Bolt ModEP7e LG11.39-42B
... 4. Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye converts light energy into neural messages. The energies we experience as visible light are a thin slice from the broad spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Our sensory experience of light is determined larg ...
... 4. Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye converts light energy into neural messages. The energies we experience as visible light are a thin slice from the broad spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Our sensory experience of light is determined larg ...
Chapter 3 – The nerve cell Study Guide Describe an integrate
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
05-First 2 years - Biosocial
... Provides antibodies (if mother has antibodies) Decreases risk of allergies, asthma, and stomach aches Decreases risk of obesity and heart disease in adulthood ...
... Provides antibodies (if mother has antibodies) Decreases risk of allergies, asthma, and stomach aches Decreases risk of obesity and heart disease in adulthood ...
Higher Visual Areas
... ----How the varied aspects of sensory information processed in different cortical areas are integrated to yield the coherent percepts and representations that we experience as the external world. --- Existence of “Grandmother cell?” Hypothesis: 1. Temporal synchrony of neuronal firing may underlie b ...
... ----How the varied aspects of sensory information processed in different cortical areas are integrated to yield the coherent percepts and representations that we experience as the external world. --- Existence of “Grandmother cell?” Hypothesis: 1. Temporal synchrony of neuronal firing may underlie b ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
pptx
... • Feedback in networks “clean up” noisy sensory information to make it consistent with what our systems expect • In a very real way, what we see, hear, taste, smell, touch and think is biased by our network’s expectation • A network’s expectation is established by its ...
... • Feedback in networks “clean up” noisy sensory information to make it consistent with what our systems expect • In a very real way, what we see, hear, taste, smell, touch and think is biased by our network’s expectation • A network’s expectation is established by its ...
Temporal Cortex
... Due to small aperture of the receptive field, motion in three directions is perceived as in one direction. Solution: Several lower-order cells project to higher order cells to integrate the local movements. ...
... Due to small aperture of the receptive field, motion in three directions is perceived as in one direction. Solution: Several lower-order cells project to higher order cells to integrate the local movements. ...
Chapter 4
... Synapses: point where connections between neurons are made http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c UGuWh2UeMk ...
... Synapses: point where connections between neurons are made http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c UGuWh2UeMk ...
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception
... • Definition: Ability to see three-dimensional space and to accurately judge distances • Visual Cliff: Apparatus that looks like the edge of an elevated platform or cliff • Depth Cues: Features of environment, and messages, that supply information about distance and space • Monocular Depth Cue: Dept ...
... • Definition: Ability to see three-dimensional space and to accurately judge distances • Visual Cliff: Apparatus that looks like the edge of an elevated platform or cliff • Depth Cues: Features of environment, and messages, that supply information about distance and space • Monocular Depth Cue: Dept ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... 2. Pons: Contains several clusters of cell bodies involved with sleep and arousal. 3. Cerebellum: critical to the coordination of movement and to the sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating s ...
... 2. Pons: Contains several clusters of cell bodies involved with sleep and arousal. 3. Cerebellum: critical to the coordination of movement and to the sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating s ...
chapter 4
... epithelium, where they are detected by hundreds of different types of auditory celia receptors. The axons of these receptor cells comprise the olfactory nerve, which transmits information to the olfactory bulbs and on to the primary olfactory cortex deep in the frontal lobes. 4.12 The environmental ...
... epithelium, where they are detected by hundreds of different types of auditory celia receptors. The axons of these receptor cells comprise the olfactory nerve, which transmits information to the olfactory bulbs and on to the primary olfactory cortex deep in the frontal lobes. 4.12 The environmental ...
Document
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
Sensation and Perception
... muscles stretch or thicken (thus changing the curvature of the lens) to bend the light at the right angle (so light is focused on retina, depending upon distance of object) this is called accommodation. ...
... muscles stretch or thicken (thus changing the curvature of the lens) to bend the light at the right angle (so light is focused on retina, depending upon distance of object) this is called accommodation. ...
Modules 16-21: Sensation and Perception
... to recognize meaningful objects and events (psychological) ● Bottom-up processing- analysis that begins with sensory receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information (data-driven) ● Top-down processing- information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when w ...
... to recognize meaningful objects and events (psychological) ● Bottom-up processing- analysis that begins with sensory receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information (data-driven) ● Top-down processing- information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when w ...
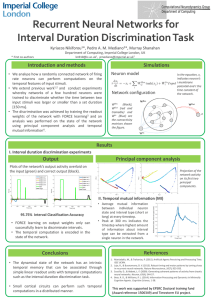
Recurrent Neural Networks for Interval Duration Discrimination Task
... • Average mutual information between individual neuron state and interval type (short or long) at every timestep. • Peak at 300 ms indicates the timestep where highest amount of information about interval type can be extracted from a single neuron in the network. ...
... • Average mutual information between individual neuron state and interval type (short or long) at every timestep. • Peak at 300 ms indicates the timestep where highest amount of information about interval type can be extracted from a single neuron in the network. ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Feature-Detector Approach • One explanation for how we analyze complex stimuli suggests that we break them down into component parts • We have feature detectors, specialized neurons that respond to the presence of certain simple features, such as angles and lines. • What are motion aftereffects? The ...
... Feature-Detector Approach • One explanation for how we analyze complex stimuli suggests that we break them down into component parts • We have feature detectors, specialized neurons that respond to the presence of certain simple features, such as angles and lines. • What are motion aftereffects? The ...
Visual categorization shapes feature selectivity in the primate
... Red circles : Neurons with statistically significant selectivity for diagnostic dimension only Blue circles : Neurons with significant selectivity for diagnostic and non-diagnostic feature Black triangles : Neurons with no significant selectivity Red star : Example neuron depicted in previous figure ...
... Red circles : Neurons with statistically significant selectivity for diagnostic dimension only Blue circles : Neurons with significant selectivity for diagnostic and non-diagnostic feature Black triangles : Neurons with no significant selectivity Red star : Example neuron depicted in previous figure ...
Unit 3 Guide: Sensation and Perception (Modules 8, 9) Module 8
... - Sound: what are the structures of the ear and how do they work to detect sound waves and change them into neural impulses? - Taste, Smell, Touch: how do receptor cells in the nose, tongue, and skin allow us to sense smells, tastes and touch? Terms to know: Sensation: - sensation: - top-down proces ...
... - Sound: what are the structures of the ear and how do they work to detect sound waves and change them into neural impulses? - Taste, Smell, Touch: how do receptor cells in the nose, tongue, and skin allow us to sense smells, tastes and touch? Terms to know: Sensation: - sensation: - top-down proces ...
Ch on Drugs and Prep for Test
... * Years of research has revealed that ingesting many drugs also causes dopamine to be released * The dopamine circuit begins in the ventral tegmental area ...
... * Years of research has revealed that ingesting many drugs also causes dopamine to be released * The dopamine circuit begins in the ventral tegmental area ...
studyingbrainpost
... The neural basis of learning • Experience and Learning result in a direct event in the nervous system • Every brain is wired differently ...
... The neural basis of learning • Experience and Learning result in a direct event in the nervous system • Every brain is wired differently ...
What we*ll sense and perceive* in this chapter:
... When light reaches the back of the retina, it triggers chemical changes in two types of receptor cells: Rods help us see the black and white actions in our peripheral view and in the dark. Cones help us see sharp colorful details in bright light. ...
... When light reaches the back of the retina, it triggers chemical changes in two types of receptor cells: Rods help us see the black and white actions in our peripheral view and in the dark. Cones help us see sharp colorful details in bright light. ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.