Psychology 312-1 - Northwestern University
... perspective (where any physical action is a behavior), is a philosophy of psychology based on the proposition that all things that organisms do—including acting, thinking and feeling—can and should be regarded as behaviors.[1] The behaviorist school of thought maintains that behaviors as such can be ...
... perspective (where any physical action is a behavior), is a philosophy of psychology based on the proposition that all things that organisms do—including acting, thinking and feeling—can and should be regarded as behaviors.[1] The behaviorist school of thought maintains that behaviors as such can be ...
Basic Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
... – Unconditioned Response (UCR) • An innate reflex response elicited by an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) ...
... – Unconditioned Response (UCR) • An innate reflex response elicited by an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) ...
Behaviorist Perspective - West Point Public Schools
... Classical Conditioning Introduced by Ivan Pavlov during his study of digestive systems in animals Learning through association of an unconditioned response (reflex) with a conditioned stimulus (that was previously ...
... Classical Conditioning Introduced by Ivan Pavlov during his study of digestive systems in animals Learning through association of an unconditioned response (reflex) with a conditioned stimulus (that was previously ...
Family Name: Name: Chapter 1 Studying learning What is the
... minutes of guided exercise are conducted every hour. After 6 months applying the treatment, management reports an increase in productivity of 80%. The psychologist concludes that such increase is due to the 5-min guided exercise program. May she reach that conclusion? Why? Present a design that woul ...
... minutes of guided exercise are conducted every hour. After 6 months applying the treatment, management reports an increase in productivity of 80%. The psychologist concludes that such increase is due to the 5-min guided exercise program. May she reach that conclusion? Why? Present a design that woul ...
Synapse formation
... • Newly learnt information to be transferred from one neuron to the next is more efficient • The more that a particular neural pathway is activated during learning, the more likely it is to be strengthened and the less likely the learning will be forgotten. ...
... • Newly learnt information to be transferred from one neuron to the next is more efficient • The more that a particular neural pathway is activated during learning, the more likely it is to be strengthened and the less likely the learning will be forgotten. ...
learners
... • The server acts as a grouping coordinator of grouping requests from teachers and a communication coordinator of synchronous interactions between paired learners. ...
... • The server acts as a grouping coordinator of grouping requests from teachers and a communication coordinator of synchronous interactions between paired learners. ...
6 Knowing and Understanding the World
... programmes and movies provide much of the learning to the young people. When children watch violence on TV they tend to learn such behaviour. We learn various social roles through observational learning. However, observational learning is a complex process, far more complex than mere imitation. Chil ...
... programmes and movies provide much of the learning to the young people. When children watch violence on TV they tend to learn such behaviour. We learn various social roles through observational learning. However, observational learning is a complex process, far more complex than mere imitation. Chil ...
Setting Up Interesting Learning Opportunities
... challenging. Some children have limited interests in their classrooms. They may be children who tend to wander around the classroom and don’t often play with peers, toys, or materials. How can teachers find interesting and meaningful opportunities to help children practice skills when children don’t ...
... challenging. Some children have limited interests in their classrooms. They may be children who tend to wander around the classroom and don’t often play with peers, toys, or materials. How can teachers find interesting and meaningful opportunities to help children practice skills when children don’t ...
Behaviourism
... ■ Behavioural psychology can be applied to individuals with a wide variety of mental disorders, as well as to groups such as those in the workplace. ...
... ■ Behavioural psychology can be applied to individuals with a wide variety of mental disorders, as well as to groups such as those in the workplace. ...
Chapter 9 - Brands Delmar
... 9:1 Culture, Ethnicity, and Race • Health care workers are involved with many different people • Respect individuality • Be aware of factors that cause each person to be unique • Influence is cultural/ethnic heritage ...
... 9:1 Culture, Ethnicity, and Race • Health care workers are involved with many different people • Respect individuality • Be aware of factors that cause each person to be unique • Influence is cultural/ethnic heritage ...
Slide 1
... Key proponent of social learning theory Based on studies of children, in particular the observation that children tend to imitate their parents People learn by observing the behaviour of others and the outcome of those behaviours, which does not necessarily involve direct exposure to reinforcement T ...
... Key proponent of social learning theory Based on studies of children, in particular the observation that children tend to imitate their parents People learn by observing the behaviour of others and the outcome of those behaviours, which does not necessarily involve direct exposure to reinforcement T ...
Identifying goals and target behaviors. The first step is
... interval schedules, which are based on the time interval that elapses before reinforcement is provided. (p. 191) • Stimulus control training (similar to stimulus discrimi nation in classical conditioning) is reinforcement of a behavior in the presence of a specific stimulus but not in its absence ...
... interval schedules, which are based on the time interval that elapses before reinforcement is provided. (p. 191) • Stimulus control training (similar to stimulus discrimi nation in classical conditioning) is reinforcement of a behavior in the presence of a specific stimulus but not in its absence ...
Learning
... Do not omit mental processes from explanations of human learning. Learning is not so much a change in observable behaviour as a change in knowledge that has the potential for affecting behaviour. Emphasize learning by observation and imitation, positive consequences, and cognitive processes such as ...
... Do not omit mental processes from explanations of human learning. Learning is not so much a change in observable behaviour as a change in knowledge that has the potential for affecting behaviour. Emphasize learning by observation and imitation, positive consequences, and cognitive processes such as ...
Associative Learning
... • If an organism has already learned that one CS predicts the UCS, that will block the conditioning of a new CS if the new CS does not provide any additional information • Example: Fear conditioning of a tone blocks conditioning of a light ...
... • If an organism has already learned that one CS predicts the UCS, that will block the conditioning of a new CS if the new CS does not provide any additional information • Example: Fear conditioning of a tone blocks conditioning of a light ...
Learning
... • If an organism has already learned that one CS predicts the UCS, that will block the conditioning of a new CS if the new CS does not provide any additional information • Example: Fear conditioning of a tone blocks conditioning of a light ...
... • If an organism has already learned that one CS predicts the UCS, that will block the conditioning of a new CS if the new CS does not provide any additional information • Example: Fear conditioning of a tone blocks conditioning of a light ...
Learning
... Learning What are some examples of other involuntary or reflexive unconditioned responses (UCR’s): - Knee jerk patellar reflex: response to doctors tap - Blinking: response to air puffs to the eye - Sweating: response to heat - Shivering: response to cold - Emotional reactions such as fear - Saliva ...
... Learning What are some examples of other involuntary or reflexive unconditioned responses (UCR’s): - Knee jerk patellar reflex: response to doctors tap - Blinking: response to air puffs to the eye - Sweating: response to heat - Shivering: response to cold - Emotional reactions such as fear - Saliva ...
Learning Chapter 6 - Mrs. Short`s AP Psychology Class
... • learning - a systematic, relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs through experience • behaviorism – a theory of learning that focuses solely on observable behaviors, discounting the importance of such mental activity as thinking, wishing, and hoping • associative learning / conditionin ...
... • learning - a systematic, relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs through experience • behaviorism – a theory of learning that focuses solely on observable behaviors, discounting the importance of such mental activity as thinking, wishing, and hoping • associative learning / conditionin ...
Constructivism Definition Constructivism is a philosophy of learning
... Behaviorism does not account for all kinds of learning, since it disregards the activities of the mind. Behaviorism does not explain some learning--such as the recognition of new language patterns by young children--for which there is no reinforcement mechanism. Reserach has shown that animals adapt ...
... Behaviorism does not account for all kinds of learning, since it disregards the activities of the mind. Behaviorism does not explain some learning--such as the recognition of new language patterns by young children--for which there is no reinforcement mechanism. Reserach has shown that animals adapt ...
Operant Conditioning, cont`d
... •Negative reinforcement: a reinforcement procedure in which a response is followed by the removal, delay or decrease in intensity of an unpleasant stimulus; as a result, the response becomes stronger and more likely to occur. ...
... •Negative reinforcement: a reinforcement procedure in which a response is followed by the removal, delay or decrease in intensity of an unpleasant stimulus; as a result, the response becomes stronger and more likely to occur. ...
Learning - ISA
... stimulus. In other words, the CS no longer elicits the CR. ◦ To acquire a CR, we repeatedly pair a neutral stimulus with the UCS. But, if we want to reverse this learning, we must weaken the strength of the connection between the two stimuli. For example, once the dogs have been conditioned to saliv ...
... stimulus. In other words, the CS no longer elicits the CR. ◦ To acquire a CR, we repeatedly pair a neutral stimulus with the UCS. But, if we want to reverse this learning, we must weaken the strength of the connection between the two stimuli. For example, once the dogs have been conditioned to saliv ...
AP Psych – Ch 6 – Learning – PRESENTATION
... • learning - a systematic, relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs through experience • behaviorism – a theory of learning that focuses solely on observable behaviors, discounting the importance of such mental activity as thinking, wishing, and hoping • associative learning / conditionin ...
... • learning - a systematic, relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs through experience • behaviorism – a theory of learning that focuses solely on observable behaviors, discounting the importance of such mental activity as thinking, wishing, and hoping • associative learning / conditionin ...
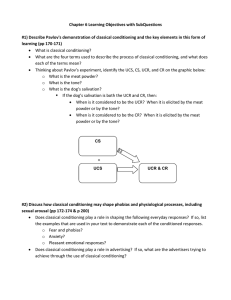
Chapter 6 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions #1) Describe
... #10) Describe punishment and distinguish between punishment and negative reinforcement (pp 186‐187 + complete the table at the end of this document to use as a study aid for this objective) • What is punishment, and what does it do to a person’s tendency to repeat a certain response? Does it str ...
... #10) Describe punishment and distinguish between punishment and negative reinforcement (pp 186‐187 + complete the table at the end of this document to use as a study aid for this objective) • What is punishment, and what does it do to a person’s tendency to repeat a certain response? Does it str ...
Critical Thinking and Environmental Studies, Jane
... textbook), what you hear in lectures and speeches, and what you see and hear on the news and in advertisements. Critical Thinking 1. Can you come up with an example in which critical thinking has helped you make a major change in one or more of your beliefs or helped you make an important personal d ...
... textbook), what you hear in lectures and speeches, and what you see and hear on the news and in advertisements. Critical Thinking 1. Can you come up with an example in which critical thinking has helped you make a major change in one or more of your beliefs or helped you make an important personal d ...