Chapter 6 – Igneous rock
... • Intrusive igneous rocks (magma that hardens belowground) include such common, coarse-grained rocks as granite, diorite, and gabbro. • When large blobs of magma harden underground, it can create different structures such as plutons (i.e. Enchanted Rock) and tabular intrusions. • Extrusive igneous ...
... • Intrusive igneous rocks (magma that hardens belowground) include such common, coarse-grained rocks as granite, diorite, and gabbro. • When large blobs of magma harden underground, it can create different structures such as plutons (i.e. Enchanted Rock) and tabular intrusions. • Extrusive igneous ...
Chapter 7 Notes - Wachter Middle School
... a. Rock layers on either side of the fault are called fault blocks. The position of a fault block determines whether it is a hanging wall or a footwall. b. When rocks are pulled apart due to tension, normal faults often result. [See Fig. 20, page 183] c. When rocks are pushed together by compression ...
... a. Rock layers on either side of the fault are called fault blocks. The position of a fault block determines whether it is a hanging wall or a footwall. b. When rocks are pulled apart due to tension, normal faults often result. [See Fig. 20, page 183] c. When rocks are pushed together by compression ...
Who developed the theory that the continents were once joined
... 18. Give an example of a divergent plate boundary involving two continental plates. Great Rift Valley of Africa 19. Plates that move towards one another are called? convergent plate boundary 20. What is a subduction zone? A more dense oceanic plate is forced under a less dense continental plate 21. ...
... 18. Give an example of a divergent plate boundary involving two continental plates. Great Rift Valley of Africa 19. Plates that move towards one another are called? convergent plate boundary 20. What is a subduction zone? A more dense oceanic plate is forced under a less dense continental plate 21. ...
Geology of Arkansas Headwaters Recreation Area
... – The west most ridge of the uplift visible approaching Coaldale from the northwest is made up of mostly tan Precambrian granite with a little metamorphic rock – From Coaldale to Texas Creek, the uplift consists of tan/pink/orange Precambrian granites with some metamorphic gneiss and schist mixed in ...
... – The west most ridge of the uplift visible approaching Coaldale from the northwest is made up of mostly tan Precambrian granite with a little metamorphic rock – From Coaldale to Texas Creek, the uplift consists of tan/pink/orange Precambrian granites with some metamorphic gneiss and schist mixed in ...
Plate Tectonics and Mountain Building – Study Guide Plate
... 6. According to the theory of plate tectonics, the __________________ was divided into _________ 7. What kind of plate boundary occurs where two plates grind past each other without destroying or producing lithosphere? 8. A divergent boundary at two oceanic plates can result in a ____. 9. What type ...
... 6. According to the theory of plate tectonics, the __________________ was divided into _________ 7. What kind of plate boundary occurs where two plates grind past each other without destroying or producing lithosphere? 8. A divergent boundary at two oceanic plates can result in a ____. 9. What type ...
Itinerary - Cin
... will see different colored rocks here, the colors reflecting different proportions and types of minerals, which are ultimately controlled by the protolith composition. Some of these include pelitic protoliths (clay-rich sediments) and mafic protoliths (metavolcanic rocks). Sketch examples of ducti ...
... will see different colored rocks here, the colors reflecting different proportions and types of minerals, which are ultimately controlled by the protolith composition. Some of these include pelitic protoliths (clay-rich sediments) and mafic protoliths (metavolcanic rocks). Sketch examples of ducti ...
Geology of the Kaimai Ranges
... andesitic-dacitic cones) which erupted between 4 and 5.6 million years ago. They are the southern end (and youngest) of a line of ...
... andesitic-dacitic cones) which erupted between 4 and 5.6 million years ago. They are the southern end (and youngest) of a line of ...
Swiss roll surgery - Earth Learning Idea
... intersection is known as the axial plane trace because the line can be ‘traced’ or ‘drawn’ on the folded bed or map. On a simple upright fold, the trace of the axial plane is a horizontal line or a straight line on a map; limb - area of usually dipping rocks between the ...
... intersection is known as the axial plane trace because the line can be ‘traced’ or ‘drawn’ on the folded bed or map. On a simple upright fold, the trace of the axial plane is a horizontal line or a straight line on a map; limb - area of usually dipping rocks between the ...
Sedimentary Rock Classification Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors
... When sediments settle out of calmer water, they form horizontal layers. One layer is deposited first, and another layer is deposited on top of it. So each layer is younger than the layer beneath it. When the sediments harden, the layers are preserved. Sedimentary rocks formed by the crystallization ...
... When sediments settle out of calmer water, they form horizontal layers. One layer is deposited first, and another layer is deposited on top of it. So each layer is younger than the layer beneath it. When the sediments harden, the layers are preserved. Sedimentary rocks formed by the crystallization ...
When Glaciers Ruled the World!
... Alfonso, the largest glacier of them all, was on a stroll in the mountains. Alfonso was a bit of a bully to the smaller rocks because after all, he was over a mile tall. As he slid over rocks the impact was so great that he would form scratches in the rocks called abrasion. As the rocks cried in pa ...
... Alfonso, the largest glacier of them all, was on a stroll in the mountains. Alfonso was a bit of a bully to the smaller rocks because after all, he was over a mile tall. As he slid over rocks the impact was so great that he would form scratches in the rocks called abrasion. As the rocks cried in pa ...
Rock Cycle
... 2. Forms over ______________________ of square miles during periods of high tectonic activity. movement of 1 tectonic plate against another generates great _______________ and pressure at the boundaries of the tectonic plates h heat and pressure --> changes existing rocks structure / form = m ...
... 2. Forms over ______________________ of square miles during periods of high tectonic activity. movement of 1 tectonic plate against another generates great _______________ and pressure at the boundaries of the tectonic plates h heat and pressure --> changes existing rocks structure / form = m ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes Page
... c. Continental – Continental: plates collide, fold, & uplift Indian & Asian plates -> HIMALAYAS One plate may move beneath Transform Boundary: Plates slide past each other •Lithosphere isn’t created or destroyed •Rock shatters •Many shallow earthquakes (San Andreas Fault) •Separates Pacific & Nort ...
... c. Continental – Continental: plates collide, fold, & uplift Indian & Asian plates -> HIMALAYAS One plate may move beneath Transform Boundary: Plates slide past each other •Lithosphere isn’t created or destroyed •Rock shatters •Many shallow earthquakes (San Andreas Fault) •Separates Pacific & Nort ...
No Slide Title
... •Basaltic, high density magma wells up from the mantle-crust interface to replace rock •New crust that forms is thinner and denser; as it cools, it sinks lower than the surrounding continental crust •Ocean water eventually fills in between the two continents ...
... •Basaltic, high density magma wells up from the mantle-crust interface to replace rock •New crust that forms is thinner and denser; as it cools, it sinks lower than the surrounding continental crust •Ocean water eventually fills in between the two continents ...
A. Direction of Forces and the Movements B. Effects of Diastrophism
... Rock is strained beyond ability to remain intact; rock fractures; one side is displaced with respect to the other . ...
... Rock is strained beyond ability to remain intact; rock fractures; one side is displaced with respect to the other . ...
Brief History of the White Tank Mountains and the Western Phoenix
... the White Tank Mountains to a Tertiary age. The Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) absolute dating shows that an event reset the radioactive decay in part of the mountain range to this relatively young age (Tertiary), despite the Proterozoic gneiss and schist found there. The west side of the White Tank Mountai ...
... the White Tank Mountains to a Tertiary age. The Potassium-Argon (K-Ar) absolute dating shows that an event reset the radioactive decay in part of the mountain range to this relatively young age (Tertiary), despite the Proterozoic gneiss and schist found there. The west side of the White Tank Mountai ...
Geologic Time
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
Geologic Time
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
Volcano Lab 16-17 File
... basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra andesite composition variable; alternating basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra with an overall andesite composition Gentle lower slopes, but steep upper slopes; concave upward; small summit crater ...
... basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra andesite composition variable; alternating basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra with an overall andesite composition Gentle lower slopes, but steep upper slopes; concave upward; small summit crater ...
PETLAB3-14
... known as ’spinifex’ that has a platy habit. Spinifex texture is best developed in the upper chilled margin of komatiite lava flows. Komatiites are typically somewhat lighter green in colour than associated mafic volcanic rocks such as basalts because of the formers high Mg content, and they were oft ...
... known as ’spinifex’ that has a platy habit. Spinifex texture is best developed in the upper chilled margin of komatiite lava flows. Komatiites are typically somewhat lighter green in colour than associated mafic volcanic rocks such as basalts because of the formers high Mg content, and they were oft ...
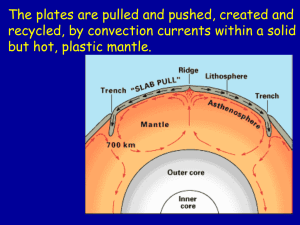
The Earth
... inches) & powered by mantle’s heat Crust is formed and consumed Plate boundaries – Convergence – Divergence – Transform ...
... inches) & powered by mantle’s heat Crust is formed and consumed Plate boundaries – Convergence – Divergence – Transform ...
Detrital Remanent Magnetization (DRM)
... • formed during or soon after deposition of sediments • locked in by compaction and lithification to sedimentary rock • relatively weak ...
... • formed during or soon after deposition of sediments • locked in by compaction and lithification to sedimentary rock • relatively weak ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.