SMSA - Introduction
... • No clear time limit for medical treatment • Relief of symptoms has been observed from 2 to 12 days; nevertheless, it has been also reported up to 169 days* and even up to 7 months in different cases *Lee CS, Mangla JC: Superior mesenteric artery compression syndrome. Am J ...
... • No clear time limit for medical treatment • Relief of symptoms has been observed from 2 to 12 days; nevertheless, it has been also reported up to 169 days* and even up to 7 months in different cases *Lee CS, Mangla JC: Superior mesenteric artery compression syndrome. Am J ...
QUESTION
... – 3rd trimester – injury to uterus and premature labor – Control symptoms – wait for 2nd trimester or delivery. Recurrence 50-75% – If pain intractable or course worsens – cholesystostomy is reasonable until 2nd trimester/ delivery is reached. ...
... – 3rd trimester – injury to uterus and premature labor – Control symptoms – wait for 2nd trimester or delivery. Recurrence 50-75% – If pain intractable or course worsens – cholesystostomy is reasonable until 2nd trimester/ delivery is reached. ...
Carbohydrates (CHO)
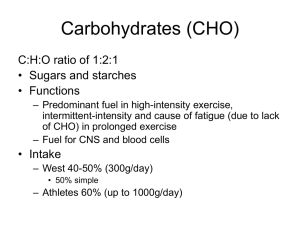
... e.g. 50g of CHO from carrots = 750g of carrots • Glycaemic Load (GL) is more practical and takes into account GI and serving size. ...
... e.g. 50g of CHO from carrots = 750g of carrots • Glycaemic Load (GL) is more practical and takes into account GI and serving size. ...
LINGUISTICS 330 Lecture #5
... it runs from the inner part of the thyroid to the anterior and lateral surfaces of the arytenoids VOCALIS MUSCLE (MEDIAL COMPONENT OF THE THYROARYTENOID MUSCLE): it runs parallel to the vocal ligaments as part of the vocal fold structure proper ...
... it runs from the inner part of the thyroid to the anterior and lateral surfaces of the arytenoids VOCALIS MUSCLE (MEDIAL COMPONENT OF THE THYROARYTENOID MUSCLE): it runs parallel to the vocal ligaments as part of the vocal fold structure proper ...
Phylum chordata and protochordates
... dorsal nerve cord notochord. pharyngeal slits (100 )which are used to strain food particles out of the water. The musculature of the body is divided up into V-shaped blocks, or myomeres. post-anal tail. On the other hand, cephalochordates lack features found in most or all true vertebrat ...
... dorsal nerve cord notochord. pharyngeal slits (100 )which are used to strain food particles out of the water. The musculature of the body is divided up into V-shaped blocks, or myomeres. post-anal tail. On the other hand, cephalochordates lack features found in most or all true vertebrat ...
Lobes of thyroid gland and carotid sheath (with its contents).
... – Skin, superficial fascia, investing deep fascia, pretracheal fascia, isthmus of thyroid gland, jugular arch, thyroidea ima artery, sternothyroid and sternohyoid muscles. Posterior: – Right and left recurrent laryngeal nerves, esophagus and vertebral column. Lateral: – Lobes of thyroid gland and ca ...
... – Skin, superficial fascia, investing deep fascia, pretracheal fascia, isthmus of thyroid gland, jugular arch, thyroidea ima artery, sternothyroid and sternohyoid muscles. Posterior: – Right and left recurrent laryngeal nerves, esophagus and vertebral column. Lateral: – Lobes of thyroid gland and ca ...
The 12 Cranial Nerves - Moebius Syndrome Foundation
... and face. Also carries sensory information for ear and tympanic membrane. Provides motor supply to the muscles of masticulation (chewing), and to some of the muscles on the floor of the mouth. Also provides motor supply to tensor tympani (small muscle in the middle ear which tenses to protect the ea ...
... and face. Also carries sensory information for ear and tympanic membrane. Provides motor supply to the muscles of masticulation (chewing), and to some of the muscles on the floor of the mouth. Also provides motor supply to tensor tympani (small muscle in the middle ear which tenses to protect the ea ...
Pharynx Larynx - Dr. Gudas
... of the auditory tube, with the torus tubarus projecting inferiorly from the orifice. Extending inferiorly from the torus is the salpingopharyngeal fold, and behind it a recess, the pharyngeal recess, that extends up to the superior limit of the pharynx. Pharyngeal tonsils, collections of lymphoi ...
... of the auditory tube, with the torus tubarus projecting inferiorly from the orifice. Extending inferiorly from the torus is the salpingopharyngeal fold, and behind it a recess, the pharyngeal recess, that extends up to the superior limit of the pharynx. Pharyngeal tonsils, collections of lymphoi ...
lnternal morphology and histology of the fish mite
... The internal morphology and histology of the adult digestive system of Lardoglyphits konoi an Acaridiae, are described from serial paraffin sections. The alimentary tract has a typical acarid form, with a •vell developed stomach armed with a pair of caeca, a distinct colon and a rectum. At least thr ...
... The internal morphology and histology of the adult digestive system of Lardoglyphits konoi an Acaridiae, are described from serial paraffin sections. The alimentary tract has a typical acarid form, with a •vell developed stomach armed with a pair of caeca, a distinct colon and a rectum. At least thr ...
FOR THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ANSWER: A. if choices 1, 2
... 2. A wide subpubic arch 3. Widely spaced ischial spines 4. Resemblance to a shallow, flat bowl 21. Which of the following structures can be palpated through the rectum? 1. Ischial spines 2. Enlarged internal iliac lymph nodes 3. Ischiorectal abscess 4. Prostate ...
... 2. A wide subpubic arch 3. Widely spaced ischial spines 4. Resemblance to a shallow, flat bowl 21. Which of the following structures can be palpated through the rectum? 1. Ischial spines 2. Enlarged internal iliac lymph nodes 3. Ischiorectal abscess 4. Prostate ...
NERVE SUPPLY OF ABDOMEN
... Receives filaments from both the right and left vagus as well as from the phrenic nerves. Accompanies the hepatic artery and the portal vein and their branches and also supplies the cystic plexus to the gallbladder. Branches may also supply the pylorus, greater curvature of stomach as well as the lo ...
... Receives filaments from both the right and left vagus as well as from the phrenic nerves. Accompanies the hepatic artery and the portal vein and their branches and also supplies the cystic plexus to the gallbladder. Branches may also supply the pylorus, greater curvature of stomach as well as the lo ...
Urogenital triangle in female + Perineal pouches
... of skin containing fatty tissue and covered with hair Located on either side of the vaginal opening, extending from the mons pubis to the perineum ...
... of skin containing fatty tissue and covered with hair Located on either side of the vaginal opening, extending from the mons pubis to the perineum ...
Respiratory System
... TRACT/Lungs continued - Lobes * Right Lung - 3 Lobes: Superior, Middle, Inferior * Left Lung - 2 Lobes: Superior, Inferior - Fissures * Horizontal Fissure (Between Superior & Middle Lobes, Right Lung) * Right Oblique Fissure (Middle & Inferior) * Left Oblique Fissure (Superior & Inferior) ...
... TRACT/Lungs continued - Lobes * Right Lung - 3 Lobes: Superior, Middle, Inferior * Left Lung - 2 Lobes: Superior, Inferior - Fissures * Horizontal Fissure (Between Superior & Middle Lobes, Right Lung) * Right Oblique Fissure (Middle & Inferior) * Left Oblique Fissure (Superior & Inferior) ...
Development of respiratory system
... Since musculature of the larynx is derived from mesenchyme of the 4th & 6th pharyngeal arches, all laryngeal muscles are innervated by branches of the 10th cranial nerve (vagus nerve). The superior laryngeal nerve innervates derivatives of the fourth pharyngeal arch, and the recurrent laryngeal ne ...
... Since musculature of the larynx is derived from mesenchyme of the 4th & 6th pharyngeal arches, all laryngeal muscles are innervated by branches of the 10th cranial nerve (vagus nerve). The superior laryngeal nerve innervates derivatives of the fourth pharyngeal arch, and the recurrent laryngeal ne ...
Peritoneum and Intraperitoneal Viscera
... 3.1.1 Development of the Digestive Tube Until the end of the second gestational week, the embryonic disk (blastodisk) consists of two germ layers, the endoderm and ectoderm, separated from each other by a basal membrane. Both germ layers participate in forming the third layer, the mesoderm, which d ...
... 3.1.1 Development of the Digestive Tube Until the end of the second gestational week, the embryonic disk (blastodisk) consists of two germ layers, the endoderm and ectoderm, separated from each other by a basal membrane. Both germ layers participate in forming the third layer, the mesoderm, which d ...
Surgical Anatomy of the Gastroduodenal Artery
... Distance from the Pylorus to the Retroduodenal Segment of the Gastroduodenal Artery: — In 23 specimens the distance from the pylorus to the retroduodenal segment.of the gastroduodenal artery averaged 2,5 cm ± 0.3 cm variation. In two specimens the entire first portion of the duodenum had a mesentery ...
... Distance from the Pylorus to the Retroduodenal Segment of the Gastroduodenal Artery: — In 23 specimens the distance from the pylorus to the retroduodenal segment.of the gastroduodenal artery averaged 2,5 cm ± 0.3 cm variation. In two specimens the entire first portion of the duodenum had a mesentery ...
AS 12-13 Cards 1-137_Layout 1
... ethmoid bone, the vomer bone, and the septal cartilage. The rest of the framework of the nose consists of several plates of cartilage, specifically, the lateral nasal cartilage and the greater and lesser alar cartilage. The cartilage is held together by fibrous connective tissue. The nasal cavity op ...
... ethmoid bone, the vomer bone, and the septal cartilage. The rest of the framework of the nose consists of several plates of cartilage, specifically, the lateral nasal cartilage and the greater and lesser alar cartilage. The cartilage is held together by fibrous connective tissue. The nasal cavity op ...
Page 1 of 2 The Larynx, Basic Anatomy The larynx, or voicebox, is
... cartilage. The anterior portion of the thyroid cartilage can be easily felt in thin necks as the "Adam's apple". Superior to the larynx (sometimes considered part of the larynx itself) is a U-shaped bone called the hyoid. The hyoid bone supports the larynx from above and is itself attached to the ma ...
... cartilage. The anterior portion of the thyroid cartilage can be easily felt in thin necks as the "Adam's apple". Superior to the larynx (sometimes considered part of the larynx itself) is a U-shaped bone called the hyoid. The hyoid bone supports the larynx from above and is itself attached to the ma ...
Minerals
... – mostly found in the food in ferric form (Fe3+), bound to protein or organic acid. – In the acid medium provided by gastric HCl, the Fe3+ is released from food. – Reducing substances such as ascorbate (Vitamin C) and cystein reduces ferric form (Fe3+) to ferrous form (Fe2+). – Iron in ferrous form ...
... – mostly found in the food in ferric form (Fe3+), bound to protein or organic acid. – In the acid medium provided by gastric HCl, the Fe3+ is released from food. – Reducing substances such as ascorbate (Vitamin C) and cystein reduces ferric form (Fe3+) to ferrous form (Fe2+). – Iron in ferrous form ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... branches to the respiratory structures. The involuntary, rhythmic activities that deliver and remove respiratory gases are regulated in the brainstem. Regulatory respiratory centers are located within the reticular formation through both the medulla oblongata and pons. ...
... branches to the respiratory structures. The involuntary, rhythmic activities that deliver and remove respiratory gases are regulated in the brainstem. Regulatory respiratory centers are located within the reticular formation through both the medulla oblongata and pons. ...
Survey of the phyla: Porifera through Annelida
... Show metamerism = true segmentation (characteristic of higher animals) Organs are paired in segments ...
... Show metamerism = true segmentation (characteristic of higher animals) Organs are paired in segments ...
Biochemie jater
... 1. The liver takes up glucose and other monosaccharides from the blood plasma -These sugars are then converted to glucose 6-phosphate and other intermediates of glycolysis (subsequently, they are either stored as the reserve carbohydrate glycogen or degraded) -Another large part is converted into fa ...
... 1. The liver takes up glucose and other monosaccharides from the blood plasma -These sugars are then converted to glucose 6-phosphate and other intermediates of glycolysis (subsequently, they are either stored as the reserve carbohydrate glycogen or degraded) -Another large part is converted into fa ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.