CHEMISTRY
... number of molecules • 3O2 represents 3 molecules of oxygen or (3x2) or 6 atoms of oxygen ...
... number of molecules • 3O2 represents 3 molecules of oxygen or (3x2) or 6 atoms of oxygen ...
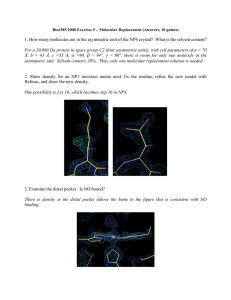
1. How many molecules are in the asymmetric unit of the NP4 crystal
... 1. How many molecules are in the asymmetric unit of the NP4 crystal? What is the solvent content? For a 20,000 Da protein in space group C2 (four asymmetric units), with cell parameters of a = 70 Å, b = 43 Å, c =53 Å, α =90, β = 94°, γ = 90°, there is room for only one molecule in the asymmetric uni ...
... 1. How many molecules are in the asymmetric unit of the NP4 crystal? What is the solvent content? For a 20,000 Da protein in space group C2 (four asymmetric units), with cell parameters of a = 70 Å, b = 43 Å, c =53 Å, α =90, β = 94°, γ = 90°, there is room for only one molecule in the asymmetric uni ...
Overview
... Yuan Lecture 2, Class 24: Protein Folding and Molecular Chaperones April 20th, 2017 Overview The intracellular concentration of protein in bacterial cells can be estimated to be ~135 mg/ml. In this session, we will explore how bacteria employ a suite of molecular machines collectively known as chape ...
... Yuan Lecture 2, Class 24: Protein Folding and Molecular Chaperones April 20th, 2017 Overview The intracellular concentration of protein in bacterial cells can be estimated to be ~135 mg/ml. In this session, we will explore how bacteria employ a suite of molecular machines collectively known as chape ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 8.) An Enzyme speeds up an reaction by ___________ A. decrease activation energy of a reaction. B. increase the ΔG of a reaction C. decrease the Δ G of a reaction D. increase the activation energy of the reaction 9.) Polypeptide chains are always synthesized from _______ to _______. a.) hydrophobic ...
... 8.) An Enzyme speeds up an reaction by ___________ A. decrease activation energy of a reaction. B. increase the ΔG of a reaction C. decrease the Δ G of a reaction D. increase the activation energy of the reaction 9.) Polypeptide chains are always synthesized from _______ to _______. a.) hydrophobic ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Q ...
... Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to the numbered statements immediately following it. Select the one lettered choice that best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Q ...
8th Grade Sixth Six Weeks Vocabulary
... An atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons. A table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number (number of protons), usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in ...
... An atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons. A table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number (number of protons), usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... 3. Define a compound and explain how compounds in living organisms are different from compounds in nonliving things. 4. Describe the structure of an atom. 5. Distinguish between atomic number and atomic weight or mass number of an atom. 6. Define an isotope and explain what makes some isotopes radio ...
... 3. Define a compound and explain how compounds in living organisms are different from compounds in nonliving things. 4. Describe the structure of an atom. 5. Distinguish between atomic number and atomic weight or mass number of an atom. 6. Define an isotope and explain what makes some isotopes radio ...
For complex multicellular organisms to function, individual
... For complex multicellular organisms to function, individual cells need mechanisms to bind to each other. In humans, cell-to-cell adhesion maintains the architecture of tissues, drives the response of the immune system, and allows for wound healing. All of the contacts involved in these processes are ...
... For complex multicellular organisms to function, individual cells need mechanisms to bind to each other. In humans, cell-to-cell adhesion maintains the architecture of tissues, drives the response of the immune system, and allows for wound healing. All of the contacts involved in these processes are ...
Proceedings of a meeting held at Allerton House, Monticello, Illinois
... containing 150 amino acids, for example. Of these 450 degrees of freedom, 300 would be due to rotations and 150 would be due to relative bond angles of the side chains. ...
... containing 150 amino acids, for example. Of these 450 degrees of freedom, 300 would be due to rotations and 150 would be due to relative bond angles of the side chains. ...
Globular proteins
... When a beam of X-ray of a given wave length falls on a crystal, the xrays are diffracted by the electrons of various atoms of the crystal. The diffracted X-rays are recorded on a photographic film or x-ray film by producing a pattern of spots with various intensities. By analysis of the x-ray diffra ...
... When a beam of X-ray of a given wave length falls on a crystal, the xrays are diffracted by the electrons of various atoms of the crystal. The diffracted X-rays are recorded on a photographic film or x-ray film by producing a pattern of spots with various intensities. By analysis of the x-ray diffra ...
Klauda-NCTU-Oct31
... binding conformations before 100ns. These binding events were an order of magnitude faster than with the all-atom membrane and agree with its bound structure demonstrating the accuracy of this enhanced approach. Lactose permease (LacY) of E. coli has been a historical model transmembrane protein for ...
... binding conformations before 100ns. These binding events were an order of magnitude faster than with the all-atom membrane and agree with its bound structure demonstrating the accuracy of this enhanced approach. Lactose permease (LacY) of E. coli has been a historical model transmembrane protein for ...
A sample for a final examination
... BLOSUM 62 matrix) fitting the designed sequence into the shape of lysozyme was found to be extremely high. Should the experimentalist seize the opportunity and start synthesizing immediately?? Explain. 2. A new energy function for protein threading includes contacts between four structural sites tha ...
... BLOSUM 62 matrix) fitting the designed sequence into the shape of lysozyme was found to be extremely high. Should the experimentalist seize the opportunity and start synthesizing immediately?? Explain. 2. A new energy function for protein threading includes contacts between four structural sites tha ...
FRENCH PHYSICIST RECEIVES 2012 GEP AWARD
... living organism, amino acids emit sequences of quantum signals. These signals were identified and “composed” into a specific melody for each protein by Dr. Sternheimer. Through scale waves, the transposition of these melodies (“proteodies”) in the audible range can influence the protei ...
... living organism, amino acids emit sequences of quantum signals. These signals were identified and “composed” into a specific melody for each protein by Dr. Sternheimer. Through scale waves, the transposition of these melodies (“proteodies”) in the audible range can influence the protei ...
Chapter 3 USU - BEHS Science
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
NUR101ModB
... are composed of one or more smaller units called atoms. ATOMS are composed of several kinds of subatomic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. ...
... are composed of one or more smaller units called atoms. ATOMS are composed of several kinds of subatomic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. ...
Why Proteins Fold How Proteins Fold? ΔG
... Non-Bonding Interactions Recap Amino acids of a protein are joined by covalent bonding interactions. The polypeptide is folded in three dimension by non-bonding interactions. These interactions, which can easily be disrupted by extreme pH, temperature, pressure, and denaturants, are: • Electrostatic ...
... Non-Bonding Interactions Recap Amino acids of a protein are joined by covalent bonding interactions. The polypeptide is folded in three dimension by non-bonding interactions. These interactions, which can easily be disrupted by extreme pH, temperature, pressure, and denaturants, are: • Electrostatic ...
File
... • Heterogeneous Mixture-a mixture in which the presence of a t least two different substances is visible to the eye. • Homogenous Mixture-a mixture with a composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbo ...
... • Heterogeneous Mixture-a mixture in which the presence of a t least two different substances is visible to the eye. • Homogenous Mixture-a mixture with a composition that is uniform throughout, all the way down to the molecular level. • Hydrocarbon-any molecule consisting of only hydrogen and carbo ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
... 15. Which substance should form an acidic solution in water? a. Na2O b. SO2 c. CO d. BaO 16. Which of the following is the largest in size? a. Clb. Cl c. I+ d. I17. When an alkali metal reacts with water, a metal hydroxide and a gas form. Which gas forms? a. Carbon dioxide b. Oxygen c. Ozone d. Hydr ...
Ch 2 test review 13
... Atoms are the smallest basic unit of matter Difference between atoms and elements Difference and charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons Covalent and ionic bonding Properties of water Hydrogen bonding in water molecules Difference between an element, compound, and molecule pH – definition, scale, ...
... Atoms are the smallest basic unit of matter Difference between atoms and elements Difference and charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons Covalent and ionic bonding Properties of water Hydrogen bonding in water molecules Difference between an element, compound, and molecule pH – definition, scale, ...
Glossary
... The locus of points on the boundary of at least one atom and not on the inside of any atoms of the molecule. May be artificially smoothed to remove internal voids and channels. ...
... The locus of points on the boundary of at least one atom and not on the inside of any atoms of the molecule. May be artificially smoothed to remove internal voids and channels. ...
Alpha Shapes and molecular Representations
... that consist of possibly thousands of atoms But why proteins? “prota” is Greek and means “of primary importance”. They are essential to all living organisms and were first mentioned in 1838 by Jöns Jakob Berzelius, a Swedish researcher ...
... that consist of possibly thousands of atoms But why proteins? “prota” is Greek and means “of primary importance”. They are essential to all living organisms and were first mentioned in 1838 by Jöns Jakob Berzelius, a Swedish researcher ...
Section 1.2 Properties of Water
... 5. Compare and contrast an ionic bond and a covalent bond. Section 1.2 Properties of Water 1. What does it mean when a molecule is said to be polar? 2. What is a hydrogen bond? 3. Describe some properties of water? 4. Why does water make a good solvent? 5. How does a mixture differ from a compound? ...
... 5. Compare and contrast an ionic bond and a covalent bond. Section 1.2 Properties of Water 1. What does it mean when a molecule is said to be polar? 2. What is a hydrogen bond? 3. Describe some properties of water? 4. Why does water make a good solvent? 5. How does a mixture differ from a compound? ...