Section 11.2 Folds, Faults, and Mountains
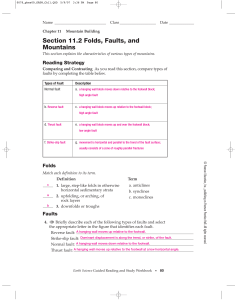
... 10. Select the letter from the figure that identifies each formation. B graben A horst 11. Which type of fault is illustrated normal fault in the figure? 12. Circle the letter of each true statement about fault-block mountains. a. Normal faulting occurs where tensional stresses cause the crust to be ...
... 10. Select the letter from the figure that identifies each formation. B graben A horst 11. Which type of fault is illustrated normal fault in the figure? 12. Circle the letter of each true statement about fault-block mountains. a. Normal faulting occurs where tensional stresses cause the crust to be ...
Hercynian Metamorphism in the Catalonian Coastal Ranges
... which reach shallow crustal levels and were intruded after the development of crenulation cleavages (Enrique 1984, 1985). The country rocks are often affected by a previous regional metamorphism usually not exceeding greenschist facies. The shallow intrusives produced thermal aureoles, which range b ...
... which reach shallow crustal levels and were intruded after the development of crenulation cleavages (Enrique 1984, 1985). The country rocks are often affected by a previous regional metamorphism usually not exceeding greenschist facies. The shallow intrusives produced thermal aureoles, which range b ...
Exam 1 Study Guide - Napa Valley College
... method? What are the four “spheres” and what does each include? Heat engines – what are the two major sources of energy for the Earth? Where does the internal energy come from? Rock cycle – be able identify all the items on the rock cycle such as rocks and magma as well as the processes such as crys ...
... method? What are the four “spheres” and what does each include? Heat engines – what are the two major sources of energy for the Earth? Where does the internal energy come from? Rock cycle – be able identify all the items on the rock cycle such as rocks and magma as well as the processes such as crys ...
EarthComm 8.1
... contains the oldest preserved crust of a continental landmass. It is 3.8 billion years old. It is Earth’s oldest surviving accretionary orogen. Here, oceanic lithosphere was subducted, and new continental crust was produced. However, it is highly fragmented and metamorphosed. This makes it difficult ...
... contains the oldest preserved crust of a continental landmass. It is 3.8 billion years old. It is Earth’s oldest surviving accretionary orogen. Here, oceanic lithosphere was subducted, and new continental crust was produced. However, it is highly fragmented and metamorphosed. This makes it difficult ...
Tectonic Impacts #3
... Yilgarn block begins to forms (3.5bya) Crust begins to form, rivers, igneous intrusions (3.4 – 3.09bya) Yilgarn block forms (3.09 – 2.7bya) Banded iron formations form, emerging crust, large tectonic forces (2.7 – 2.32bya) Large crustal areas form in the north coast, west coast and south coast (1.93 ...
... Yilgarn block begins to forms (3.5bya) Crust begins to form, rivers, igneous intrusions (3.4 – 3.09bya) Yilgarn block forms (3.09 – 2.7bya) Banded iron formations form, emerging crust, large tectonic forces (2.7 – 2.32bya) Large crustal areas form in the north coast, west coast and south coast (1.93 ...
Section 1: Classifying Rocks Mineral Composition and Color
... Where oceanic plate is subducted beneath a continental plate magma forms and rises. The result is a volcano made of igneous rock. A collision of continental plates may push rocks so deep they melt and form magma. This magma slowly cools and hardens to form igneous rock ...
... Where oceanic plate is subducted beneath a continental plate magma forms and rises. The result is a volcano made of igneous rock. A collision of continental plates may push rocks so deep they melt and form magma. This magma slowly cools and hardens to form igneous rock ...
Plate Tectonics - Canvas by Instructure
... found in very old rocks in South America and Africa. It could not have been possible that this animal swam across the ocean to get from one continent to another. ...
... found in very old rocks in South America and Africa. It could not have been possible that this animal swam across the ocean to get from one continent to another. ...
Mineral - Weebly
... (below) or lava (surface) sedimentary rock – forms when particles of other rocks or remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together – layers below surface metamorphic rock – formed when existing rock is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions – most forms deep undergroun ...
... (below) or lava (surface) sedimentary rock – forms when particles of other rocks or remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together – layers below surface metamorphic rock – formed when existing rock is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions – most forms deep undergroun ...
Continental Drift - sciencewithskinner
... - Fossil evidence (coal deposits) indicate a matching tropical or subtropical swamps in the northern hemisphere 4. Seafloor spreading 5. Paleomagnetism ...
... - Fossil evidence (coal deposits) indicate a matching tropical or subtropical swamps in the northern hemisphere 4. Seafloor spreading 5. Paleomagnetism ...
8th Earth Science Chapter 4 – Rocks
... upon the amount of ____________ and ________________ applied, one type of rock can change into ____________ different metamorphic rocks. Each type of metamorphic rock can come from several kinds of _______________ ___________. The sedimentary rock ___________ will change into slate. As increasing pr ...
... upon the amount of ____________ and ________________ applied, one type of rock can change into ____________ different metamorphic rocks. Each type of metamorphic rock can come from several kinds of _______________ ___________. The sedimentary rock ___________ will change into slate. As increasing pr ...
an overview of the geology of the great lakes basin
... Lakes basin. Multiple repeated advances of continental glaciers, up to one mile thick and originating from the north, sculpted the surface of the bedrock. The glaciers carved out the basins that are now occupied by the Great Lakes (11). The less competent rocks tend to be more easily scoured and res ...
... Lakes basin. Multiple repeated advances of continental glaciers, up to one mile thick and originating from the north, sculpted the surface of the bedrock. The glaciers carved out the basins that are now occupied by the Great Lakes (11). The less competent rocks tend to be more easily scoured and res ...
Lecture 2.5 - St. Mark`s Boise
... crust of the earth is broken up into plates that float on the liquid mantel and is driven by convection currents within the mantle. ...
... crust of the earth is broken up into plates that float on the liquid mantel and is driven by convection currents within the mantle. ...
Metasedimentary rocks, intrusions and deformation history
... facies psammitic, semipelitic and lesser amounts of pelitic rocks are the dominant lithologies in the Psammite Zone; minor metavolcanic and volcaniclastic rocks are also present. In the south-western part of the Psammite Zone a number of intrusive sheets of granodiorite, diorite and gabbro s.l. are ...
... facies psammitic, semipelitic and lesser amounts of pelitic rocks are the dominant lithologies in the Psammite Zone; minor metavolcanic and volcaniclastic rocks are also present. In the south-western part of the Psammite Zone a number of intrusive sheets of granodiorite, diorite and gabbro s.l. are ...
Practice 1 - WordPress.com
... 1Earth comprises three principal layers: the dense, iron-rich core, the mantle made of 2silicate rocks that are semimolten at depth, and the thin,, solid-surface crust. There are 3two kinds of crust, a lower and denser oceanic crust and an upper, lighter continental 4crust found over only about 40 p ...
... 1Earth comprises three principal layers: the dense, iron-rich core, the mantle made of 2silicate rocks that are semimolten at depth, and the thin,, solid-surface crust. There are 3two kinds of crust, a lower and denser oceanic crust and an upper, lighter continental 4crust found over only about 40 p ...
Physical Geology
... • Igneous Rocks: When rocks melt, Magma is formed, rises, cools and crystallizes. • Sedimentary Rocks: All rocks weather and erode to form sediments (e.g., gravel, sand, silt, and clay). When these sediments accumulate they are compressed and cemented ...
... • Igneous Rocks: When rocks melt, Magma is formed, rises, cools and crystallizes. • Sedimentary Rocks: All rocks weather and erode to form sediments (e.g., gravel, sand, silt, and clay). When these sediments accumulate they are compressed and cemented ...
Evolution and the History of Life
... although there are some in South America and one in North America. – Why is a question that requires careful thought not just a “because”. – The answer that geophysicists have developed is called plate tectonics which explains why Australia is so different. – Australia separated from the main landma ...
... although there are some in South America and one in North America. – Why is a question that requires careful thought not just a “because”. – The answer that geophysicists have developed is called plate tectonics which explains why Australia is so different. – Australia separated from the main landma ...
Notes - Rock Formation and Age File
... carbonate, siliciclastic, evaporite, and organoclastic strata of sedimentary origin that range in age from Upper Ordovician to Upper Carboniferous-Lower Permian. At depth, as illustrated in the cross section, older sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks that range from Lower Ordovician to Mesop ...
... carbonate, siliciclastic, evaporite, and organoclastic strata of sedimentary origin that range in age from Upper Ordovician to Upper Carboniferous-Lower Permian. At depth, as illustrated in the cross section, older sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks that range from Lower Ordovician to Mesop ...
File
... Describe each of the three types of faults. Be sure to include ALL types of features and stress that causes that fault. normal – hanging wall drops down from footwall; caused by tension stress; usually at ...
... Describe each of the three types of faults. Be sure to include ALL types of features and stress that causes that fault. normal – hanging wall drops down from footwall; caused by tension stress; usually at ...
Examples posted for the midterm test.
... Note that the test covers the following material: Geomagnetism (from slide 25) Plate Tectonics Earthquakes (up to slide 115) Several of these example questions will appear on the test. The test will be made up of 35 questions, all of which can be answered on a SCANTRON sheet. In each case select the ...
... Note that the test covers the following material: Geomagnetism (from slide 25) Plate Tectonics Earthquakes (up to slide 115) Several of these example questions will appear on the test. The test will be made up of 35 questions, all of which can be answered on a SCANTRON sheet. In each case select the ...
460:102 Notes Historical Geology Notes
... When Layers formed only the fluid was overlying. Therefore, no overlying layers could have been present when the lower layers were formed. Superposition! The oldest layer is at the bottom and successively higher layers are successively younger in an sequence of undisturbed strata. Probably not the f ...
... When Layers formed only the fluid was overlying. Therefore, no overlying layers could have been present when the lower layers were formed. Superposition! The oldest layer is at the bottom and successively higher layers are successively younger in an sequence of undisturbed strata. Probably not the f ...
Rocks & The Rock Cycle
... Have light coloring of their main mineral components, orthoclase feldspar & quartz ...
... Have light coloring of their main mineral components, orthoclase feldspar & quartz ...
3.4 How are the rock classes Rocks and Rock
... Classic regional metamorphic structures in Scotland Note bands, but also that they are folded back on one another, attesting to the pressure that drives such change. ...
... Classic regional metamorphic structures in Scotland Note bands, but also that they are folded back on one another, attesting to the pressure that drives such change. ...
Inner Core - Net Start Class
... Below the lithosphere, rocks are so hot that tiny bits melt. When this happens, the rocks are no longer brittle. They begin to flow. Scientists use the term “plastic” to describe rocks that flow in this way. The plastic layer within the mantle is called the asthenosphere. The word plastic refers to ...
... Below the lithosphere, rocks are so hot that tiny bits melt. When this happens, the rocks are no longer brittle. They begin to flow. Scientists use the term “plastic” to describe rocks that flow in this way. The plastic layer within the mantle is called the asthenosphere. The word plastic refers to ...
EARTH SYSTEMS SCIENCE LECTURE TEST # 2
... 16. The San Andreas Fault is an example of a ? plate boundary. A.divergent B.oceanic-oceanic convergent C.oceanic-continental convergent D.continental-continental convergent E.transform 17. The study of fossil plants is A.invertebrate paleontology B.paleozoology C.micropaleontology D.paleoecology E ...
... 16. The San Andreas Fault is an example of a ? plate boundary. A.divergent B.oceanic-oceanic convergent C.oceanic-continental convergent D.continental-continental convergent E.transform 17. The study of fossil plants is A.invertebrate paleontology B.paleozoology C.micropaleontology D.paleoecology E ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.