download
... – Overview Windows 2000 and product variations – Introduce key Windows 2000 concepts such as the Win32 API, processes, threads, virtual memory, kernel mode and user mode – Introduce tools that can be used to examine Windows 2000 internal behaviour ...
... – Overview Windows 2000 and product variations – Introduce key Windows 2000 concepts such as the Win32 API, processes, threads, virtual memory, kernel mode and user mode – Introduce tools that can be used to examine Windows 2000 internal behaviour ...
COSC A365 Chapter 2
... Exact type and amount of information vary according to OS and call Three general methods used to pass parameters to the OS Simplest: pass the parameters in registers In some cases, may be more parameters than registers Parameters stored in a block, or table, in memory, and address of block p ...
... Exact type and amount of information vary according to OS and call Three general methods used to pass parameters to the OS Simplest: pass the parameters in registers In some cases, may be more parameters than registers Parameters stored in a block, or table, in memory, and address of block p ...
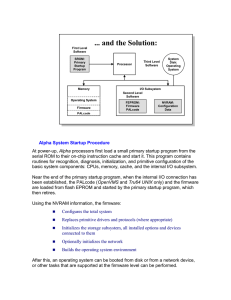
Alpha System Startup Procedure
... when testing application compatibility across different versions of Windows NT. Each time you install a separate version of Windows NT, a new operating system selection is created. Although you can start any of the installed versions of Windows NT, one of the installed versions must be the primary o ...
... when testing application compatibility across different versions of Windows NT. Each time you install a separate version of Windows NT, a new operating system selection is created. Although you can start any of the installed versions of Windows NT, one of the installed versions must be the primary o ...
Questionaire
... 6. Why does caching result in a speed-up most of the time? In which situations will caching not work? ...
... 6. Why does caching result in a speed-up most of the time? In which situations will caching not work? ...
Abstract View of System Components
... data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection wit ...
... data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection wit ...
memory is
... Talked with Mr. Feuer and Prof. Hafner. We provide guidance to what you should learn. (If you say “give us A without any exam or project”…) Most OS are implemented in C. Java hides many low-level details. This is a place to strengthen your C skills. ...
... Talked with Mr. Feuer and Prof. Hafner. We provide guidance to what you should learn. (If you say “give us A without any exam or project”…) Most OS are implemented in C. Java hides many low-level details. This is a place to strengthen your C skills. ...
Unix and shell programming
... What is Unix ? The UNIX operating system is a set of programs that act as a link between the computer and the user. The computer programs that allocate the system resources and coordinate all the details of the computer's internals is called the operating system or kernel. Users communicates ...
... What is Unix ? The UNIX operating system is a set of programs that act as a link between the computer and the user. The computer programs that allocate the system resources and coordinate all the details of the computer's internals is called the operating system or kernel. Users communicates ...
Course Form - Bluegrass Community and Technical College
... 19. Proposed Course Competencies/Student Outcomes (If part of an organized curriculum, how does it relate to program competencies /outcomes? Begin statement with a capital letter and end with a period.): Upon completion of this course, the student can: ...
... 19. Proposed Course Competencies/Student Outcomes (If part of an organized curriculum, how does it relate to program competencies /outcomes? Begin statement with a capital letter and end with a period.): Upon completion of this course, the student can: ...
Chorus and other Microkernels
... Systems as Sub-Systems means you could develop “Multiple Personalities” – OS/2 – Unix – Windows ...
... Systems as Sub-Systems means you could develop “Multiple Personalities” – OS/2 – Unix – Windows ...
Ch1 Introduction to the Linux Kernel
... Sometimes referred to as the supervisor, core, or internals of the operating system. ...
... Sometimes referred to as the supervisor, core, or internals of the operating system. ...
System Management
... • Total system performance is the efficiency with which computer system meets goals • System efficiency ...
... • Total system performance is the efficiency with which computer system meets goals • System efficiency ...
OS Overview
... Hello everybody out there using minix - I'm doing a (free) operating system (just a hobby, won't be big and professional like gnu) for 386(486) AT clones. This has been brewing since april, and is starting to get ready. I'd like any feedback on things people like/dislike in minix, as my OS resembles ...
... Hello everybody out there using minix - I'm doing a (free) operating system (just a hobby, won't be big and professional like gnu) for 386(486) AT clones. This has been brewing since april, and is starting to get ready. I'd like any feedback on things people like/dislike in minix, as my OS resembles ...
Operating Systems - CTAE Resource Network
... Students will identify the fundamental principles of operating systems. a. Identify differences between operating systems (e.g. Mac, Windows, Linux) and describe operating system revision levels including GUI, system requirements, application, and hardware compatibility. b. Identify names, purposes, ...
... Students will identify the fundamental principles of operating systems. a. Identify differences between operating systems (e.g. Mac, Windows, Linux) and describe operating system revision levels including GUI, system requirements, application, and hardware compatibility. b. Identify names, purposes, ...
Cindy - Anatomy of a Window
... © Pearson Education Computer Forensics: Principles and Practices ...
... © Pearson Education Computer Forensics: Principles and Practices ...
The concept of operating system
... Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. A trap (exception) is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request. The operating system is interrupt driven. ...
... Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt. A trap (exception) is a software-generated interrupt caused either by an error or a user request. The operating system is interrupt driven. ...
2. OS Structures - FSU Computer Science
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other ...
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other ...
PPT Chapter 01
... Same real resource may support several virtual ones Started with the use of virtual devices • E.g., a print server ...
... Same real resource may support several virtual ones Started with the use of virtual devices • E.g., a print server ...
ch2
... loaders, linkage editors, and overlay-loaders, debugging systems for higher-level and machine language Communications - Provide the mechanism for creating virtual connections among processes, users, and computer systems Allow users to send messages to one another’s screens, browse web pages, sen ...
... loaders, linkage editors, and overlay-loaders, debugging systems for higher-level and machine language Communications - Provide the mechanism for creating virtual connections among processes, users, and computer systems Allow users to send messages to one another’s screens, browse web pages, sen ...
1.01 - Kau
... Memory management of I/O including buffering (storing data temporarily while it is being transferred), caching (storing parts of data in faster storage for performance), spooling (the overlapping of output of one job with input of other jobs) ...
... Memory management of I/O including buffering (storing data temporarily while it is being transferred), caching (storing parts of data in faster storage for performance), spooling (the overlapping of output of one job with input of other jobs) ...
Operating systems
... instructions until it either encounters an input/output operation or the time allocated for that program has expired Then, it saves the address of the memory location where the last instruction was executed and moves to the next program. The same procedure is repeated with the second program After a ...
... instructions until it either encounters an input/output operation or the time allocated for that program has expired Then, it saves the address of the memory location where the last instruction was executed and moves to the next program. The same procedure is repeated with the second program After a ...
Web-Based Operating Systems
... Can a Web Desktop Environment dethrone the current status-quo Desktop? ...
... Can a Web Desktop Environment dethrone the current status-quo Desktop? ...
Interfacing with the Operating System
... opening, reading, writing and closing files. • When you open a file in "C" (or Java) you will be invoking the appropriate operating system call. • Opening a file involves locating it, and bringing into memory information necessary to access it. • Reading it involves accessing the file and the first ...
... opening, reading, writing and closing files. • When you open a file in "C" (or Java) you will be invoking the appropriate operating system call. • Opening a file involves locating it, and bringing into memory information necessary to access it. • Reading it involves accessing the file and the first ...