Geology 111 - A8 - New ideas on continental drift
... b) Ocean-continent At an ocean-continent convergent boundary the oceanic plate is pushed under the continental plate in the same manner as an ocean-ocean collision. Similar geological features apply, and an offshore oceanic trench will normally be present. The mafic magma produced adjacent to the su ...
... b) Ocean-continent At an ocean-continent convergent boundary the oceanic plate is pushed under the continental plate in the same manner as an ocean-ocean collision. Similar geological features apply, and an offshore oceanic trench will normally be present. The mafic magma produced adjacent to the su ...
1 0 .
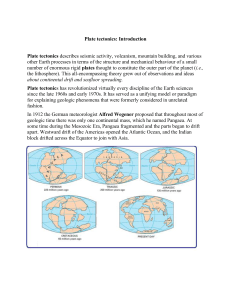
... 10. Lithosphere – Movements of Tectonic Plates The Earth’s Crust was divided into many segments – litospheric (tectonic) plates. These plates are moving. The speed of this movement is 1 – 5 cm per year. Crustal plates can converge, diverge, collide with each other, slide under each other or move hor ...
... 10. Lithosphere – Movements of Tectonic Plates The Earth’s Crust was divided into many segments – litospheric (tectonic) plates. These plates are moving. The speed of this movement is 1 – 5 cm per year. Crustal plates can converge, diverge, collide with each other, slide under each other or move hor ...
The Geology of Grahamstown: the Regional Setting
... Karoo Supergroup The base of the Karoo Supergroup consists of sedimentary rocks of the Dwyka Group. These rocks rest directly on top of the upper Witteberg shales, and consist of boulders, cobbles and pebbles of a variety of older rocks in a very-fine-grained bluegrey matrix. The rock is a “lithic b ...
... Karoo Supergroup The base of the Karoo Supergroup consists of sedimentary rocks of the Dwyka Group. These rocks rest directly on top of the upper Witteberg shales, and consist of boulders, cobbles and pebbles of a variety of older rocks in a very-fine-grained bluegrey matrix. The rock is a “lithic b ...
Lab 8
... EAS-450 – Physics and Chemistry of the Earth LAB 8 - Geomagnetism Objective: Manipulate basic concepts about the Earth’s magnetic field. ...
... EAS-450 – Physics and Chemistry of the Earth LAB 8 - Geomagnetism Objective: Manipulate basic concepts about the Earth’s magnetic field. ...
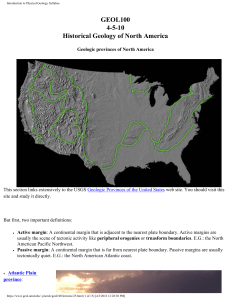
GEOL100 4-5-10 Historical Geology of North America
... (aka Great Basin): Image Here, the Earth's crust and upper mantle has been stretched up to 100% of its original width. Beginning in the Paleogene, the entire region was subjected to extension that thinned and cracked the crust as it was pulled apart, creating long parallel normal faults. Along these ...
... (aka Great Basin): Image Here, the Earth's crust and upper mantle has been stretched up to 100% of its original width. Beginning in the Paleogene, the entire region was subjected to extension that thinned and cracked the crust as it was pulled apart, creating long parallel normal faults. Along these ...
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
... volcanoes erupt and the igneous rocks formed weather to other sedimentary rocks rivers change their courses depending upon the ever-changing terrain seas inundate the lowlands, only to recede or to evaporate, leaving behind series of sediments rivers can eventually cut through mountains and ...
... volcanoes erupt and the igneous rocks formed weather to other sedimentary rocks rivers change their courses depending upon the ever-changing terrain seas inundate the lowlands, only to recede or to evaporate, leaving behind series of sediments rivers can eventually cut through mountains and ...
metamorphic rocks - Math/Science Nucleus
... boundaries. There is localized metamorphism called contact metamorphism. Usually this occurs near molten magma or lava, under high temperature and low pressure. Metamorphism affecting a large area or regional metamorphism involves large increases of temperature and pressure. Contact metamorphism is ...
... boundaries. There is localized metamorphism called contact metamorphism. Usually this occurs near molten magma or lava, under high temperature and low pressure. Metamorphism affecting a large area or regional metamorphism involves large increases of temperature and pressure. Contact metamorphism is ...
File - Varsity Field
... A. shorten and thicken the crust B. thin and shorten the crust C. thin and extend the crust D. shorten and thin the crust ...
... A. shorten and thicken the crust B. thin and shorten the crust C. thin and extend the crust D. shorten and thin the crust ...
ppt - Discover Earth Science
... • The sliding movement often causes earthquakes to occur along faults • A fault is nothing more than a crack in the Earth’s crust where movement has occurred – Ex. North American Plate and the Pacific Plate are sliding past each other along the San Andreas Fault in California ...
... • The sliding movement often causes earthquakes to occur along faults • A fault is nothing more than a crack in the Earth’s crust where movement has occurred – Ex. North American Plate and the Pacific Plate are sliding past each other along the San Andreas Fault in California ...
GEO143_final_key
... A) Magmas are more viscous than solid rocks in the crust and upper mantle. B) Most magmas are richer in silica than most crustal and upper mantle rocks. C) Magmas are mainly liquid and contain dissolved fluids such as water; most are less dense than the adjacent solid rock. D) all of the above (42) ...
... A) Magmas are more viscous than solid rocks in the crust and upper mantle. B) Most magmas are richer in silica than most crustal and upper mantle rocks. C) Magmas are mainly liquid and contain dissolved fluids such as water; most are less dense than the adjacent solid rock. D) all of the above (42) ...
Calc-alkaline volcanic rocks in mélange formations from the South
... a field of productive dispute for over the last 30 years. Many questions lie not only about the geotectonic environment and the petrogenetic processes which took place, but also on the number of oceanic basins which contributed to the formation of Othris magmatic rocks. Unanswered questions may be a ...
... a field of productive dispute for over the last 30 years. Many questions lie not only about the geotectonic environment and the petrogenetic processes which took place, but also on the number of oceanic basins which contributed to the formation of Othris magmatic rocks. Unanswered questions may be a ...
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
... kyanite, sillimanite and andalusite form. Because of the abundance of sheet silicates, pelitic rocks commonly form slates, phyllites, schists, and gneisses during metamorphism. Mafic - These are Mg and Fe rich rocks with low amounts of Si. Minerals like biotite, hornblende and plagioclase form durin ...
... kyanite, sillimanite and andalusite form. Because of the abundance of sheet silicates, pelitic rocks commonly form slates, phyllites, schists, and gneisses during metamorphism. Mafic - These are Mg and Fe rich rocks with low amounts of Si. Minerals like biotite, hornblende and plagioclase form durin ...
principles of STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY and TECTONICS
... • Branches of geology that deal with the reconstruc;on of movements that have occurred over ;me in Earth’s Lithosphere • from La;n (struere) and Greek (tektos) = to build • movements include – simple mo;on – bending – breaking ...
... • Branches of geology that deal with the reconstruc;on of movements that have occurred over ;me in Earth’s Lithosphere • from La;n (struere) and Greek (tektos) = to build • movements include – simple mo;on – bending – breaking ...
CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Sea Floor
... Continent Orogens - elongate regions of crust intensely deformed and metamorphosed during continental collisions Age of folding and faulting is younger than age of rocks deformed. ...
... Continent Orogens - elongate regions of crust intensely deformed and metamorphosed during continental collisions Age of folding and faulting is younger than age of rocks deformed. ...
Plate Tectonic Theory
... • Subduction of higher density (mafic) oceanic lithosphere beneath lower density (felsic) continental lithosphere – Formation of magma in the mantle wedge – Formation of a continental margin volcanic arc on the overriding continental lithosphere • Examples: Cascade Range, Andean Range ...
... • Subduction of higher density (mafic) oceanic lithosphere beneath lower density (felsic) continental lithosphere – Formation of magma in the mantle wedge – Formation of a continental margin volcanic arc on the overriding continental lithosphere • Examples: Cascade Range, Andean Range ...
Cardigan rock sequence revealed
... Lower Palaeozoic these fossils are second to none for producing refined biostratigraphies. Many graptolite biozones have been calibrated with radiometric dates from volcanic tuffs, and can be used to indicate periods of time of a million years or less, while graptolite subzones can represent even sh ...
... Lower Palaeozoic these fossils are second to none for producing refined biostratigraphies. Many graptolite biozones have been calibrated with radiometric dates from volcanic tuffs, and can be used to indicate periods of time of a million years or less, while graptolite subzones can represent even sh ...
III Naprendszer kemiai osszetetele [Compatibility Mode]
... with the evolution of a differentiated crust. Nevertheless, by about the Late Precambrian, most of the minerals that we know of today probably already existed. Some of the important mineral-forming environments are summarized in Figure 35.4. The interaction of the convective mantle and the crust is ...
... with the evolution of a differentiated crust. Nevertheless, by about the Late Precambrian, most of the minerals that we know of today probably already existed. Some of the important mineral-forming environments are summarized in Figure 35.4. The interaction of the convective mantle and the crust is ...
Layers of Earth Comparisons
... Earth’s layers are compared by: • Temperature • Density – (the thickness or depth of the layer) ...
... Earth’s layers are compared by: • Temperature • Density – (the thickness or depth of the layer) ...
Review for Exam 32 & 33
... The plates move in conveyor-belt fashion as new crust is generated at the continental margins and destroyed at the mid-ocean ridge The lithosphere is broken up into large palates that move as the result of convection within the asthenosphere Earthquakes & volcanic activity results from convection mo ...
... The plates move in conveyor-belt fashion as new crust is generated at the continental margins and destroyed at the mid-ocean ridge The lithosphere is broken up into large palates that move as the result of convection within the asthenosphere Earthquakes & volcanic activity results from convection mo ...
Earth History
... and target rocks. A lot of hot material would have been ejected into the upper atmosphere if not beyond. As material came back down, friction heated the material. This would have been a world wide event so the atmosphere became like a pizza oven for several hours. Lots of fires! Material in the uppe ...
... and target rocks. A lot of hot material would have been ejected into the upper atmosphere if not beyond. As material came back down, friction heated the material. This would have been a world wide event so the atmosphere became like a pizza oven for several hours. Lots of fires! Material in the uppe ...
Plate tectonics - Geological Society of India
... spreading, was formulated in the mid-1960s by J. Tuzo Wilson. This theory holds that the Earth's upper shell, or lithosphere, consists of six major and 22 or so minor rigid slabs called plates. The thickness of each of these plates extends to a depth of roughly 80 to 150 kilometers. These plates mov ...
... spreading, was formulated in the mid-1960s by J. Tuzo Wilson. This theory holds that the Earth's upper shell, or lithosphere, consists of six major and 22 or so minor rigid slabs called plates. The thickness of each of these plates extends to a depth of roughly 80 to 150 kilometers. These plates mov ...
Earth Systems 3209 Answer Key
... Some sedimentary features that could be used to determine if a sedimentary layer has been overturned include: graded bedding; ripple marks (i.e. current or oscillation); mud cracks; and fossil shell orientation. If either of these sedimentary features appear as inverted in contrast to the normal ori ...
... Some sedimentary features that could be used to determine if a sedimentary layer has been overturned include: graded bedding; ripple marks (i.e. current or oscillation); mud cracks; and fossil shell orientation. If either of these sedimentary features appear as inverted in contrast to the normal ori ...
Ch - Mr. Neason`s Earth Science
... Southern Rocky Mountains and mountains of the Basin and Range region from upwarping and faulting. Southern Rockies began to form about 60 million years ago with the subduction of an oceanic plate more than 1600 kilometers away. The subducting plate separated the lithosphere above, allowed hot rock t ...
... Southern Rocky Mountains and mountains of the Basin and Range region from upwarping and faulting. Southern Rockies began to form about 60 million years ago with the subduction of an oceanic plate more than 1600 kilometers away. The subducting plate separated the lithosphere above, allowed hot rock t ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.














![III Naprendszer kemiai osszetetele [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007880701_1-b98b24bd5e9e65888f0b10fb338ea606-300x300.png)