Advanced Interactive Executive (AIX) operating system overview
... real hardware and provides a stable, high-level machine interface to the advanced hardware features and devices. (See Figure 3.) The kernel received corresponding enhancements to use the services of the VRM and to provide essential additional facilities. Although the VRM and the AIX kernel proper ha ...
... real hardware and provides a stable, high-level machine interface to the advanced hardware features and devices. (See Figure 3.) The kernel received corresponding enhancements to use the services of the VRM and to provide essential additional facilities. Although the VRM and the AIX kernel proper ha ...
Chapter 8 - Operating Systems And Utility Programs - Elearning-KL
... Identify devices that use several embedded operating systems ...
... Identify devices that use several embedded operating systems ...
CHAPTER 1: Computer Systems
... Placed in queue based on level of priority and eventually executed ...
... Placed in queue based on level of priority and eventually executed ...
UNIT 1
... Program execution – system capability to load a program into memory and to run it. I/O operations – since user programs cannot execute I/O operations directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delet ...
... Program execution – system capability to load a program into memory and to run it. I/O operations – since user programs cannot execute I/O operations directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delet ...
2.01 - SEJONG
... File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Obviously, programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission ...
... File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Obviously, programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission ...
Operating System (OS)
... Usage of Virtual Machine provides complete protection of system resources a means to solve system compatibility problems a perfect vehicle for operating-systems research and development A mean to increase resources utilization in cloud computing ...
... Usage of Virtual Machine provides complete protection of system resources a means to solve system compatibility problems a perfect vehicle for operating-systems research and development A mean to increase resources utilization in cloud computing ...
slides.01.pdf
... Problem: We need to have a means for storing and retrieving data associated with a program, independent of whether a process is executing that program. Model: A file is an abstraction of a real storage device (e.g. disk): you can read/write data from/to a file by providing (1) a position in that fil ...
... Problem: We need to have a means for storing and retrieving data associated with a program, independent of whether a process is executing that program. Model: A file is an abstraction of a real storage device (e.g. disk): you can read/write data from/to a file by providing (1) a position in that fil ...
Chapter03
... • Allocation of main memory to processes • Allocation of secondary memory to processes • Protection attributes for access to shared ...
... • Allocation of main memory to processes • Allocation of secondary memory to processes • Protection attributes for access to shared ...
Unit 3 Operation System
... Linux is and has always been a very secure operating system. Although it still can be attacked when compared to Windows, it has been much more secure. Even if Microsoft has made great improvements over the years with security on their operating system, their operating system continues to be the most ...
... Linux is and has always been a very secure operating system. Although it still can be attacked when compared to Windows, it has been much more secure. Even if Microsoft has made great improvements over the years with security on their operating system, their operating system continues to be the most ...
JNI Fault Tolerance Using Java ProcessBuilder
... Processes and threads are the basic units of execution. A process is an active entity spawned from a program during runtime, whose instructions are being executed sequentially in the CPU until completion [3]. It has a self-contained execution environment, i.e. a private set of basic run-time resourc ...
... Processes and threads are the basic units of execution. A process is an active entity spawned from a program during runtime, whose instructions are being executed sequentially in the CPU until completion [3]. It has a self-contained execution environment, i.e. a private set of basic run-time resourc ...
Operating System Structures - McMaster Computing and Software
... However, lower level task written in assembly. Accessed by programs via a high-level Application Programming Interface (API) rather than direct system call use ...
... However, lower level task written in assembly. Accessed by programs via a high-level Application Programming Interface (API) rather than direct system call use ...
SCADA Systems, RTOS
... Task scheduling – micro-kernel Tread/task control, block management – nano-kernel All 3 lower levels may be realized by kernel, but these functions may be split on different levels. When threads are created, Thread Control Blocks are associated with them. In addition to commonly used here such data ...
... Task scheduling – micro-kernel Tread/task control, block management – nano-kernel All 3 lower levels may be realized by kernel, but these functions may be split on different levels. When threads are created, Thread Control Blocks are associated with them. In addition to commonly used here such data ...
Operating System for Parallel Computing
... facilities. Two well-known examples of such libraries are Message Passing Interface (MPI) [2] and Parallel Virtual Machine (PVM) [3]. This approach allows easily building a distributed programming environment on the basis of a network of computers running conventional operating systems like UNIX or ...
... facilities. Two well-known examples of such libraries are Message Passing Interface (MPI) [2] and Parallel Virtual Machine (PVM) [3]. This approach allows easily building a distributed programming environment on the basis of a network of computers running conventional operating systems like UNIX or ...
Hardware architecture of a Real Time Operating System
... A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system that supports and guarantees timely responses to external and internal events of real-time systems. An RTOS monitors, responds to, and controls an external environment, which is connected to the computer system through sensors, actuators, or ...
... A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system that supports and guarantees timely responses to external and internal events of real-time systems. An RTOS monitors, responds to, and controls an external environment, which is connected to the computer system through sensors, actuators, or ...
lecture2
... Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code Some instructions designated as privileged, only executable in kernel mode System call changes mode to kernel, return from call resets it to user ...
... Provides ability to distinguish when system is running user code or kernel code Some instructions designated as privileged, only executable in kernel mode System call changes mode to kernel, return from call resets it to user ...
Process Control Management
... • At the end of this lecture YOU should be able to: - explain the importance of CPU scheduling - distinguish between preemptive and non-preemptive algorithms - calculate waiting time and turnaround time ...
... • At the end of this lecture YOU should be able to: - explain the importance of CPU scheduling - distinguish between preemptive and non-preemptive algorithms - calculate waiting time and turnaround time ...
I/O Systems 2.
... Easy to use and understand Insufficient for some needs Nonblocking - I/O call returns as much as available User interface, data copy (buffered I/O) ...
... Easy to use and understand Insufficient for some needs Nonblocking - I/O call returns as much as available User interface, data copy (buffered I/O) ...
Technology in Action
... – Created by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry – The first electrically powered digital computer – Used vacuum tubes to store data – The first computer to use the binary system Atansoff-Berry Computer ...
... – Created by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry – The first electrically powered digital computer – Used vacuum tubes to store data – The first computer to use the binary system Atansoff-Berry Computer ...
Chapter 10 Exercises and Answers
... Answers are in blue. For Exercises 1- 18, mark the answers true and false as follows: A. True B. False ...
... Answers are in blue. For Exercises 1- 18, mark the answers true and false as follows: A. True B. False ...
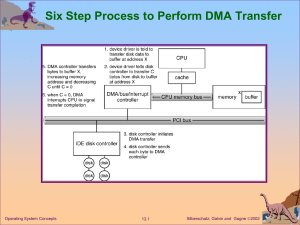
Operating-System Structures
... Some ask the system for info - date, time, amount of available memory, disk space, number of users Others provide detailed performance, logging, and debugging information Typically, these programs format and print the output to the terminal or other output devices Some systems implement a registry - ...
... Some ask the system for info - date, time, amount of available memory, disk space, number of users Others provide detailed performance, logging, and debugging information Typically, these programs format and print the output to the terminal or other output devices Some systems implement a registry - ...
Linux+ Guide to Linux Certification
... • A well-designed application program releases memory block it no longer needs • If two free memory blocks are contiguous, they are merged immediately into one block and linked to the list ...
... • A well-designed application program releases memory block it no longer needs • If two free memory blocks are contiguous, they are merged immediately into one block and linked to the list ...
Operating Systems
... All data in memory before and after processing All instructions in memory in order to execute ...
... All data in memory before and after processing All instructions in memory in order to execute ...