Geotechnical Properties of the Rodessa Formation in East
... The estimation of rock mass strength is becoming more and more important because this is a key parameter in rock mechanics and geotechnics which are used in the design of geotechnical structures like tunnels, dams, and slopes. The main focus of this study is to calculate the shear strength of certai ...
... The estimation of rock mass strength is becoming more and more important because this is a key parameter in rock mechanics and geotechnics which are used in the design of geotechnical structures like tunnels, dams, and slopes. The main focus of this study is to calculate the shear strength of certai ...
Geology of the Australian Alps - Australian Alps National Parks
... The volcanoes of the Silurian and Devonian periods were quite explosive, erupting towering clouds of hot volcanic ash which formed a rock known as ignimbrite. In Victoria this type of rock occurs at lake Mountain, Mt Donna Buang and the Snowy River area, while similar rocks occur around Lake Talbing ...
... The volcanoes of the Silurian and Devonian periods were quite explosive, erupting towering clouds of hot volcanic ash which formed a rock known as ignimbrite. In Victoria this type of rock occurs at lake Mountain, Mt Donna Buang and the Snowy River area, while similar rocks occur around Lake Talbing ...
L
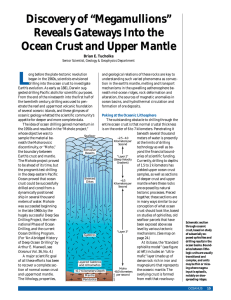
... they would almost exclusively expose mantle rocks (which they do not). Rather, it appears that a single fault is normally active for only a short period of time (a few tens to hundreds of thousand of years) before it is abandoned and replaced by a new fault closer to the spreading axis. What, then, ...
... they would almost exclusively expose mantle rocks (which they do not). Rather, it appears that a single fault is normally active for only a short period of time (a few tens to hundreds of thousand of years) before it is abandoned and replaced by a new fault closer to the spreading axis. What, then, ...
Practice for Chapter 9
... C. True or False? Circle the correct answer. 1. The general term for the change in shape of a rock when sufficient stress is applied is strain. True or False? 2. A rock that undergoes sufficient stress to change its original shape has exceeded its elastic limit. True or False? 3. Rocks in which pla ...
... C. True or False? Circle the correct answer. 1. The general term for the change in shape of a rock when sufficient stress is applied is strain. True or False? 2. A rock that undergoes sufficient stress to change its original shape has exceeded its elastic limit. True or False? 3. Rocks in which pla ...
1 Minerals - yr11geology
... 3.1 (a) Describe the rock cycle and the processes that make it up (Range: weathering, erosion, transport, deposition, burial, lithification, metamorphism, melting, intrusion, eruption, uplift, deformation); (b) relate rock types to their place in the cycle; (c) relate this to the plate tectonic mode ...
... 3.1 (a) Describe the rock cycle and the processes that make it up (Range: weathering, erosion, transport, deposition, burial, lithification, metamorphism, melting, intrusion, eruption, uplift, deformation); (b) relate rock types to their place in the cycle; (c) relate this to the plate tectonic mode ...
petrological classification of redeposited red siliciclastic sediments
... metamorphic rocks (gneisses, micaschists, phyllites) and clastic sedimentary rocks. Redeposited siliciclastic sediments consist of grey-coloured silstones, sandstones and conglomerates (Upper Carboniferous), and red clastic sedimentary rocks of different origin (Szakmány and Józsa 1994). In this stu ...
... metamorphic rocks (gneisses, micaschists, phyllites) and clastic sedimentary rocks. Redeposited siliciclastic sediments consist of grey-coloured silstones, sandstones and conglomerates (Upper Carboniferous), and red clastic sedimentary rocks of different origin (Szakmány and Józsa 1994). In this stu ...
Geologic Structure Part I – Folds
... Types of Metamorphism Regional metamorphism – Large scale – large volume of rock is affected – Associated with convergent plate margins and mountain building – Folding and faulting increase thickness of the crust – Occurs over a range of temperatures and pressures – Fluids are also present – Low gra ...
... Types of Metamorphism Regional metamorphism – Large scale – large volume of rock is affected – Associated with convergent plate margins and mountain building – Folding and faulting increase thickness of the crust – Occurs over a range of temperatures and pressures – Fluids are also present – Low gra ...
The Dynamic Crust
... travel fastest (~2X faster than S-waves) S-waves second fastest Increases in denser material The waves are refracted (bent) as they pass from a material of one density to a material of a higher or lower density. ...
... travel fastest (~2X faster than S-waves) S-waves second fastest Increases in denser material The waves are refracted (bent) as they pass from a material of one density to a material of a higher or lower density. ...
Orogenesis.
... About 20 million years ago - India was separated from Asia by a progressively narrowing ocean basin - the Tethys Sea. The “collision” begun with the subduction of the oceanic plate beneath the Tethys Sea. This caused the onset of orogenesis in Tibet (uplift, folding, faulting, metamorphism, volcanis ...
... About 20 million years ago - India was separated from Asia by a progressively narrowing ocean basin - the Tethys Sea. The “collision” begun with the subduction of the oceanic plate beneath the Tethys Sea. This caused the onset of orogenesis in Tibet (uplift, folding, faulting, metamorphism, volcanis ...
IGNEOUS NEPHELINE - BEARING ROCKS OF
... grains. In addition, some samples contain an accessory amount of biotite. Nepheline is mostly fresh, but in some samples it is changed into zeolite, cancrinite or into sodalite. Sometimes nepheline is partly calcitized and sericitized. Nepheline-syenites consist of nepheline and kalifeldspar (isorth ...
... grains. In addition, some samples contain an accessory amount of biotite. Nepheline is mostly fresh, but in some samples it is changed into zeolite, cancrinite or into sodalite. Sometimes nepheline is partly calcitized and sericitized. Nepheline-syenites consist of nepheline and kalifeldspar (isorth ...
PEER Module Test Template - Partnerships for Environmental
... Fault: A break in the rock that makes up the Earth’s crust. Strike-slip fault: A fault with a change in horizontal direction (side to side). Normal fault: A fault in which the moving piece moves downward. Thrust fault: A fault in which the moving piece thrusts upward. ...
... Fault: A break in the rock that makes up the Earth’s crust. Strike-slip fault: A fault with a change in horizontal direction (side to side). Normal fault: A fault in which the moving piece moves downward. Thrust fault: A fault in which the moving piece thrusts upward. ...
File
... bread in which they are found? A) principle of superposition B) principle of original horizontality C) principle of cross-cutting relationships D) principle of inclusions True or False 1) The process by which geologists identify and match sedimentary strata and other rocks of the same ages in differ ...
... bread in which they are found? A) principle of superposition B) principle of original horizontality C) principle of cross-cutting relationships D) principle of inclusions True or False 1) The process by which geologists identify and match sedimentary strata and other rocks of the same ages in differ ...
EXTRA PRACTICE TEST #3
... Which of the following is the most likely set of conditions necessary for the formation of the texture seen in the sample? A. ...
... Which of the following is the most likely set of conditions necessary for the formation of the texture seen in the sample? A. ...
KS4 Extraction of Metals 1
... Describe the structure of the Earth as a sphere with a thin rocky crust, mantle and core Describe the outer layer of the Earth as oceanic plates under oceans and continental plates forming continents Describe the lithosphere as formed of a number of large interlocking tectonic plates that can move s ...
... Describe the structure of the Earth as a sphere with a thin rocky crust, mantle and core Describe the outer layer of the Earth as oceanic plates under oceans and continental plates forming continents Describe the lithosphere as formed of a number of large interlocking tectonic plates that can move s ...
Ch 7 study guide answers
... 6. How does a mid-ocean ridge form, and where would you find the youngest and oldest rocks on the seafloor (explain)? A mid-ocean ridge is a mountain chain found on the ocean floor. It is formed at a divergent boundary where plates are separating. The magma is pushing up through the plate boundary c ...
... 6. How does a mid-ocean ridge form, and where would you find the youngest and oldest rocks on the seafloor (explain)? A mid-ocean ridge is a mountain chain found on the ocean floor. It is formed at a divergent boundary where plates are separating. The magma is pushing up through the plate boundary c ...
chapter 15A - plate tectonics 1
... adds thin, lowelevation ocean crust to landmass. In time, water fills in and an ocean basin will develop • Arabian peninsula split from African continent • Process continues in East Africa rift valleys (note lakes filling in low lying ocean crust). ...
... adds thin, lowelevation ocean crust to landmass. In time, water fills in and an ocean basin will develop • Arabian peninsula split from African continent • Process continues in East Africa rift valleys (note lakes filling in low lying ocean crust). ...
measuring the earth - Mepham Earth Science
... Note the diagrams below taken from Regents exams. Diagrams 1 and 2 represent IGNEOUS rocks. The mineral grains (crystals) are intergrown with no spaces between them. Diagram 3 is a sedimentary rock such as sandstone or siltstone. The grains here are not intergrown. There are spaces between them. The ...
... Note the diagrams below taken from Regents exams. Diagrams 1 and 2 represent IGNEOUS rocks. The mineral grains (crystals) are intergrown with no spaces between them. Diagram 3 is a sedimentary rock such as sandstone or siltstone. The grains here are not intergrown. There are spaces between them. The ...
Math 1513
... semi-flat spot under the arch with its huge boulders strewn about is fairly steep. The rocks you hike through are the Lyons and the Fountain Formations, sandstones and conglomerates that date from about 250 million years ago where Colorado looked like beaches along the Sea of Cortez today. There wer ...
... semi-flat spot under the arch with its huge boulders strewn about is fairly steep. The rocks you hike through are the Lyons and the Fountain Formations, sandstones and conglomerates that date from about 250 million years ago where Colorado looked like beaches along the Sea of Cortez today. There wer ...
lesson-2-explore-page-115-shaping-earths-surface
... Faults are largest where one plate subducts into the mantle. The strongest and most damaging earthquakes occur at these locations. How Earthquakes Change Earth’s Surface The movement of crust along faults can make mountains, valleys, and other landforms. Different types of movement occur at th ...
... Faults are largest where one plate subducts into the mantle. The strongest and most damaging earthquakes occur at these locations. How Earthquakes Change Earth’s Surface The movement of crust along faults can make mountains, valleys, and other landforms. Different types of movement occur at th ...
Every Pebble Tells a Story
... melting point of typical Earth materials ranges from about 600 and 1300 degrees Celsius, the molten material that forms igneous rocks comes from depths in the Earth where these high temperatures exist (tens to hundreds of kilometers). Volcanic igneous rocks are the result of liquid rock materials (c ...
... melting point of typical Earth materials ranges from about 600 and 1300 degrees Celsius, the molten material that forms igneous rocks comes from depths in the Earth where these high temperatures exist (tens to hundreds of kilometers). Volcanic igneous rocks are the result of liquid rock materials (c ...
Evolution of the Ocean Basins
... • The Red Sea Rift began during the Miocene Epoch (about 25 million years ago) and continues today. – Its formation is related to the formation of the Aden Rift. – The two rifts have now effectively separated Africa from Arabia, although the two were once part of the same landmass, the Afro-Arabi ...
... • The Red Sea Rift began during the Miocene Epoch (about 25 million years ago) and continues today. – Its formation is related to the formation of the Aden Rift. – The two rifts have now effectively separated Africa from Arabia, although the two were once part of the same landmass, the Afro-Arabi ...
Topography and Faults
... layers create breaks (faults) in the earth’s crust. These stresses are caused by things like: • Plate boundary movements • Thermal expansion and contraction • Gravitational forces ...
... layers create breaks (faults) in the earth’s crust. These stresses are caused by things like: • Plate boundary movements • Thermal expansion and contraction • Gravitational forces ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.