The Han Dynasty
... expedition: a journey or voyage of some length, usually to other lands Section 2.5 Communist Revolution (page 548-549) The Chinese Communist Party under Mao Zedong significantly changed life in the People’s Republic of China China was controlled by European powers in the 1800s The Chinese Nati ...
... expedition: a journey or voyage of some length, usually to other lands Section 2.5 Communist Revolution (page 548-549) The Chinese Communist Party under Mao Zedong significantly changed life in the People’s Republic of China China was controlled by European powers in the 1800s The Chinese Nati ...
Making of the Modern World 13 New Ideas and Cultural Contacts
... “Two things: the first is that you are the sultan of the universe and the ruler of the world, and I do not beliee that there has appeared among men from Adam until this epoch a ruler like you. I am not one of those who speak about matters by conjecture, for I am a scholar and I will explain this, an ...
... “Two things: the first is that you are the sultan of the universe and the ruler of the world, and I do not beliee that there has appeared among men from Adam until this epoch a ruler like you. I am not one of those who speak about matters by conjecture, for I am a scholar and I will explain this, an ...
ch 12
... Ilkhans and Timurids – intellectual developments • Iran to China • shared artistic trends; politics ...
... Ilkhans and Timurids – intellectual developments • Iran to China • shared artistic trends; politics ...
The Expansion of Europe in the Eighteenth Century
... 1. Europeans vied for dominance of Asian trade. 2. At the end of the sixteenth century, the Dutch became major players in the Asian spice trade. 3. The Dutch replaced the Portuguese as the dominant European power in the Indian Ocean trade world, transforming Asian business partners into dependents. ...
... 1. Europeans vied for dominance of Asian trade. 2. At the end of the sixteenth century, the Dutch became major players in the Asian spice trade. 3. The Dutch replaced the Portuguese as the dominant European power in the Indian Ocean trade world, transforming Asian business partners into dependents. ...
The Human Web—2nd Assignment, Chapter I (pages 9-24)
... When you have finished the chapter reading and these tasks, fill out the “L” column also. 3. This chapter explains how, during this period, China became the world’s first market economy, and then retreated from extensive world contact. List three factors that led to China’s rise to market monster (p ...
... When you have finished the chapter reading and these tasks, fill out the “L” column also. 3. This chapter explains how, during this period, China became the world’s first market economy, and then retreated from extensive world contact. List three factors that led to China’s rise to market monster (p ...
History of China Notes
... expedition: a journey or voyage of some length, usually to other lands Section 2.5 Communist Revolution (page 548-549) The Chinese Communist Party under Mao Zedong significantly changed life in the People’s Republic of China China was controlled by European powers in the 1800s The Chinese Nati ...
... expedition: a journey or voyage of some length, usually to other lands Section 2.5 Communist Revolution (page 548-549) The Chinese Communist Party under Mao Zedong significantly changed life in the People’s Republic of China China was controlled by European powers in the 1800s The Chinese Nati ...
The New 2009-2010 World History Curriculum has many changes to
... World History: Teacher’s Guide The New 2009-2010 World History Curriculum has many changes to content. These changes include the incorporation of elements from the former World Cultures Class and additional Global History and Geography content. In short, World History is not just about Europe anymor ...
... World History: Teacher’s Guide The New 2009-2010 World History Curriculum has many changes to content. These changes include the incorporation of elements from the former World Cultures Class and additional Global History and Geography content. In short, World History is not just about Europe anymor ...
China Class 3 - Steam Mills Primary School
... China Class 3 Essential Knowledge By the end of this unit children will know... ...
... China Class 3 Essential Knowledge By the end of this unit children will know... ...
China Chapter Review Questions and Answers
... The growth of agriculture, increased food produc?on, and trade led to the growth of ci?es. Most were large, prosperous, and had people from many cultures. 14c. Which Chinese inven?on has had a ...
... The growth of agriculture, increased food produc?on, and trade led to the growth of ci?es. Most were large, prosperous, and had people from many cultures. 14c. Which Chinese inven?on has had a ...
World History II (Level 1)
... ‰ Explain how the ideas of the Enlightenment influenced worldwide society and government ‰ Explain the consequences of Napoleon Bonaparte’s policies across Europe and throughout the western world ‰ Describe the revolutions against conservatism in the early nineteenth century ‰ Explain Otto von Bisma ...
... ‰ Explain how the ideas of the Enlightenment influenced worldwide society and government ‰ Explain the consequences of Napoleon Bonaparte’s policies across Europe and throughout the western world ‰ Describe the revolutions against conservatism in the early nineteenth century ‰ Explain Otto von Bisma ...
Michigan World History & Geography Era 4: 300-1500 CE
... China was the largest economy in the world in the 15th century. China was still the greatest economic power on earth [in the 15th century]. It had a population probably in excess of 100 million, a prodigiously productive agricultural sector, a vast and sophisticated trading network, and handicraft ...
... China was the largest economy in the world in the 15th century. China was still the greatest economic power on earth [in the 15th century]. It had a population probably in excess of 100 million, a prodigiously productive agricultural sector, a vast and sophisticated trading network, and handicraft ...
MMW 13 Lecture 8 - Eleanor Roosevelt College
... Expansive state a) civilian-led army Civil-military transformation b) State bureaucracy caused financial problems ...
... Expansive state a) civilian-led army Civil-military transformation b) State bureaucracy caused financial problems ...
WHAP Teacher Copy Western Christendom after the fall of Rome
... plantations using slave labor from Muslims 5. Muslim scholarship, together with the Greek learning it incorporated, also flowed into Europe, largely through Spain and Sicily 6. European empire building, especially in the Americas, continued the crusading spirit D. Yet More Reasons for Europe’s Rise ...
... plantations using slave labor from Muslims 5. Muslim scholarship, together with the Greek learning it incorporated, also flowed into Europe, largely through Spain and Sicily 6. European empire building, especially in the Americas, continued the crusading spirit D. Yet More Reasons for Europe’s Rise ...
ETHN 119: Filipino American Experience Dr. Sobredo: Terms
... Brief History of International & World Trade Alexander the Great, Silk roads Dutch East India Company (1602) -‐1st Multicultural Corporation and issued stocks British East India Company -‐2nd largest tradin ...
... Brief History of International & World Trade Alexander the Great, Silk roads Dutch East India Company (1602) -‐1st Multicultural Corporation and issued stocks British East India Company -‐2nd largest tradin ...
Curriculum – Scope and Sequence/STAAR
... the spread of Christianity, the decline of Rome and the formation of medieval Europe; the development of Islamic caliphates and their impact on Asia, Africa, and Europe; the Mongol invasions and their impact on Europe, China, India, and Southwest Asia WH.1.D identify major causes and describe the ma ...
... the spread of Christianity, the decline of Rome and the formation of medieval Europe; the development of Islamic caliphates and their impact on Asia, Africa, and Europe; the Mongol invasions and their impact on Europe, China, India, and Southwest Asia WH.1.D identify major causes and describe the ma ...
World Economic History
... 1. Economic history as a science. The origins and development of economic history. 2. Economic development in Ancient Times (Near and Middle East, Greece, Roman empire). 3. Economic development in Medieval Europe (feudalism, economic consequences of Crusades, development of European cities, beginnin ...
... 1. Economic history as a science. The origins and development of economic history. 2. Economic development in Ancient Times (Near and Middle East, Greece, Roman empire). 3. Economic development in Medieval Europe (feudalism, economic consequences of Crusades, development of European cities, beginnin ...
The Post-Classical Period, 500-1450
... B. This period also marked by the emergence of the Arabs and Islam as a new force in world history, beginning around 600. In this period, Arab-Islamic civilization becomes the first worldclass civilization that we have dealt. C. The end of the postclassical period is described primarily in terms of ...
... B. This period also marked by the emergence of the Arabs and Islam as a new force in world history, beginning around 600. In this period, Arab-Islamic civilization becomes the first worldclass civilization that we have dealt. C. The end of the postclassical period is described primarily in terms of ...
National Upgrading in a Regional World
... say" economy would require the countries of east-central Europe to dramatically raise their income tax rates, spend much more money on infrastructure, and - ideally - to delink their currencies from the Euro. The keys to growth are high levels of sitespecific infrastructure on the supply side and wi ...
... say" economy would require the countries of east-central Europe to dramatically raise their income tax rates, spend much more money on infrastructure, and - ideally - to delink their currencies from the Euro. The keys to growth are high levels of sitespecific infrastructure on the supply side and wi ...
PowerPoint
... Painted the Mona Lisa; designed plans for flying machines Painter and sculptor; student of Michelangelo and da Vinci Paintings of the Madonna (mother of Jesus) Author of The Prince; advised rulers how to gain and keep power English playwright; wrote in the vernacular; wrote about the joys and sorrow ...
... Painted the Mona Lisa; designed plans for flying machines Painter and sculptor; student of Michelangelo and da Vinci Paintings of the Madonna (mother of Jesus) Author of The Prince; advised rulers how to gain and keep power English playwright; wrote in the vernacular; wrote about the joys and sorrow ...
Freshman World History World History, the requi
... CENTURIES • Imperialists Divide Africa • African Resistance to Imperialism • British Rule in India • Indian Nationalist Movements • Western Powers Rule Southeast Asia • China Responds to Pressure from the West ...
... CENTURIES • Imperialists Divide Africa • African Resistance to Imperialism • British Rule in India • Indian Nationalist Movements • Western Powers Rule Southeast Asia • China Responds to Pressure from the West ...
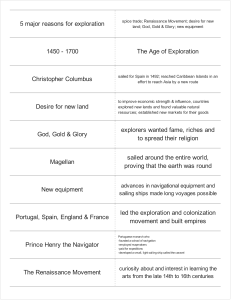
The Age of Exploration Notes
... _________________ - slaves -died from European diseases (no immunity), or escaped. The solution- the _____________________ - biggest forced migration in history. __________did not invent slavery- they followed a long history going back to ancient times. The exact number is not known but more than 11 ...
... _________________ - slaves -died from European diseases (no immunity), or escaped. The solution- the _____________________ - biggest forced migration in history. __________did not invent slavery- they followed a long history going back to ancient times. The exact number is not known but more than 11 ...
World History: Connections to Today World History: Connections to
... The nations of Western Europe recovered fairly quickly from World War II. They expanded social programs and introduced the welfare state. By the 1980s, however, an economic slowdown forced cuts in social programs. ...
... The nations of Western Europe recovered fairly quickly from World War II. They expanded social programs and introduced the welfare state. By the 1980s, however, an economic slowdown forced cuts in social programs. ...
Great Divergence
The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington (also known as the European miracle, a term coined by Eric Jones in 1981), referring to the process by which the Western world (i.e. Western Europe and the parts of the New World where its people became the dominant populations) overcame pre-modern growth constraints and emerged during the 19th century as the most powerful and wealthy world civilization of the time, eclipsing Qing China, Mughal India, Tokugawa Japan, and the Ottoman Empire.The process was accompanied and reinforced by the Age of Discovery and the subsequent rise of the colonial empires, the Age of Enlightenment, the Commercial Revolution, the Scientific Revolution and finally the Industrial Revolution. Scholars have proposed a wide variety of theories to explain why the Great Divergence happened, including lack of government intervention, geography, colonialism, and customary traditions.Before the Great Divergence, the core developed areas included Europe, East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and the Middle East. In each of these core areas, differing political and cultural institutions allowed varying degrees of development. Western Europe, China, and Japan had developed to a relatively high level and began to face constraints on energy and land use, while India still possessed large amounts of unused resources. Shifts in government policy from mercantilism to laissez-faire liberalism aided Western development.Technological advances, such as railroads, steamboats, mining, and agriculture were embraced to a higher degree in the West than the East during the Great Divergence. Technology led to increased industrialization and economic complexity in the areas of agriculture, trade, fuel and resources, further separating the East and the West. Europe's use of coal as an energy substitute for wood in the mid-19th century gave Europe a major head start in modern energy production. Although China had used coal earlier during the Song and Ming, its use declined due to the shift of Chinese industry to the south, far from major deposits, during the destruction of Mongol and Jurchen invasions between 1100 and 1400. The West also had the advantage of larger quantities of raw materials and a substantial trading market. China and Asia did participate in trading, but colonization brought a distinct advantage to the West. ""In the twentieth century, the Great Divergence peaked before the First World War and continued until the early 1970s, then, after two decades of indeterminate fluctuations, in the late 1980s it was replaced by the Great Convergence as the majority of Third World countriesreached economic growth rates significantly higher than those in most First World countries"".