals. sand. Chalk is soft limestone Pebbles are smooth & round, because they are Coal: weathered by water. Made from dead plants Also called puddingstone. Breccia – sharp/angular Sand ...
Chapter 22 Notes
... by the solidification of magma. They are classified according to their size and shape and their orientation with respect to the surrounding rock. Discordant means the pluton cuts across the grain of the surrounding rock and concordant means it lies in the same direction as the grain of the surroundi ...
... by the solidification of magma. They are classified according to their size and shape and their orientation with respect to the surrounding rock. Discordant means the pluton cuts across the grain of the surrounding rock and concordant means it lies in the same direction as the grain of the surroundi ...
Name - mrspilkington
... Mountains are found on every continent. They cover about one-fifth of the surface of the earth. What forces caused the majestic mountains that have formed on the earth's landscape? Many mountains form at or near plate boundaries. Remember that the lithosphere is broken up into large plates. These pl ...
... Mountains are found on every continent. They cover about one-fifth of the surface of the earth. What forces caused the majestic mountains that have formed on the earth's landscape? Many mountains form at or near plate boundaries. Remember that the lithosphere is broken up into large plates. These pl ...
Volcano Directed Reading
... 21. Describe what happens to volcanic activity when the lithospheric plate above a mantle plume continues to drift. _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 13. 2 DIRECTED READING 22. Lava provides an opportu ...
... 21. Describe what happens to volcanic activity when the lithospheric plate above a mantle plume continues to drift. _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 13. 2 DIRECTED READING 22. Lava provides an opportu ...
STEM-Exam-3-Earth-Sci-Study-Guide
... Metamorphic rock is rock that was once form of rock but has changed to another under the influence of heat, pressure, or some other agent without passing through a liquid phase Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies ...
... Metamorphic rock is rock that was once form of rock but has changed to another under the influence of heat, pressure, or some other agent without passing through a liquid phase Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies ...
Picture Review Name
... 83. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 84. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 85. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 86. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 87. What is the relationship between o ...
... 83. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 84. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 85. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 86. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 87. What is the relationship between o ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.