Chapter 32
... • A fracture along which visible movement can be detected on one side relative to the other. ...
... • A fracture along which visible movement can be detected on one side relative to the other. ...
METAMORPHISM & METAMORPHIC ROCKS
... Deep-sea sediments, those found at depths greater than about 500 m, cover roughly two-thirds of the Earth. The predominant deep sediment is carbonate ooze, which covers nearly half the ocean floor ...
... Deep-sea sediments, those found at depths greater than about 500 m, cover roughly two-thirds of the Earth. The predominant deep sediment is carbonate ooze, which covers nearly half the ocean floor ...
Lab 06-Plate Tectonics
... is also referred to as a spreading center, such as the Mid Atlantic Ridge… ...
... is also referred to as a spreading center, such as the Mid Atlantic Ridge… ...
sequences
... craton may be divide into two parts – the first dealing with the relatively stable continental interior over which epeiric seas transgressed and regressed, – and the other dealing with the mobile belts where mountain building occurred ...
... craton may be divide into two parts – the first dealing with the relatively stable continental interior over which epeiric seas transgressed and regressed, – and the other dealing with the mobile belts where mountain building occurred ...
Lab 506-Plate Tectonics
... is also referred to as a spreading center, such as the Mid Atlantic Ridge… ...
... is also referred to as a spreading center, such as the Mid Atlantic Ridge… ...
Sedimentary Rocks and their processes
... Graded bedding refers to an upward decrease in grain size within an individual bed. It is often found in the deposits of turbidity currents, high density submarine flows. As turbidity currents slow, larger particles are deposited first and progressively smaller ones deposited as flow continues to we ...
... Graded bedding refers to an upward decrease in grain size within an individual bed. It is often found in the deposits of turbidity currents, high density submarine flows. As turbidity currents slow, larger particles are deposited first and progressively smaller ones deposited as flow continues to we ...
Interactive Plate Tectonics - Fredericksburg City Schools
... fixed and moved over time, but also _____________ how and why_____________, __________________, and other geologic events occur. ...
... fixed and moved over time, but also _____________ how and why_____________, __________________, and other geologic events occur. ...
Forces that Shape Earth
... Ocean trenches – one plate goes under another during collision forming a deep trench where the two plates meet Volcanic arcs – curved line of volcanoes that forms parallel to plate boundaries Landforms Created by Tension Mid-ocean ridges – tension causes oceanic crust to spread allowing hot ro ...
... Ocean trenches – one plate goes under another during collision forming a deep trench where the two plates meet Volcanic arcs – curved line of volcanoes that forms parallel to plate boundaries Landforms Created by Tension Mid-ocean ridges – tension causes oceanic crust to spread allowing hot ro ...
Subduction Zones
... • Formation of new crust - behind the arc. 3 models o Spreading caused by forceable injection of a diapir rising from the downgoing slab. o Spreading induced in the overriding plate by the viscous drag in the mantle wedge caused by the motion of the downgoing plate (comer flow). o Spreading induced ...
... • Formation of new crust - behind the arc. 3 models o Spreading caused by forceable injection of a diapir rising from the downgoing slab. o Spreading induced in the overriding plate by the viscous drag in the mantle wedge caused by the motion of the downgoing plate (comer flow). o Spreading induced ...
formation of magma and igneous rocks (2)
... PLUTONIC ROCKS IN THE LANDSCAPE (4) In some cases, larger magma chambers may form deep within the Earth’s crust. These large intrusions, which solidify at depths of several kilometers to more than 10 km, are exposed only when substantial uplift and erosion of surrounding rocks has occurred. The resu ...
... PLUTONIC ROCKS IN THE LANDSCAPE (4) In some cases, larger magma chambers may form deep within the Earth’s crust. These large intrusions, which solidify at depths of several kilometers to more than 10 km, are exposed only when substantial uplift and erosion of surrounding rocks has occurred. The resu ...
Geologic History of the - Teacher Friendly Guides
... dramatically over the last greenstone beds found along billion years, and geologic the eastern shore of Hudson Bay processes continue these changes today. The Earth is in northern Quebec. The oldest estimated to be approximately known materials are 4.4-billion4.6 billion years old. The year-old zirc ...
... dramatically over the last greenstone beds found along billion years, and geologic the eastern shore of Hudson Bay processes continue these changes today. The Earth is in northern Quebec. The oldest estimated to be approximately known materials are 4.4-billion4.6 billion years old. The year-old zirc ...
Plate Tectonics Notes # 2
... the plastic mantle because it behaves and flows like silly putty , bread dough, or HONEY . This zone was discovered because it was found that seismic waves decrease in velocity from 100km to 700km below the Earth’s surface. (Seismic waves travel more slowly through liquids than solids). It is a plas ...
... the plastic mantle because it behaves and flows like silly putty , bread dough, or HONEY . This zone was discovered because it was found that seismic waves decrease in velocity from 100km to 700km below the Earth’s surface. (Seismic waves travel more slowly through liquids than solids). It is a plas ...
Chapter 7 Directed Reading B
... 16. You can tell a fault is normal by looking at the order of ______________________ layers. Strike-Slip Faults ...
... 16. You can tell a fault is normal by looking at the order of ______________________ layers. Strike-Slip Faults ...
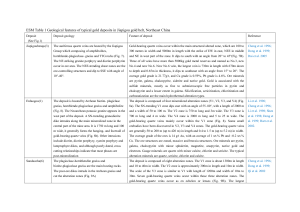
Alteration processes in the Maliman (hipo) bentonite
... the Blanco river (Fig. 1A), northeastern Precorillera. In this area, the Precordillera which runs along the Argentine border in the Andean Ranges is characterized by a thick sequence of Tertiary volcanic and volcaniclastic arc rocks associated with both epithermal and porphyry Au-Cu type mineral dep ...
... the Blanco river (Fig. 1A), northeastern Precorillera. In this area, the Precordillera which runs along the Argentine border in the Andean Ranges is characterized by a thick sequence of Tertiary volcanic and volcaniclastic arc rocks associated with both epithermal and porphyry Au-Cu type mineral dep ...
126_2013_475_MOESM1_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... Group which composing of amphibolites, ...
... Group which composing of amphibolites, ...
Synthetic Seismicity of Multiple Interacting Faults and its use for
... Cell Size: 1 x 1 km Coefficient of Friction: Asperity regions: Random between 0.65 and 0.95 ...
... Cell Size: 1 x 1 km Coefficient of Friction: Asperity regions: Random between 0.65 and 0.95 ...
The Geologic Time Scale
... Original horizontality – Sedimentary rocks are deposited in horizontal or nearly horizontal layers. Superposition - In an undisturbed rock sequence, the oldest rocks are at the bottom and each successive layer is younger than the layer beneath. Cross-cutting relationships - An intrusion or a fault i ...
... Original horizontality – Sedimentary rocks are deposited in horizontal or nearly horizontal layers. Superposition - In an undisturbed rock sequence, the oldest rocks are at the bottom and each successive layer is younger than the layer beneath. Cross-cutting relationships - An intrusion or a fault i ...
File
... continents could not just plow through the oceans Later evidence revealed Wegener was correct – he just didn’t have the technology to prove how the continents had moved ...
... continents could not just plow through the oceans Later evidence revealed Wegener was correct – he just didn’t have the technology to prove how the continents had moved ...
Rocking our world - University of Victoria
... a train derailment than a wrinkle. There are huge shards of land folded up against each other—and they contain mineral deposits unlike the surrounding land.” Johnston believes this is evidence that what is now the western edge of North America was once a completely different continent—an 8,000 km-lo ...
... a train derailment than a wrinkle. There are huge shards of land folded up against each other—and they contain mineral deposits unlike the surrounding land.” Johnston believes this is evidence that what is now the western edge of North America was once a completely different continent—an 8,000 km-lo ...
Terra Nova 2012 Jagoutz
... remains whether the observed change in chemistry between GG and TTG rocks be reconciled with subduction zone processes or does it require the existence of a different crust forming process in the Archean? The depletion of the HREE is only indicative of the involvement of garnet in the formation of th ...
... remains whether the observed change in chemistry between GG and TTG rocks be reconciled with subduction zone processes or does it require the existence of a different crust forming process in the Archean? The depletion of the HREE is only indicative of the involvement of garnet in the formation of th ...
The Precambrian - Ms. Alderson`s Earth and Space Science course
... The evolution of life can be divided into two very unequal periods: the very long Precambrian (lasting over 3 billion years), when life for the most part remained at the microbial grade of organization, and the much shorter Phanerozoic, encompassing the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras (about ...
... The evolution of life can be divided into two very unequal periods: the very long Precambrian (lasting over 3 billion years), when life for the most part remained at the microbial grade of organization, and the much shorter Phanerozoic, encompassing the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras (about ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
... • Cape fold belt and equivalent – S.Africa & Argentina • Appalachian Mtns and equivalent – U.S., Canada, Scotland & Norway • Only occur in rocks > 145 mya ...
... • Cape fold belt and equivalent – S.Africa & Argentina • Appalachian Mtns and equivalent – U.S., Canada, Scotland & Norway • Only occur in rocks > 145 mya ...
Algoman orogeny

The Algoman orogeny, known as the Kenoran orogeny in Canada, was an episode of mountain-building (orogeny) during the Late Archean Eon that involved repeated episodes of continental collisions, compressions and subductions. The Superior province and the Minnesota River Valley terrane collided about 2,700 to 2,500 million years ago. The collision folded the Earth's crust and produced enough heat and pressure to metamorphose the rock. Blocks were added to the Superior province along a 1,200 km (750 mi) boundary that stretches from present-day eastern South Dakota into the Lake Huron area. The Algoman orogeny brought the Archaen Eon to a close, about 2,500 million years ago; it lasted less than 100 million years and marks a major change in the development of the earth’s crust.The Canadian shield contains belts of metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks formed by the action of metamorphism on volcanic and sedimentary rock. The areas between individual belts consist of granites or granitic gneisses that form fault zones. These two types of belts can be seen in the Wabigoon, Quetico and Wawa subprovinces; the Wabigoon and Wawa are of volcanic origin and the Quetico is of sedimentary origin. These three subprovinces lie linearly in southwestern- to northeastern-oriented belts about 140 km (90 mi) wide on the southern portion of the Superior Province.The Slave province and portions of the Nain province were also affected. Between about 2,000 and 1,700 million years ago these combined with the Sask and Wyoming cratons to form the first supercontinent, the Kenorland supercontinent.