Redalyc.Effects of aversive classical conditioning on habituation of
... by morphine is likely to by followed by a period of hyperactivity and they demostrated in companion experiments that the conditioned response mimicked the secondary response to morphine (hyperactivity). However, in other cases, depending on the nature of the UR, the two behavioral components of the ...
... by morphine is likely to by followed by a period of hyperactivity and they demostrated in companion experiments that the conditioned response mimicked the secondary response to morphine (hyperactivity). However, in other cases, depending on the nature of the UR, the two behavioral components of the ...
rl.
... C) classical and operant conditioning. 21. After learning to fear a white rat, Little Albert responded with fear to the sight of a rabbit. This best illustrates the process of: A) secondary reinforcement. B) generaliz.ation. C) shaping. 0) latent learning. E) spontaneous recovery. 22. Two years ...
... C) classical and operant conditioning. 21. After learning to fear a white rat, Little Albert responded with fear to the sight of a rabbit. This best illustrates the process of: A) secondary reinforcement. B) generaliz.ation. C) shaping. 0) latent learning. E) spontaneous recovery. 22. Two years ...
SV3 Learning Nov 22 2009
... In CC, an organism can be taught a connection between any CS and any US In OC, an organism can be taught a connection between any response and any reinforcer ...
... In CC, an organism can be taught a connection between any CS and any US In OC, an organism can be taught a connection between any response and any reinforcer ...
Chapter 6
... 20. Explain how extinction and spontaneous recovery occur in operant conditioning. 21. Describe how negative attention seeking demonstrates reinforcement and extinction in operant conditioning. (See also Table 6.3.) 22. Compare and contrast positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment, ...
... 20. Explain how extinction and spontaneous recovery occur in operant conditioning. 21. Describe how negative attention seeking demonstrates reinforcement and extinction in operant conditioning. (See also Table 6.3.) 22. Compare and contrast positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment, ...
SV4 Learning Nov 22 2009
... Assumptions about Learning Associationist principles are sufficient to account for all learning All stimuli are created equal In CC, an organism can be taught a connection between any CS and any US In OC, an organism can be taught a connection between any response and any reinforcer ...
... Assumptions about Learning Associationist principles are sufficient to account for all learning All stimuli are created equal In CC, an organism can be taught a connection between any CS and any US In OC, an organism can be taught a connection between any response and any reinforcer ...
Artificial Neural Networks : An Introduction
... • How a fish or tadpole learns • All similar input patterns are grouped together as clusters. • If a matching input pattern is not found a new cluster is formed ...
... • How a fish or tadpole learns • All similar input patterns are grouped together as clusters. • If a matching input pattern is not found a new cluster is formed ...
Classical Conditioning
... e. Temporal conditioning – Occurs when the nominal CS is a fixed period of time between presentations of the UCS/US – Combined with trace conditioning based on a period of time • i.e. dog starts to salivate at 7:59am because s/he is fed at 8am everyday ...
... e. Temporal conditioning – Occurs when the nominal CS is a fixed period of time between presentations of the UCS/US – Combined with trace conditioning based on a period of time • i.e. dog starts to salivate at 7:59am because s/he is fed at 8am everyday ...
Psychology as a Science
... The O refers to cognitive process- how persons think, understand and know about the world. A reaction to behaviorism is humanistic psychology. Emphasis on the whole person and argued against the analytic approach. Focus on human potential and personal development, free will or choice (vs. determinis ...
... The O refers to cognitive process- how persons think, understand and know about the world. A reaction to behaviorism is humanistic psychology. Emphasis on the whole person and argued against the analytic approach. Focus on human potential and personal development, free will or choice (vs. determinis ...
Unit 6, Learning
... relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience experience (nurture) is the key to learning ...
... relatively permanent change in an organism’s behavior due to experience experience (nurture) is the key to learning ...
Moss Lane School
... • be aware that their feelings and actions have an impact on others • make a friend, talk with them and share feelings • use simple rules for dealing with strangers and for resisting pressure when they feel uncomfortable or at risk. Pupils will know and understand: • that animals, including humans, ...
... • be aware that their feelings and actions have an impact on others • make a friend, talk with them and share feelings • use simple rules for dealing with strangers and for resisting pressure when they feel uncomfortable or at risk. Pupils will know and understand: • that animals, including humans, ...
EFFECTS OF AVERSIVE CLASSICAL CONDITIONING ON
... by morphine is likely to by followed by a period of hyperactivity and they demostrated in companion experiments that the conditioned response mimicked the secondary response to morphine (hyperactivity). However, in other cases, depending on the nature of the UR, the two behavioral components of the ...
... by morphine is likely to by followed by a period of hyperactivity and they demostrated in companion experiments that the conditioned response mimicked the secondary response to morphine (hyperactivity). However, in other cases, depending on the nature of the UR, the two behavioral components of the ...
The Implications of Neurological Models of Memory for Learning and
... students via multimedia teaching leads to better retention. Multiple teaching strategies including oral communication, writing, metaphor, reiteration, interactive activities, humour, music that independently benefits learning enhances information retention through the pedagogic principle of extra in ...
... students via multimedia teaching leads to better retention. Multiple teaching strategies including oral communication, writing, metaphor, reiteration, interactive activities, humour, music that independently benefits learning enhances information retention through the pedagogic principle of extra in ...
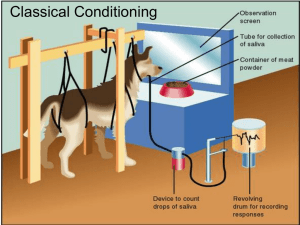
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
... lever that activates a recording device (far left). During conditioning, various stimuli can be paired with a dish of food placed in front of the dog. The device pictured here is more elaborate than the one www.soran.edu.iq Pavlov used in his early experiments. ...
... lever that activates a recording device (far left). During conditioning, various stimuli can be paired with a dish of food placed in front of the dog. The device pictured here is more elaborate than the one www.soran.edu.iq Pavlov used in his early experiments. ...
general psychology Firouz meroei milan Conditioning and Learning
... lever that activates a recording device (far left). During conditioning, various stimuli can be paired with a dish of food placed in front of the dog. The device pictured here is more elaborate than the one www.soran.edu.iq Pavlov used in his early experiments. ...
... lever that activates a recording device (far left). During conditioning, various stimuli can be paired with a dish of food placed in front of the dog. The device pictured here is more elaborate than the one www.soran.edu.iq Pavlov used in his early experiments. ...
PDF (2_RMC_CH1_Introduction)
... reaction, such as salivation, to only the meaningful stimulus. Over time, the subject begins to respond to the previously neutral stimulus in the same way as the meaningful one. The subject has formed an association; he or she now begins salivating to the presence of the bell alone without food. In ...
... reaction, such as salivation, to only the meaningful stimulus. Over time, the subject begins to respond to the previously neutral stimulus in the same way as the meaningful one. The subject has formed an association; he or she now begins salivating to the presence of the bell alone without food. In ...
Competitive Learning Lecture 10
... neighboring neurons respond to “similar” input patterns" SOMs are typically organized as one- or two- dimensional lattices (i.e., a string or a mesh) for the purpose of visualization and dimensionality reduction" ...
... neighboring neurons respond to “similar” input patterns" SOMs are typically organized as one- or two- dimensional lattices (i.e., a string or a mesh) for the purpose of visualization and dimensionality reduction" ...
DGL_Dyslexia
... The word dyslexia is derived from the Greek “dys” (meaning poor or inadequate) and “lexis” (words or language). Dyslexia is a learning disability characterized by problems in expressive or receptive, oral or written language. Problems many emerge in reading, spelling, writing, speaking, or listening ...
... The word dyslexia is derived from the Greek “dys” (meaning poor or inadequate) and “lexis” (words or language). Dyslexia is a learning disability characterized by problems in expressive or receptive, oral or written language. Problems many emerge in reading, spelling, writing, speaking, or listening ...
Behaviorist Perspective
... Classical Conditioning Introduced by Ivan Pavlov during his study of digestive systems in animals Learning through association of an unconditioned response (reflex) with a conditioned stimulus (that was previously ...
... Classical Conditioning Introduced by Ivan Pavlov during his study of digestive systems in animals Learning through association of an unconditioned response (reflex) with a conditioned stimulus (that was previously ...
PS210-03 History of Psychology Unit 1
... Who is the founding father of behaviorism? John Watson Basic ideas did not originate with him, but he organized and promoted it According to Watson, what was behaviorism? Psychology dealing only with observable, behavioral acts Things should be described in terms of stimulus and response ...
... Who is the founding father of behaviorism? John Watson Basic ideas did not originate with him, but he organized and promoted it According to Watson, what was behaviorism? Psychology dealing only with observable, behavioral acts Things should be described in terms of stimulus and response ...
LCog read ch 5
... effective it is. However, an intense punisher also generates negative emotional by-products such as fear, anger, etc. Also, a longer lasting punisher is more effective (e.g., grounding for 2 weeks is more effective than grounding for 1 day). Learned helplessness: refers to the phenomenon observed ...
... effective it is. However, an intense punisher also generates negative emotional by-products such as fear, anger, etc. Also, a longer lasting punisher is more effective (e.g., grounding for 2 weeks is more effective than grounding for 1 day). Learned helplessness: refers to the phenomenon observed ...
Building a Field
... take on the identities of experts (Gee, 2003; Shaffer, Squire, Halverson, & Gee, 2005). These games give us access to the ways of thinking (including knowledge, skills, values, and dispositions) of experts, and invite us to experience the world in new ways. This approach is much more specific than s ...
... take on the identities of experts (Gee, 2003; Shaffer, Squire, Halverson, & Gee, 2005). These games give us access to the ways of thinking (including knowledge, skills, values, and dispositions) of experts, and invite us to experience the world in new ways. This approach is much more specific than s ...
Behaviorism Review
... Conditioning could not account for all learning. He argued that most of our behaviors are learned by watching other people. What does the Bobo Doll experiment tell us about how children learn? ...
... Conditioning could not account for all learning. He argued that most of our behaviors are learned by watching other people. What does the Bobo Doll experiment tell us about how children learn? ...
IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging Special Issue Call for Papers
... extensive prior knowledge for superior diagnostic performance. Since machine learning for image reconstruction is a new area, we are open to innovative ideas and significant results in the spirit of artificial intelligence especially learning from data. A strong evaluation component is required to c ...
... extensive prior knowledge for superior diagnostic performance. Since machine learning for image reconstruction is a new area, we are open to innovative ideas and significant results in the spirit of artificial intelligence especially learning from data. A strong evaluation component is required to c ...
Learning program
... A simple form of learning that occurs as a result repeated association of two or more stimuli. One of the two stimuli would normally elicit a reflexive involuntary or automatic response - The Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) - as it doesn't need to be conditioned in order to elicit the involuntary respo ...
... A simple form of learning that occurs as a result repeated association of two or more stimuli. One of the two stimuli would normally elicit a reflexive involuntary or automatic response - The Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS) - as it doesn't need to be conditioned in order to elicit the involuntary respo ...