Unit 3 Essential Vocabulary File - District 196 e
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
Chapter1 (new window)
... • As intensity increases, the perceived magnitude increases more slowly than the intensity. – Response expansion • As intensity increases, the perceived magnitude increases more quickly than the intensity. ...
... • As intensity increases, the perceived magnitude increases more slowly than the intensity. – Response expansion • As intensity increases, the perceived magnitude increases more quickly than the intensity. ...
Final answers - Center for Neural Science
... a) refers to the fact that damage to the cortex causes blindness. b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. ...
... a) refers to the fact that damage to the cortex causes blindness. b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. ...
Sensation and Perception
... One can also identify top-down processing influences on sensation and perception ...
... One can also identify top-down processing influences on sensation and perception ...
Perception - Department of Psychology
... 90% H, 40% FA, 90 - 40 = 50% 60% H, 10% FA, 60 - 10 = 50% ...
... 90% H, 40% FA, 90 - 40 = 50% 60% H, 10% FA, 60 - 10 = 50% ...
Percept
... Top-Down Processing • Bottom-up processing – Analysis that emphasizes characteristics of the stimulus, rather than internal concepts (stimulus-driven processing). • Top-down processing – Emphasizes perceiver's expectations, memories, and other cognitive factors (conceptually-driven processing). ...
... Top-Down Processing • Bottom-up processing – Analysis that emphasizes characteristics of the stimulus, rather than internal concepts (stimulus-driven processing). • Top-down processing – Emphasizes perceiver's expectations, memories, and other cognitive factors (conceptually-driven processing). ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... Techniques to examine functions of the brain 1. Remove part of the brain & see what effect it has on behavior 2. Examine humans who have suffered brain damage ...
... Techniques to examine functions of the brain 1. Remove part of the brain & see what effect it has on behavior 2. Examine humans who have suffered brain damage ...
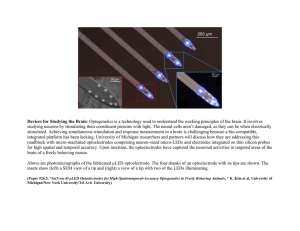
26-5 Devices for Studying the Brain
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
PsychScich04
... relaxation) can close the pain gate • Some mental processes, such as worrying about or focusing on the painful stimulus, seem to open pain gates – Well-rested research participants rated the same level of a painful stimulus as less painful than did participants who were fearful, anxious, or depresse ...
... relaxation) can close the pain gate • Some mental processes, such as worrying about or focusing on the painful stimulus, seem to open pain gates – Well-rested research participants rated the same level of a painful stimulus as less painful than did participants who were fearful, anxious, or depresse ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
04/09 PPT
... -- Depth Perception for near objects (<100 ft). binocular disparity The difference between the images of an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for ...
... -- Depth Perception for near objects (<100 ft). binocular disparity The difference between the images of an object on the two retinas due to the slightly different location of the two eyes relative to the viewed object (Look at one figure with alternative closing of the left and right eye). Cues for ...
doc psych 100 review summary
... There are two types of physical responses that are obtained from electrical stimulation and each can be mapped to a specific brain region Interpretative: “Déjà vu” phenomenon (false memories) False interpretations (called illusions). Stereotyped Symptoms: judgments of familiarity, strangeness, dista ...
... There are two types of physical responses that are obtained from electrical stimulation and each can be mapped to a specific brain region Interpretative: “Déjà vu” phenomenon (false memories) False interpretations (called illusions). Stereotyped Symptoms: judgments of familiarity, strangeness, dista ...
Sensation & Perception
... information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take information from retina to the brain) and eventuall ...
... information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to the optic nerve (bundle of neurons that take information from retina to the brain) and eventuall ...
Review 2 - Texas A&M University
... square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
... square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
THE BRAIN - Dublin City Schools
... Different centers which control different things Despite being 90-95 percent of its adult size by age six, the brain is still “under construction” until age 18. ...
... Different centers which control different things Despite being 90-95 percent of its adult size by age six, the brain is still “under construction” until age 18. ...
Chapter 12
... • 1.6 kg in males/1.45 kg in females (size is not representative of intelligence, only overall average body size) • Complexity dictates processing power ...
... • 1.6 kg in males/1.45 kg in females (size is not representative of intelligence, only overall average body size) • Complexity dictates processing power ...
Final - Center for Neural Science
... a) action potentials that all have the same duration b) different firing rates for different types of stimuli c) changes in the timing of action potentials with different types of stimuli d) changes in the amplitude of action potentials with different types of stimuli 3) Which of the following is no ...
... a) action potentials that all have the same duration b) different firing rates for different types of stimuli c) changes in the timing of action potentials with different types of stimuli d) changes in the amplitude of action potentials with different types of stimuli 3) Which of the following is no ...
Chapter
... Top-Down Processing • Bottom-up processing – Analysis that emphasizes characteristics of the stimulus, rather than internal concepts (stimulus-driven processing). • Top-down processing – Emphasizes perceiver's expectations, memories, and other cognitive factors (conceptually-driven processing). ...
... Top-Down Processing • Bottom-up processing – Analysis that emphasizes characteristics of the stimulus, rather than internal concepts (stimulus-driven processing). • Top-down processing – Emphasizes perceiver's expectations, memories, and other cognitive factors (conceptually-driven processing). ...
PSYC 2314 Chapter 6
... • Which particular affordance an individual perceives and acts on depends on that person’s: ...
... • Which particular affordance an individual perceives and acts on depends on that person’s: ...
Nature Reviews Neuroscience Highlight
... stimuli from that category irrespective of the amount of dog in the stimulus. Further analysis of the response properties revealed that the typical neuron was more sensitive to category than identity. Finally, the monkeys could be trained with stimuli that were assigned to a new category, illustrati ...
... stimuli from that category irrespective of the amount of dog in the stimulus. Further analysis of the response properties revealed that the typical neuron was more sensitive to category than identity. Finally, the monkeys could be trained with stimuli that were assigned to a new category, illustrati ...
Introduction to Perception
... points) and Regina (red points) by means of the method of constant stimuli. These data indicate that Julie’s threshold is lower than Regina’s. But is Julie really more sensitive to the light than Regina, or does she just appear to be more sensitive because she is a more liberal responder? ...
... points) and Regina (red points) by means of the method of constant stimuli. These data indicate that Julie’s threshold is lower than Regina’s. But is Julie really more sensitive to the light than Regina, or does she just appear to be more sensitive because she is a more liberal responder? ...
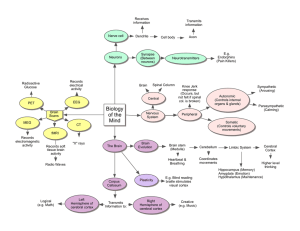
Psychology Unit 2 over Chapters 3 and 4 Chapter 3 “Biological
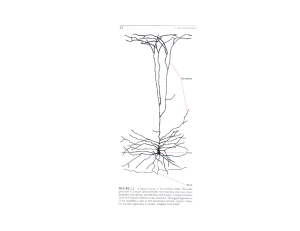
... Clarify how the autonomic nervous system works in emergency and everyday situations Describe what hormones are and how they affect behavior Distinguish the parts of neurons and what they do Describe electrical responses of neurons and what makes them possible Explain how neurons use neurot ...
... Clarify how the autonomic nervous system works in emergency and everyday situations Describe what hormones are and how they affect behavior Distinguish the parts of neurons and what they do Describe electrical responses of neurons and what makes them possible Explain how neurons use neurot ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.