Variant origin of thyrolingual trunk from left common carotid artery
... The right common carotid artery originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk while the left arise from the aortic arch in the thoracic region. The cervical portion of common carotids resembles each other very closely. The common carotid artery is contained in a sheath known as the carotid s ...
... The right common carotid artery originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk while the left arise from the aortic arch in the thoracic region. The cervical portion of common carotids resembles each other very closely. The common carotid artery is contained in a sheath known as the carotid s ...
High origin of ulnar artery in South Indian male cadaver
... The same variation was observed in our dissection. The Course of SUA over the forearm flexor muscles and underneath the bicipital aponeurosis was also observed in this case, which is also not well reported in the literature. Many theories on the development of the arterial system of the upper limb h ...
... The same variation was observed in our dissection. The Course of SUA over the forearm flexor muscles and underneath the bicipital aponeurosis was also observed in this case, which is also not well reported in the literature. Many theories on the development of the arterial system of the upper limb h ...
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial
... canal in the posterior wall of the middle ear . It runs forward over the medial surface of the upper part of the tympanic membrane and leaves the middle ear through the petrotympanic fissure, thus entering the infratemporal fossa and joining the lingual nerve. The chorda tympani contains preganglion ...
... canal in the posterior wall of the middle ear . It runs forward over the medial surface of the upper part of the tympanic membrane and leaves the middle ear through the petrotympanic fissure, thus entering the infratemporal fossa and joining the lingual nerve. The chorda tympani contains preganglion ...
Anatomical Variations in the Arteries and Nerves of the Right Carotid
... The Superior thyroid artery (STA) is the first branch of External carotid artery given off from its anterior aspect, just below the level of the greater cornu of hyoid bone. This artery runs along the lateral border of thyrohyoid muscle to reach the apex of the lobe of thyroid gland, thus furnishing ...
... The Superior thyroid artery (STA) is the first branch of External carotid artery given off from its anterior aspect, just below the level of the greater cornu of hyoid bone. This artery runs along the lateral border of thyrohyoid muscle to reach the apex of the lobe of thyroid gland, thus furnishing ...
Fat-Soluble Vitamins Guide
... reported for individuals supplementing or consuming higher amounts of vitamin K. Vitamin K from diet is often limited. Symptoms of vitamin K deficiency include easy brisability, epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleeding, menorrhagia and hameturia. ...
... reported for individuals supplementing or consuming higher amounts of vitamin K. Vitamin K from diet is often limited. Symptoms of vitamin K deficiency include easy brisability, epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleeding, menorrhagia and hameturia. ...
A rare variation of the inferior alveolar artery with potential clinical
... The maxillary artery arises posterior to the neck of the mandible as the larger terminal branch of the external carotid artery. Along its course the artery gives off branches to various structures such as the external acoustic meatus, the middle ear, the muscles of mastication, the skull, the dura m ...
... The maxillary artery arises posterior to the neck of the mandible as the larger terminal branch of the external carotid artery. Along its course the artery gives off branches to various structures such as the external acoustic meatus, the middle ear, the muscles of mastication, the skull, the dura m ...
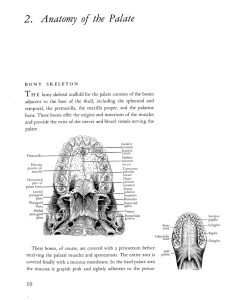
2 m – 25. Aorta. External carotid artery
... oesophagus. They do not give off any branches in the neck. At the level of the superior margin of the thyroid cartilage (C4), the carotid arteries split into the external and internal carotid arteries. This bifurcation occurs in an anatomical area known as the carotid triangle. The common carotid an ...
... oesophagus. They do not give off any branches in the neck. At the level of the superior margin of the thyroid cartilage (C4), the carotid arteries split into the external and internal carotid arteries. This bifurcation occurs in an anatomical area known as the carotid triangle. The common carotid an ...
Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis with Gastric Necrosis in a Female
... Hereditary pancreatitis (HP) is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by chronic pancreatitis during childhood without the identification of known inciting factors. There is no consensus about the diagnostic criteria for HP, but the EUROPAC trial defined it as two first-degree relatives or at ...
... Hereditary pancreatitis (HP) is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by chronic pancreatitis during childhood without the identification of known inciting factors. There is no consensus about the diagnostic criteria for HP, but the EUROPAC trial defined it as two first-degree relatives or at ...
Essential Functional Hepatic and Biliary Anatomy for the
... 1) a failure to possess sufficient knowledge of normal anatomy and function, 2) a failure to recognize anatomic variants when they present, and 3) a failure to ask for help when uncertain or unsure. All but the last of these errors are remediable with study and effort. In regard to the last error, m ...
... 1) a failure to possess sufficient knowledge of normal anatomy and function, 2) a failure to recognize anatomic variants when they present, and 3) a failure to ask for help when uncertain or unsure. All but the last of these errors are remediable with study and effort. In regard to the last error, m ...
Surgical Anatomy of Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands and Basic
... makes this procedure almost completely bloodless. The drainage of the network of the capsular veins is done through three vein trunks. The superior thyroid veins, directly or indirectly (via truncus thyreolinguofacialis), flow into the internal jugular vein just in front of and laterally from the su ...
... makes this procedure almost completely bloodless. The drainage of the network of the capsular veins is done through three vein trunks. The superior thyroid veins, directly or indirectly (via truncus thyreolinguofacialis), flow into the internal jugular vein just in front of and laterally from the su ...
Chapter 2 Immobilization of Enzymes
... nineteenth century, immobilized microorganisms were being employed industrially on an empirical basis. This was the case of the microbial production of vinegar by letting alcohol-containing solutions trickle over wood shavings overgrown with bacteria, and that of the trickling filter or percolating ...
... nineteenth century, immobilized microorganisms were being employed industrially on an empirical basis. This was the case of the microbial production of vinegar by letting alcohol-containing solutions trickle over wood shavings overgrown with bacteria, and that of the trickling filter or percolating ...
Flavin coenzymes
... III. Water-soluble vitamins 1. Vitamin B1: Thiamine and thiamine pyrophosphate 2. Vitamins related to adenine nucleotides 1) Nicotinic acid and the nicotinamide coenzymes ...
... III. Water-soluble vitamins 1. Vitamin B1: Thiamine and thiamine pyrophosphate 2. Vitamins related to adenine nucleotides 1) Nicotinic acid and the nicotinamide coenzymes ...
ORIGIN OF THE FACIAL ARTERY FROM THE LINGUAL
... origin and the course of the facial artery in the right digastric triangle of an approximately 60year-old male cadaver of Indian origin. The dissection of this region was carried out according to the instructions by Cunningham’s manual of practical anatomy (Romanes, 2004). In the present case, the f ...
... origin and the course of the facial artery in the right digastric triangle of an approximately 60year-old male cadaver of Indian origin. The dissection of this region was carried out according to the instructions by Cunningham’s manual of practical anatomy (Romanes, 2004). In the present case, the f ...
Week 2 Notes - UWI St. Augustine
... ∙ The lung bud develops into 2 endodermal bronchial buds which grow into the pericardioperitoneal cavities, the primordia of the pleural cavities. • Early in week 5, each bronchial bud enlarges into the primordium of a primary bronchus. The right one is slightly larger than the left and is oriented ...
... ∙ The lung bud develops into 2 endodermal bronchial buds which grow into the pericardioperitoneal cavities, the primordia of the pleural cavities. • Early in week 5, each bronchial bud enlarges into the primordium of a primary bronchus. The right one is slightly larger than the left and is oriented ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... Vitamin B12 deficiency is rarely a result of an absence of the vitamin in the diet. It is much more common to find deficiencies in patients who fail to absorb the vitamin from the intestine, resulting in pernicious anemia. The disease is most commonly a result of an autoimmune destruction of the gas ...
... Vitamin B12 deficiency is rarely a result of an absence of the vitamin in the diet. It is much more common to find deficiencies in patients who fail to absorb the vitamin from the intestine, resulting in pernicious anemia. The disease is most commonly a result of an autoimmune destruction of the gas ...
Multiple arterial, neural and muscular variations in upper limb of a
... of the arm. It then descended along the arm superficial and lateral to the median nerve (Figure 1). At the elbow level, the artery ran superficial to the bicipital aponeurosis, coursed obliquely downwards and medially, superficial to the forearm flexor muscles over the antebrachial fascia and under ...
... of the arm. It then descended along the arm superficial and lateral to the median nerve (Figure 1). At the elbow level, the artery ran superficial to the bicipital aponeurosis, coursed obliquely downwards and medially, superficial to the forearm flexor muscles over the antebrachial fascia and under ...
Thyroid and parathyroid ultrasound
... Lymph nodes of the anterior and lateral regions of the neck must be investigated especially when a suspicious nodule is detected in the thyroid. Normal lymph nodes are small (< 1 cm), hypoechoic, with a central hyperechoic line representing the vascular hilum (fig 10). The lymph nodes number and loc ...
... Lymph nodes of the anterior and lateral regions of the neck must be investigated especially when a suspicious nodule is detected in the thyroid. Normal lymph nodes are small (< 1 cm), hypoechoic, with a central hyperechoic line representing the vascular hilum (fig 10). The lymph nodes number and loc ...
SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE SUPERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY
... artery were reviewed in 90 patients who underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Results: Gross arterial communication between the superior and inferior epigastric arteries was observed in (33%) of the cadavers where it was located above the umbilicus. In the epigastric region, the main stem of the s ...
... artery were reviewed in 90 patients who underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Results: Gross arterial communication between the superior and inferior epigastric arteries was observed in (33%) of the cadavers where it was located above the umbilicus. In the epigastric region, the main stem of the s ...
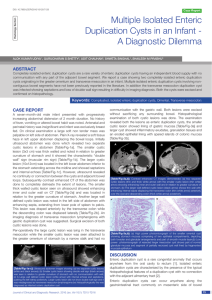
Multiple Isolated Enteric Duplication Cysts in an Infant
... cyst and reported that frequency of malignancy is highest in colonic duplication cysts and most occur in adults [9]. Though the association of mesenteric lymphangioma with volvulus is well known few case reports also point to association of volvulus with duplication cyst [10]. These cases lend suppo ...
... cyst and reported that frequency of malignancy is highest in colonic duplication cysts and most occur in adults [9]. Though the association of mesenteric lymphangioma with volvulus is well known few case reports also point to association of volvulus with duplication cyst [10]. These cases lend suppo ...
The interaction between bacteria and bile
... bile form mixed micelles with phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. When bile enters the small intestine, phosphatidylcholine is hydrolysed and absorbed and cholesterol precipitates from solution enhancing its elimination. The amphipathic nature of bile acids allows them to have detergent action on p ...
... bile form mixed micelles with phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol. When bile enters the small intestine, phosphatidylcholine is hydrolysed and absorbed and cholesterol precipitates from solution enhancing its elimination. The amphipathic nature of bile acids allows them to have detergent action on p ...
- Journal of Hepatology
... Diren Beyoğlu, Jeffrey R. Idle⇑ Hepatology Research Group, Department of Clinical Research, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland ...
... Diren Beyoğlu, Jeffrey R. Idle⇑ Hepatology Research Group, Department of Clinical Research, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland ...
THYROID/PARATHYROID - Orange Coast College
... I. Introduction/General Information A. Thyroid 1. Endocrine gland a. Lobes are cone shaped b. Apex extends to oblique line of thyroid cartilage ...
... I. Introduction/General Information A. Thyroid 1. Endocrine gland a. Lobes are cone shaped b. Apex extends to oblique line of thyroid cartilage ...
multiple variations of branches of abdominal aorta
... Multiple variations of the branches of abdominal aorta were observed during a routine dissection of the abdominal region in a 66-yearold male cadaver in the Department of Anatomy, Yenepoya Medical College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore. In the present case, both the inferior phrenic arteries arise ...
... Multiple variations of the branches of abdominal aorta were observed during a routine dissection of the abdominal region in a 66-yearold male cadaver in the Department of Anatomy, Yenepoya Medical College, Yenepoya University, Mangalore. In the present case, both the inferior phrenic arteries arise ...
An autonomic pathway from the central nervous system to the
... A. Its sensory branch can become activated and initiate the cough reflex if food or water enters the laryngeal inlet. B. Its external branch innervates the cricothyroid muscle, whose action is to alter the pitch of the voice. C. Its internal branch provides sensory innervation to the larynx below th ...
... A. Its sensory branch can become activated and initiate the cough reflex if food or water enters the laryngeal inlet. B. Its external branch innervates the cricothyroid muscle, whose action is to alter the pitch of the voice. C. Its internal branch provides sensory innervation to the larynx below th ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.