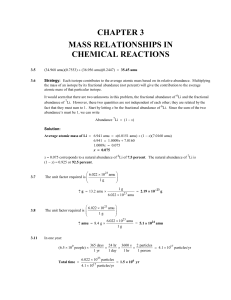
2. Solution Guide to Supplementary Exercises
... 42 A (3) Zinc exists as compounds in its ores. For example, the main metallic compound in zinc blende is zinc sulphide. 43 B (1) Aluminium is the most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. (3) Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, chromium and ...
... 42 A (3) Zinc exists as compounds in its ores. For example, the main metallic compound in zinc blende is zinc sulphide. 43 B (1) Aluminium is the most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. (3) Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, chromium and ...
CHAPTER 4 REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
... Strategy: Hydrogen displacement: Any metal above hydrogen in the activity series will displace it from water or from an acid. Metals below hydrogen will not react with either water or an acid. Solution: Only (b) Li and (d) Ca are above hydrogen in the activity series, so they are the only metals in ...
... Strategy: Hydrogen displacement: Any metal above hydrogen in the activity series will displace it from water or from an acid. Metals below hydrogen will not react with either water or an acid. Solution: Only (b) Li and (d) Ca are above hydrogen in the activity series, so they are the only metals in ...
chapter 20 - Chemistry
... Thus iron(III) should oxidize iodide ion to iodine. This makes the iodide ion/iodine half-reaction the anode. The standard emf can be found using Equation (18.1). ...
... Thus iron(III) should oxidize iodide ion to iodine. This makes the iodide ion/iodine half-reaction the anode. The standard emf can be found using Equation (18.1). ...
Phylogenetic Classification of Protozoa Based on the
... ChDHFR-TS illustrates that the enzyme is a homodimer based on the canonical dimer interface of TS (Fig. 2). Based on structural comparisons with other DHFR and TS proteins, the DHFR domain is 178 residues, the linker domain is 58 residues, and the TS domain is 284 residues, yielding a 63-kDa monomer ...
... ChDHFR-TS illustrates that the enzyme is a homodimer based on the canonical dimer interface of TS (Fig. 2). Based on structural comparisons with other DHFR and TS proteins, the DHFR domain is 178 residues, the linker domain is 58 residues, and the TS domain is 284 residues, yielding a 63-kDa monomer ...
Unit 8 Stoichiometry Notes
... 5. A reaction between hydrazine, N2H4 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 , has been used to launch rockets into space. The reaction produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. a. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2 N2 H 4 + N 2 O 4 → 3 N 2 + 4 H 2 O b. How many moles of N2 will be produ ...
... 5. A reaction between hydrazine, N2H4 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 , has been used to launch rockets into space. The reaction produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. a. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2 N2 H 4 + N 2 O 4 → 3 N 2 + 4 H 2 O b. How many moles of N2 will be produ ...
Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes
... 5. A reaction between hydrazine, N2H4 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 , has been used to launch rockets into space. The reaction produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. a. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2 N2H4 + N2O4 → 3 N2 + 4 H2O ...
... 5. A reaction between hydrazine, N2H4 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 , has been used to launch rockets into space. The reaction produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. a. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2 N2H4 + N2O4 → 3 N2 + 4 H2O ...
Unit 10A Stoichiometry Notes
... 5. A reaction between hydrazine, N2H4 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 , has been used to launch rockets into space. The reaction produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. a. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2 N2H4 + N2O4 → 3 N2 + 4 H2O b. How many moles of N2 will be produced if 2 ...
... 5. A reaction between hydrazine, N2H4 , and dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 , has been used to launch rockets into space. The reaction produces nitrogen gas and water vapor. a. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2 N2H4 + N2O4 → 3 N2 + 4 H2O b. How many moles of N2 will be produced if 2 ...
Schaum`s Outline of Theory and Problems of
... combine elements. Changing one combination of elements to another is the chief interest of the chemist. It has long been of interest to know the composition of the crust of the earth, the oceans, and the atmosphere, since these are the only sources of raw materials for all the products that humans r ...
... combine elements. Changing one combination of elements to another is the chief interest of the chemist. It has long been of interest to know the composition of the crust of the earth, the oceans, and the atmosphere, since these are the only sources of raw materials for all the products that humans r ...
Chapter 3 - Chemistry
... Strategy: We are asked to solve for the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 104 g of urea. We cannot convert directly from grams urea to atoms. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to atoms? How should Avogadro's number be used here? How many atoms of N, C, O, or H are in ...
... Strategy: We are asked to solve for the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 104 g of urea. We cannot convert directly from grams urea to atoms. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to atoms? How should Avogadro's number be used here? How many atoms of N, C, O, or H are in ...
9 SHS CH 9 LECTURE shs_ch_9_lecture
... In a balanced chemical equation, the coefficients allow us to calculate how much of a substance is used, produced, or needed in the reaction. ...
... In a balanced chemical equation, the coefficients allow us to calculate how much of a substance is used, produced, or needed in the reaction. ...
Lipoprotein structure
... Apolipoproteins exert little or no effect on the average dynamic properties of the surface lipids especially in LDL and VLDL. In fact, isolated surface lipids, reconstituted into vesicles or microemulsions, have similar fluidity, diffusion rates, and mobility as the lipid monolayer components in the ...
... Apolipoproteins exert little or no effect on the average dynamic properties of the surface lipids especially in LDL and VLDL. In fact, isolated surface lipids, reconstituted into vesicles or microemulsions, have similar fluidity, diffusion rates, and mobility as the lipid monolayer components in the ...
Study Guide Chapter 10: An Introduction to Chemistry
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
Chapter 10 Chemical Calculations and Chemical Equations
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
Phylogenetic Classification of Protozoa Based on the Structure of
... ChDHFR-TS illustrates that the enzyme is a homodimer based on the canonical dimer interface of TS (Fig. 2). Based on structural comparisons with other DHFR and TS proteins, the DHFR domain is 178 residues, the linker domain is 58 residues, and the TS domain is 284 residues, yielding a 63-kDa monomer ...
... ChDHFR-TS illustrates that the enzyme is a homodimer based on the canonical dimer interface of TS (Fig. 2). Based on structural comparisons with other DHFR and TS proteins, the DHFR domain is 178 residues, the linker domain is 58 residues, and the TS domain is 284 residues, yielding a 63-kDa monomer ...
HW 19
... Thus iron(III) should oxidize iodide ion to iodine. This makes the iodide ion/iodine half-reaction the anode. The standard emf can be found using Equation (19.1). D D D Ecell = Ecathode − Eanode = 0.77 V − 0.53 V = 0.24 V ...
... Thus iron(III) should oxidize iodide ion to iodine. This makes the iodide ion/iodine half-reaction the anode. The standard emf can be found using Equation (19.1). D D D Ecell = Ecathode − Eanode = 0.77 V − 0.53 V = 0.24 V ...
Chapter 4 - Chemistry
... Strategy: Hydrogen displacement: Any metal above hydrogen in the activity series will displace it from water or from an acid. Metals below hydrogen will not react with either water or an acid. Solution: Only (b) Li and (d) Ca are above hydrogen in the activity series, so they are the only metals in ...
... Strategy: Hydrogen displacement: Any metal above hydrogen in the activity series will displace it from water or from an acid. Metals below hydrogen will not react with either water or an acid. Solution: Only (b) Li and (d) Ca are above hydrogen in the activity series, so they are the only metals in ...
Sample Chapter 3
... • The mole lets us relate the number of entities to the mass of a sample of those entities. • The mole maintains the same numerical relationship between mass on the atomic scale (atomic mass units, amu) and mass on the macroscopic scale (grams, g). In everyday terms, a grocer does not know that ther ...
... • The mole lets us relate the number of entities to the mass of a sample of those entities. • The mole maintains the same numerical relationship between mass on the atomic scale (atomic mass units, amu) and mass on the macroscopic scale (grams, g). In everyday terms, a grocer does not know that ther ...
chapter 20 - United International College
... Reduction half-reaction: we add two H2O to the right-hand side of the equation to balance the O atoms. HNO3 NO 2H2O To balance the H atoms, we add 3H to the left-hand side. 3H HNO3 NO 2H2O There are three net positive charges on the left, so we add three electrons to the same side to bal ...
... Reduction half-reaction: we add two H2O to the right-hand side of the equation to balance the O atoms. HNO3 NO 2H2O To balance the H atoms, we add 3H to the left-hand side. 3H HNO3 NO 2H2O There are three net positive charges on the left, so we add three electrons to the same side to bal ...
Answers Chapters 1-3 bookwork - Dunmore High School
... Chemical property. Oxygen gas is consumed in a combustion reaction; its composition and identity are changed. ...
... Chemical property. Oxygen gas is consumed in a combustion reaction; its composition and identity are changed. ...
Teacher Edition Calculations
... The molecular mass, expressed in grams, is the sum of the molar masses of the atoms making up that molecule. Complete the following table : (Note all molar masses recorded to 4 sig figures) ...
... The molecular mass, expressed in grams, is the sum of the molar masses of the atoms making up that molecule. Complete the following table : (Note all molar masses recorded to 4 sig figures) ...
Brief Contents - Educhimica.it
... significant figure in the tenths place after the decimal, and the second number stops its significant figure in the hundredths place after the decimal. Hence, we limit our final answer to the tenths place after the decimal. The final answer is 59.4. b. 0.00665 + 1.004 = 1.01065. The first number stops its ...
... significant figure in the tenths place after the decimal, and the second number stops its significant figure in the hundredths place after the decimal. Hence, we limit our final answer to the tenths place after the decimal. The final answer is 59.4. b. 0.00665 + 1.004 = 1.01065. The first number stops its ...
Stoichiometry
... reach from the Sun to Pluto and back 7.5 million times. It would take light 9500 years to travel from the bottom to the top of a stack of 1 mole of $1 bills. ...
... reach from the Sun to Pluto and back 7.5 million times. It would take light 9500 years to travel from the bottom to the top of a stack of 1 mole of $1 bills. ...
chapter 2 - chemical equations and reaction yields
... CHAPTER 2 - CHEMICAL EQUATIONS AND REACTION YIELDS ...
... CHAPTER 2 - CHEMICAL EQUATIONS AND REACTION YIELDS ...
2 - Chemistry
... • the reactant that is present in quantity smaller to completely react other reactant; is consumed completely during the reaction; determines amount of product yielded It can be also seen as the reagent that theoretically produces the smallest amount of product(s). • excess reagent (reactant): the r ...
... • the reactant that is present in quantity smaller to completely react other reactant; is consumed completely during the reaction; determines amount of product yielded It can be also seen as the reagent that theoretically produces the smallest amount of product(s). • excess reagent (reactant): the r ...
Chapter 4 - UCF Chemistry
... • the reactant that is present in quantity smaller to completely react other reactant; is consumed completely during the reaction; determines amount of product yielded It can be also seen as the reagent that theoretically produces the smallest amount of product(s). • excess reagent (reactant): the r ...
... • the reactant that is present in quantity smaller to completely react other reactant; is consumed completely during the reaction; determines amount of product yielded It can be also seen as the reagent that theoretically produces the smallest amount of product(s). • excess reagent (reactant): the r ...