World War II
... world’s major religions Judaism (in Israel & North America) Christianity (Europe, North & South America) Islam (Middle East, Africa, & Asia) Hinduism (Concentrated in India) Buddhism (East and Southeast Asia) ...
... world’s major religions Judaism (in Israel & North America) Christianity (Europe, North & South America) Islam (Middle East, Africa, & Asia) Hinduism (Concentrated in India) Buddhism (East and Southeast Asia) ...
Curriculum – Scope and Sequence/STAAR
... the spread of Christianity, the decline of Rome and the formation of medieval Europe; the development of Islamic caliphates and their impact on Asia, Africa, and Europe; the Mongol invasions and their impact on Europe, China, India, and Southwest Asia WH.1.D identify major causes and describe the ma ...
... the spread of Christianity, the decline of Rome and the formation of medieval Europe; the development of Islamic caliphates and their impact on Asia, Africa, and Europe; the Mongol invasions and their impact on Europe, China, India, and Southwest Asia WH.1.D identify major causes and describe the ma ...
The Industrial Revolution
... The location of work places changed as more goods were produced away from the ...
... The location of work places changed as more goods were produced away from the ...
Lesson 4 Impact of Exploration
... The Spanish Armada • English attacked Spanish gold ships returning from Americas • Spainʼs King Philip II sent 130 ships to invade England • Superior English navy destroyed Spanish forces • Weakened Spain still leading European power due to gold, silver trade ...
... The Spanish Armada • English attacked Spanish gold ships returning from Americas • Spainʼs King Philip II sent 130 ships to invade England • Superior English navy destroyed Spanish forces • Weakened Spain still leading European power due to gold, silver trade ...
unit v geography: the map of the first global civilization
... Revolution, which transformed the bases of production through new technology and new sources of power. European dominance in the world economy became overwhelming. In contrast to the Early Modern Period, when Western power on land was limited, no area could escape the possibility of extensive Europe ...
... Revolution, which transformed the bases of production through new technology and new sources of power. European dominance in the world economy became overwhelming. In contrast to the Early Modern Period, when Western power on land was limited, no area could escape the possibility of extensive Europe ...
Tucker
... Learning Targets – Basic, essential information Additional Basic Proficient Advanced 4.1. Greatly improved farming methods resulted in an Agricultural Revolution Enclosures Mechanical drill Agricultural Revolution that paved the way for changes in Crop rotation manufacturing techniques. The Agricult ...
... Learning Targets – Basic, essential information Additional Basic Proficient Advanced 4.1. Greatly improved farming methods resulted in an Agricultural Revolution Enclosures Mechanical drill Agricultural Revolution that paved the way for changes in Crop rotation manufacturing techniques. The Agricult ...
AP World History Chapter 27 Notes Outline Outline Chapter 27: The
... frequent, devastating floods of the Yellow River. Above the peasantry, Chinese society was divided among many groups: landowners, wealthy merchants, and foreigners, whose luxurious lives aroused the resentment of educated, young, urban Chinese. ...
... frequent, devastating floods of the Yellow River. Above the peasantry, Chinese society was divided among many groups: landowners, wealthy merchants, and foreigners, whose luxurious lives aroused the resentment of educated, young, urban Chinese. ...
Exploration and Expansion
... investments) invested in colonies for profit Rise of Capitalism – means of production are privately owned; supply and demand Mercantalism – mother country benefits from colonies by exporting more than they import; gain large amounts of gold/wealth Triangular Trade – Europe, Africa, Americas; key pro ...
... investments) invested in colonies for profit Rise of Capitalism – means of production are privately owned; supply and demand Mercantalism – mother country benefits from colonies by exporting more than they import; gain large amounts of gold/wealth Triangular Trade – Europe, Africa, Americas; key pro ...
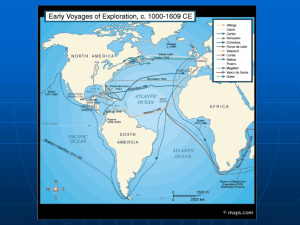
The West`s First Outreach: Maritime Power
... 9. What steps do Europeans take to increase/ensure their control of oceanic trade routes? Imbalances in World Trade 10. Redefine “mercantilism” in your own words. Explain why it was considered a beneficial economic model. A System of International Inequality 11. In what ways are the “dependent” cult ...
... 9. What steps do Europeans take to increase/ensure their control of oceanic trade routes? Imbalances in World Trade 10. Redefine “mercantilism” in your own words. Explain why it was considered a beneficial economic model. A System of International Inequality 11. In what ways are the “dependent” cult ...
AP World History Class Notes Ch 22 Cross
... ideas. Ironically, that same traffic helped spread the bubonic plague, the Black Death, which ravaged much of Eurasia in the mid-14th century. Common elements of these cross-cultural networks include: • Diplomacy. Different states used trade routes to send envoys abroad seeking either to form allian ...
... ideas. Ironically, that same traffic helped spread the bubonic plague, the Black Death, which ravaged much of Eurasia in the mid-14th century. Common elements of these cross-cultural networks include: • Diplomacy. Different states used trade routes to send envoys abroad seeking either to form allian ...
One Europe Several Europes
... will come when the only fields of battle will be markets opening up to trade and minds opening up to ideas. A day will come when the bullets and the bombs will be replaced by votes, by the universal suffrage of the peoples, by the venerable arbitration of a great sovereign senate which will be to Eu ...
... will come when the only fields of battle will be markets opening up to trade and minds opening up to ideas. A day will come when the bullets and the bombs will be replaced by votes, by the universal suffrage of the peoples, by the venerable arbitration of a great sovereign senate which will be to Eu ...
A. Paleolithic Persistence: Australia and North America
... 1. Emperor Yongle (r. 1402–1422): This emperor sponsored a number of important projects to get China back on track after the Mongols, including public works, building a new capital complete with new temples and courts, overseas missions, and the writing of an enormous Encyclopedia. 2. Confucianism a ...
... 1. Emperor Yongle (r. 1402–1422): This emperor sponsored a number of important projects to get China back on track after the Mongols, including public works, building a new capital complete with new temples and courts, overseas missions, and the writing of an enormous Encyclopedia. 2. Confucianism a ...
Name: World History Chapter 1- Section 4 and 5 Section 4
... the Middle East (largely _____________) – Demand for luxury goods in the region ________________ – Trade __________________ ...
... the Middle East (largely _____________) – Demand for luxury goods in the region ________________ – Trade __________________ ...
Unit 3 also - Lyons-AP
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids are p ...
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids are p ...
The First Global Age: Europe, the Americas, and Africa (1492
... By the 1600s, Spain, France, England, and the Netherlands were competing for trade and colonies. The arrival of European settlers in the Americas brought disaster to Native Americans. Beginning in the 1400s, Europeans began establishing trading outposts in Africa. Millions of slaves were imported fr ...
... By the 1600s, Spain, France, England, and the Netherlands were competing for trade and colonies. The arrival of European settlers in the Americas brought disaster to Native Americans. Beginning in the 1400s, Europeans began establishing trading outposts in Africa. Millions of slaves were imported fr ...
Bill of Rights (U
... 1. Bill of Rights (U.S.) - The first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. These amendments limit the powers of the federal government, protecting the rights of all citizens, residents and visitors on United States territory. 2. Bourgeoisie - In France, the class of merchants and artisan ...
... 1. Bill of Rights (U.S.) - The first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. These amendments limit the powers of the federal government, protecting the rights of all citizens, residents and visitors on United States territory. 2. Bourgeoisie - In France, the class of merchants and artisan ...
File
... *European merchant fleets seized control of key international trading routes *Spain & Portugal first began, followed by growing efforts from Britain, France, and Holland 2. Toward a World Economy *Europe’s maritime dominance generated 3 wider changes from the 1490s onward: (1) Columbian Exchange of ...
... *European merchant fleets seized control of key international trading routes *Spain & Portugal first began, followed by growing efforts from Britain, France, and Holland 2. Toward a World Economy *Europe’s maritime dominance generated 3 wider changes from the 1490s onward: (1) Columbian Exchange of ...
Ohio Learning Standard #16 The consequences of World War I and
... - Economy based on importing raw materials & exporting products like T____________ - Concentration of Businesses into few major enterprises/corporations – Z____________ (like Mitsubishi & Yasuda) ...
... - Economy based on importing raw materials & exporting products like T____________ - Concentration of Businesses into few major enterprises/corporations – Z____________ (like Mitsubishi & Yasuda) ...
Rise of the West DBQ
... overseas resources. It probably makes more sense to look at Western Europe in this period as a nonetoo-unusual economy; it became a fortunate freak only when unexpected and significant discontinuities in the late eighteenth and especially nineteenth centuries enabled it to break through the fundamen ...
... overseas resources. It probably makes more sense to look at Western Europe in this period as a nonetoo-unusual economy; it became a fortunate freak only when unexpected and significant discontinuities in the late eighteenth and especially nineteenth centuries enabled it to break through the fundamen ...
Period 4
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids are p ...
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids are p ...
1450-175-
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids ar ...
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids ar ...
1450-175-
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids ar ...
... of State Empire remains the predominant political structure. It is a coercive tribute system European states such as Spain and Portugal, but also France, England and the Dutch perfect overseas empires by claiming territory in the western hemisphere Quing, Russia, Mughals, Ottomans and Safavids ar ...
World History Final Review --- George The following questions are
... 7. Compare the impact of Europe on China and the Ottoman Empire by the opening of the twentieth century. ...
... 7. Compare the impact of Europe on China and the Ottoman Empire by the opening of the twentieth century. ...
Unit 5 Vocabulary #2
... strengthen a country’s industrial power by restricting foreign imports. 31. McDonaldization - Term used by sociologist George Ritzer in his book The McDonaldization of Society (1995). He describes it as the process by which a society takes on the characteristics of a fast-food restaurant (efficiency ...
... strengthen a country’s industrial power by restricting foreign imports. 31. McDonaldization - Term used by sociologist George Ritzer in his book The McDonaldization of Society (1995). He describes it as the process by which a society takes on the characteristics of a fast-food restaurant (efficiency ...
Great Divergence
The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington (also known as the European miracle, a term coined by Eric Jones in 1981), referring to the process by which the Western world (i.e. Western Europe and the parts of the New World where its people became the dominant populations) overcame pre-modern growth constraints and emerged during the 19th century as the most powerful and wealthy world civilization of the time, eclipsing Qing China, Mughal India, Tokugawa Japan, and the Ottoman Empire.The process was accompanied and reinforced by the Age of Discovery and the subsequent rise of the colonial empires, the Age of Enlightenment, the Commercial Revolution, the Scientific Revolution and finally the Industrial Revolution. Scholars have proposed a wide variety of theories to explain why the Great Divergence happened, including lack of government intervention, geography, colonialism, and customary traditions.Before the Great Divergence, the core developed areas included Europe, East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and the Middle East. In each of these core areas, differing political and cultural institutions allowed varying degrees of development. Western Europe, China, and Japan had developed to a relatively high level and began to face constraints on energy and land use, while India still possessed large amounts of unused resources. Shifts in government policy from mercantilism to laissez-faire liberalism aided Western development.Technological advances, such as railroads, steamboats, mining, and agriculture were embraced to a higher degree in the West than the East during the Great Divergence. Technology led to increased industrialization and economic complexity in the areas of agriculture, trade, fuel and resources, further separating the East and the West. Europe's use of coal as an energy substitute for wood in the mid-19th century gave Europe a major head start in modern energy production. Although China had used coal earlier during the Song and Ming, its use declined due to the shift of Chinese industry to the south, far from major deposits, during the destruction of Mongol and Jurchen invasions between 1100 and 1400. The West also had the advantage of larger quantities of raw materials and a substantial trading market. China and Asia did participate in trading, but colonization brought a distinct advantage to the West. ""In the twentieth century, the Great Divergence peaked before the First World War and continued until the early 1970s, then, after two decades of indeterminate fluctuations, in the late 1980s it was replaced by the Great Convergence as the majority of Third World countriesreached economic growth rates significantly higher than those in most First World countries"".