Role of Tonsils and Larynx in defence and phonation
... Muscles located within the vocal cords lateral to the vocal ligaments, the thyroarytenoid muscles, can pull the arytenoid cartilages toward thyroid cartilage thus loosen the vocal cords. Parts of these muscles within the vocal cords can change the shapes and masses of the vocal cord edges, sharpenin ...
... Muscles located within the vocal cords lateral to the vocal ligaments, the thyroarytenoid muscles, can pull the arytenoid cartilages toward thyroid cartilage thus loosen the vocal cords. Parts of these muscles within the vocal cords can change the shapes and masses of the vocal cord edges, sharpenin ...
Dissector Bold terms 3
... -Intraperitoneal organs (stomach, small intestine, liver and spleen) -Retroperitoneal organs (ureters, suprarenal glands, kidneys) -Secondarily retroperitoneal (duodenum, pancreas, ascending colon and descending colon) -Gastrointestinal tract -Liver (right/left lobes-falciform ligament) -Gallbladder ...
... -Intraperitoneal organs (stomach, small intestine, liver and spleen) -Retroperitoneal organs (ureters, suprarenal glands, kidneys) -Secondarily retroperitoneal (duodenum, pancreas, ascending colon and descending colon) -Gastrointestinal tract -Liver (right/left lobes-falciform ligament) -Gallbladder ...
Deglutition - Famona Site
... pharyngeal constrictors. The tongue of the epiglottis is gradually displaced with the bolus and is bent downwards at the side so that it is arched like a monk's hood over the larynx. Each half of the epiglottis serves as a chute to deflect the bulk of the bolus to either side of the midline. A certa ...
... pharyngeal constrictors. The tongue of the epiglottis is gradually displaced with the bolus and is bent downwards at the side so that it is arched like a monk's hood over the larynx. Each half of the epiglottis serves as a chute to deflect the bulk of the bolus to either side of the midline. A certa ...
Flatworms are soft, flattened worms that have tissues and internal
... The digestive cavity is the only body cavity in a flatworm. Flatworms have bilateral symmetry. Three germ layers of a flatworm ...
... The digestive cavity is the only body cavity in a flatworm. Flatworms have bilateral symmetry. Three germ layers of a flatworm ...
Pre-Registration Midwifery Programmes Biological Sciences Pre
... To investigate the neural and hormonal control of digestion. To discuss liver dysfunction. Learning outcomes 1. Identify the following tissues and organs of the digestive tract; oropharynx, epiglottis, oesophagus, stomach (greater and lesser curvature, fundus, body, antrum, pyloric sphincter, cardia ...
... To investigate the neural and hormonal control of digestion. To discuss liver dysfunction. Learning outcomes 1. Identify the following tissues and organs of the digestive tract; oropharynx, epiglottis, oesophagus, stomach (greater and lesser curvature, fundus, body, antrum, pyloric sphincter, cardia ...
The Muscular System Objectives Muscles Kinds of
... muscles found only in the _________ ● Skeletal muscles: muscles that move ________. ...
... muscles found only in the _________ ● Skeletal muscles: muscles that move ________. ...
2.Diaphragm
... The diaphragm is a thin muscular and tendinous septum that separates thorax & abdominal cavities. It is pierced by the structures that pass between the chest and the abdomen. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration. It is dome shaped and consists of a peripheral muscular part, whic ...
... The diaphragm is a thin muscular and tendinous septum that separates thorax & abdominal cavities. It is pierced by the structures that pass between the chest and the abdomen. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration. It is dome shaped and consists of a peripheral muscular part, whic ...
Application Project Unit 1
... 9. Enzymes are used to convert starch into sugar so yeast cells can product ethanol. 10. Enzymes are used as meat tenderizers. 11. Enzymes are now used to make drugs and control reaction rates in pharmaceutical reactions. 12. Enzymes are used as pharmaceutical supplements to treat digestive system d ...
... 9. Enzymes are used to convert starch into sugar so yeast cells can product ethanol. 10. Enzymes are used as meat tenderizers. 11. Enzymes are now used to make drugs and control reaction rates in pharmaceutical reactions. 12. Enzymes are used as pharmaceutical supplements to treat digestive system d ...
Respiratory System
... Located directly posterior to the nasal cavity and superior to the soft palate, which separates it from the posterior part of the oral cavity. Normally, only air passes through. Material from the oral cavity and oropharynx is typically blocked from entering the nasopharynx by the soft palate, which ...
... Located directly posterior to the nasal cavity and superior to the soft palate, which separates it from the posterior part of the oral cavity. Normally, only air passes through. Material from the oral cavity and oropharynx is typically blocked from entering the nasopharynx by the soft palate, which ...
Neuroendocrine gastric carcinoma in a young patient
... cells in gastric adenocarcinomas in 1927, neuroendocrine differentiation in gastric carcinomas has been repeatedly reported 7–15. However, the prevalence of neuroendocrine differentiation in gastric carcinomas still remains undefined. As already mentioned, these tumors are usually diagnosed in the s ...
... cells in gastric adenocarcinomas in 1927, neuroendocrine differentiation in gastric carcinomas has been repeatedly reported 7–15. However, the prevalence of neuroendocrine differentiation in gastric carcinomas still remains undefined. As already mentioned, these tumors are usually diagnosed in the s ...
Cranial nerve flashcards 2005 (intermediate and challenging nerves)
... branch synapse at the pterygopalatine ganglion; postganglionic fibers distribute with branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). T Visceral motor (parasympathetic) to the submandibular, sublingual, and minor salivary glands of the oral cavity. Preganglionic fibers in the chorda tympani branch synapse ...
... branch synapse at the pterygopalatine ganglion; postganglionic fibers distribute with branches of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). T Visceral motor (parasympathetic) to the submandibular, sublingual, and minor salivary glands of the oral cavity. Preganglionic fibers in the chorda tympani branch synapse ...
Chapter 14
... Chapter 13 of Gartner and Hiatt: Color Textbook of Histology, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, W.B. Saunders, 2007. ...
... Chapter 13 of Gartner and Hiatt: Color Textbook of Histology, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, W.B. Saunders, 2007. ...
Pancreatitis
... Chronic Pancreatitis • Significant majority are Binge Drinkers • 150 grams of alcohol daily for a period of more than 6 years. • Another factor that is associated with binge drinking is cigarette smoking • In up to 25% of all chronic pancreatitis cases, no cause can be identified. ...
... Chronic Pancreatitis • Significant majority are Binge Drinkers • 150 grams of alcohol daily for a period of more than 6 years. • Another factor that is associated with binge drinking is cigarette smoking • In up to 25% of all chronic pancreatitis cases, no cause can be identified. ...
The peritoneal cavity
... It is a thin, serous, continuous glistening membrane lining the abdominal & pelvic walls and clothing the abdominal and pelvic viscera. Parietal layer lines the wall & visceral layer covers the organs. The potential space between the two layers is filled with very thin film of serous fluid to facili ...
... It is a thin, serous, continuous glistening membrane lining the abdominal & pelvic walls and clothing the abdominal and pelvic viscera. Parietal layer lines the wall & visceral layer covers the organs. The potential space between the two layers is filled with very thin film of serous fluid to facili ...
Abdomen Review Sheet
... Omental herniation: If loop passes through, none of the boundaries can be incised, bowel must be deflected and withdrawn Second most frequently infected abdominal space, pulmonary abscess may erode across diaphragm When supine it is the lowest portion of the abdominal cavity ⇒ fluid will collect her ...
... Omental herniation: If loop passes through, none of the boundaries can be incised, bowel must be deflected and withdrawn Second most frequently infected abdominal space, pulmonary abscess may erode across diaphragm When supine it is the lowest portion of the abdominal cavity ⇒ fluid will collect her ...
Clinical Anatomy of Oral Cavity
... The clear, tasteless, odorless viscid fluid, saliva, secreted by these glands and the mucous glands of the oral cavity: – Keeps the mucous membrane of the mouth moist. – Lubricates the food during mastication. – Begins the digestion of starches. – Serves as an intrinsic mouthwash. – Plays significan ...
... The clear, tasteless, odorless viscid fluid, saliva, secreted by these glands and the mucous glands of the oral cavity: – Keeps the mucous membrane of the mouth moist. – Lubricates the food during mastication. – Begins the digestion of starches. – Serves as an intrinsic mouthwash. – Plays significan ...
Mrs. Sudha_cockroach
... ovaries. They are arranged in segments 4, 5 and 6 on lateral sides. • Ovarian tubules of each line join and form an oviduct. Oviducts from two ovaries join and form uterus. Uterus opens into vagina. • Vagina opens through a vaginal opening to the outside through segment number eight • A pair of bran ...
... ovaries. They are arranged in segments 4, 5 and 6 on lateral sides. • Ovarian tubules of each line join and form an oviduct. Oviducts from two ovaries join and form uterus. Uterus opens into vagina. • Vagina opens through a vaginal opening to the outside through segment number eight • A pair of bran ...
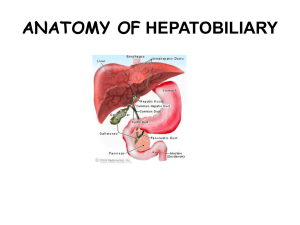
the portal vein
... The usual functional division of the liver into right and left lobes lies along this plane. The liver is further subdivided into segments, each supplied by a principal branch of the hepatic artery, portal vein and bile duct. Segments I, II, III and IV make up the functional left lobe, and segments V ...
... The usual functional division of the liver into right and left lobes lies along this plane. The liver is further subdivided into segments, each supplied by a principal branch of the hepatic artery, portal vein and bile duct. Segments I, II, III and IV make up the functional left lobe, and segments V ...
The Umbilical Cord and Body- stalk. The umbilical cord (Fig. 28
... the gland tubes are greatly dilated and very tortuous, and are ultimately separated from one another by only a small amount of interglandular tissue, while their lining cells are flattened or cubical; • (3) a thin unaltered or boundary layer, next the uterine muscular fibers, containing the deepest ...
... the gland tubes are greatly dilated and very tortuous, and are ultimately separated from one another by only a small amount of interglandular tissue, while their lining cells are flattened or cubical; • (3) a thin unaltered or boundary layer, next the uterine muscular fibers, containing the deepest ...
SBI 3U Pig Dissection Booklet
... 9. Locating the liver and the gallbladder: The liver is easily seen in the anterior aspect of the abdominal cavity. The gallbladder is located underneath the liver. Identify the gallbladder. Look carefully ...
... 9. Locating the liver and the gallbladder: The liver is easily seen in the anterior aspect of the abdominal cavity. The gallbladder is located underneath the liver. Identify the gallbladder. Look carefully ...
Bob Caruthers, CST, PLD - Association of Surgical Technologists
... plexus, the levator veli palantini, musculus uvulae, pharyngopalatinus, and glossopalatinus, salpingopharyngeus and pharyngeal constrictors are innervated. The glottis, epiglottic and lingual rami, inferior pharyngeal constrictor and cricothyroid muscle are reached by fibers traveling in the superio ...
... plexus, the levator veli palantini, musculus uvulae, pharyngopalatinus, and glossopalatinus, salpingopharyngeus and pharyngeal constrictors are innervated. The glottis, epiglottic and lingual rami, inferior pharyngeal constrictor and cricothyroid muscle are reached by fibers traveling in the superio ...
Skeletal System
... defecation and urination, inhaled air is held temporarily in the lower respiratory tract by closing the epiglottis The abdominal muscle then contract and the interabdominal pressure rises The action know as the Valsalva manuever can also stabilize the trunk when one lifts a ...
... defecation and urination, inhaled air is held temporarily in the lower respiratory tract by closing the epiglottis The abdominal muscle then contract and the interabdominal pressure rises The action know as the Valsalva manuever can also stabilize the trunk when one lifts a ...
Odormute Breakdown Industrial Digester
... both with and without oxygen. Since grease traps, drains and septic tanks are anaerobic systems (without oxygen), it is very important to have facultative anaerobes in the formula. Breakdown Industrial Digester PowderTM contains strains of Bacteria Producing Enzymes that produce digestive enzymes wh ...
... both with and without oxygen. Since grease traps, drains and septic tanks are anaerobic systems (without oxygen), it is very important to have facultative anaerobes in the formula. Breakdown Industrial Digester PowderTM contains strains of Bacteria Producing Enzymes that produce digestive enzymes wh ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.