What is learning? - Business Information Management
... disappear if the CS is repeteadly presented by itself; without the Unconditioned Stimulus – Bell but no food ...
... disappear if the CS is repeteadly presented by itself; without the Unconditioned Stimulus – Bell but no food ...
Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to
... Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Reinforcement: Any event that increases the probability that a response will recur Focus on what can be seen and measured. Classical Conditioning – Pavlov/Watson Operant Conditioning- Skinner Social Cognitive Theory – Bandura (emerg ...
... Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Reinforcement: Any event that increases the probability that a response will recur Focus on what can be seen and measured. Classical Conditioning – Pavlov/Watson Operant Conditioning- Skinner Social Cognitive Theory – Bandura (emerg ...
Classical Conditioning Features of Classical Conditioning Theorists
... Postulates of Change: Change occurs as an automatic learning response through a repeated stimulus that is administered with another stimulus over time. Eventually, one stimulus is taken away and if the learning occurred, the response still occurs with only one stimulus present. The mechanism of lear ...
... Postulates of Change: Change occurs as an automatic learning response through a repeated stimulus that is administered with another stimulus over time. Eventually, one stimulus is taken away and if the learning occurred, the response still occurs with only one stimulus present. The mechanism of lear ...
Adult Learning Theory
... Orientation to learning aspects: this provided me with the understating that adults can be utilized in the production of learning experiences by integration them into resources for learning. Often times, people do not utilize this reservoir of experiences and talents. At the same time, relating lear ...
... Orientation to learning aspects: this provided me with the understating that adults can be utilized in the production of learning experiences by integration them into resources for learning. Often times, people do not utilize this reservoir of experiences and talents. At the same time, relating lear ...
What is Development
... ◦ Focus on important overarching aspects of lessons ◦ Use active learning ...
... ◦ Focus on important overarching aspects of lessons ◦ Use active learning ...
Corps & Cognition team meeting, 2014/12/02 A (new) non
... subject may learn to stay erect just by experiencing moments of vertical equilibrium (moments during which he does not received any information). How neurons can learn something in absence of events? ...
... subject may learn to stay erect just by experiencing moments of vertical equilibrium (moments during which he does not received any information). How neurons can learn something in absence of events? ...
Universidade do Algarve
... common-sense notion of learning covers a limited scope:-usually associated with o school materials; o mastery of a skill or specific activity. ...
... common-sense notion of learning covers a limited scope:-usually associated with o school materials; o mastery of a skill or specific activity. ...
File - MAJU SUPPORT
... transferred from one situation to another and the extent of such transfer is a function of the extent of similarity in response. Generalization (repetition of initial behaviour) No two situations are alike. Responses to certain situations can be applied to similar but different situations. The indiv ...
... transferred from one situation to another and the extent of such transfer is a function of the extent of similarity in response. Generalization (repetition of initial behaviour) No two situations are alike. Responses to certain situations can be applied to similar but different situations. The indiv ...
learning and memory
... Advertising Recall as function of timing and number of exposures (Zielske 1959) ...
... Advertising Recall as function of timing and number of exposures (Zielske 1959) ...
Learning
... The failure to avoid or escape from an unpleasant or aversive stimulus that occurs as a result of previous exposure to unavoidable painful stimuli is referred to as learned helplessness. Learned helplessness, which has been demonstrated in both animals and humans, is associated with many of the symp ...
... The failure to avoid or escape from an unpleasant or aversive stimulus that occurs as a result of previous exposure to unavoidable painful stimuli is referred to as learned helplessness. Learned helplessness, which has been demonstrated in both animals and humans, is associated with many of the symp ...
5 Behavioural - WordPress.com
... • Observational Learning – learning of a new behaviour through the observation of a model (watching someone else who is doing that behaviour) • Children observe adults’ behaviours at home, during social ceremonies and functions etc. • Children learn and develop various personality characteristics th ...
... • Observational Learning – learning of a new behaviour through the observation of a model (watching someone else who is doing that behaviour) • Children observe adults’ behaviours at home, during social ceremonies and functions etc. • Children learn and develop various personality characteristics th ...
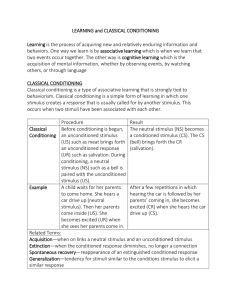
LEARNING and Classical Conditioning
... acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language CLASSICAL CONDITIONING Classical conditioning is a type of associative learning that is strongly tied to behaviorism. Classical conditioning is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus crea ...
... acquisition of mental information, whether by observing events, by watching others, or through language CLASSICAL CONDITIONING Classical conditioning is a type of associative learning that is strongly tied to behaviorism. Classical conditioning is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus crea ...
cb2-12
... – Positive reinforcers are stimuli that tend to increase the probability that the behavior/response which preceded it will be repeated (e.g., premiums). – Negative reinforcers are stimuli that increase the probability of a behavior/response by removing a negative, aversive stimulus that usually foll ...
... – Positive reinforcers are stimuli that tend to increase the probability that the behavior/response which preceded it will be repeated (e.g., premiums). – Negative reinforcers are stimuli that increase the probability of a behavior/response by removing a negative, aversive stimulus that usually foll ...
Socio-Bio-Cognitive Learning ppt.
... Retention (need to remember situation to imitate it) Motivation (this is where vicarious punishments and rewards come in) Production (can't imitate something you are unable to do) ...
... Retention (need to remember situation to imitate it) Motivation (this is where vicarious punishments and rewards come in) Production (can't imitate something you are unable to do) ...
Chapter 6: Learning and Language PPT
... 2. In one experiment, noticed that dog would salivate at site of Pavlov or assistant even if food was not being carried a. salivation is part of digestion ...
... 2. In one experiment, noticed that dog would salivate at site of Pavlov or assistant even if food was not being carried a. salivation is part of digestion ...
Learning Practice Questions
... Learning Practice Questions 1. The type of learning most associated B.F. Skinner is a. classical conditioning b. operant conditioning c. observational learning d. modeling e. insight learning 2. In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as a a. CS b. CR c. discriminative stimulus d. ...
... Learning Practice Questions 1. The type of learning most associated B.F. Skinner is a. classical conditioning b. operant conditioning c. observational learning d. modeling e. insight learning 2. In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as a a. CS b. CR c. discriminative stimulus d. ...
Learning - WordPress.com
... Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior , that is brought about by experience Behaviorism: The theory of learning focuses solely on observable behaviors ...
... Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior , that is brought about by experience Behaviorism: The theory of learning focuses solely on observable behaviors ...
Psy 331 study guide week 13
... 1. Describe the area of the brain that is involved in fear learning and reward learning. 2. What is LTP? Why is this important for learning? 3. What medications are used to treat behavioral conditions in dog and cats? How do these drugs affect the brain and learning? 4. According to Overall, how muc ...
... 1. Describe the area of the brain that is involved in fear learning and reward learning. 2. What is LTP? Why is this important for learning? 3. What medications are used to treat behavioral conditions in dog and cats? How do these drugs affect the brain and learning? 4. According to Overall, how muc ...
LEARNING NOTES Over the years there are so many things that
... lot of this learning. How did we expand our learning? What helped us learn? Who helped us to learn? By understanding what exactly is the process of learning we can answer these and related questions. It would also help if we understand the various psychological processes that occur during learning L ...
... lot of this learning. How did we expand our learning? What helped us learn? Who helped us to learn? By understanding what exactly is the process of learning we can answer these and related questions. It would also help if we understand the various psychological processes that occur during learning L ...
File
... • Learning is a relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience. • How do we learn things? – Associative Learning – Observational Learning ...
... • Learning is a relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience. • How do we learn things? – Associative Learning – Observational Learning ...
learning behavior
... animals with, well developed brains. It is also shown even by smaller creatures like earthworms. An earthworm is placed in the stem of T-shaped tube. If it turns left it is given the electric shock, if it turns right it is returned to its box without punishment. It is claimed by scientists that the ...
... animals with, well developed brains. It is also shown even by smaller creatures like earthworms. An earthworm is placed in the stem of T-shaped tube. If it turns left it is given the electric shock, if it turns right it is returned to its box without punishment. It is claimed by scientists that the ...
Learning - School of Computing | University of Leeds
... • reinforcement learning • agent interacts with environment and receives • rewards (positive reinforcement) • punishments (negative reinforcement) ...
... • reinforcement learning • agent interacts with environment and receives • rewards (positive reinforcement) • punishments (negative reinforcement) ...