Unit 3 PowerPoint notes
... = portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... = portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
Lecture 6C
... neurological disorders characterized by epileptic seizures. Prevalence: 1 in 100 • Epileptic seizures are episodes that can vary from brief and nearly undetectable to long periods of vigorous shaking. • Often brought on by factors such as lack of sleep, stress or flickering light among others. • In ...
... neurological disorders characterized by epileptic seizures. Prevalence: 1 in 100 • Epileptic seizures are episodes that can vary from brief and nearly undetectable to long periods of vigorous shaking. • Often brought on by factors such as lack of sleep, stress or flickering light among others. • In ...
NMSI - 4 Central Nervous System
... • Frontal lobe damage may impair decision making and emotional responses but leave intellect and ...
... • Frontal lobe damage may impair decision making and emotional responses but leave intellect and ...
Central nervous system
... • Frontal lobe damage may impair decision making and emotional responses but leave intellect and ...
... • Frontal lobe damage may impair decision making and emotional responses but leave intellect and ...
Nervous-System
... the appropriate part of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and retrieving them when necessary. Hypothalamus - about the size of a pearl, this structure directs a multitude of important functions. It wakes you up in the morning, and gets the adrenaline flowing. The hypothalamus is also an ...
... the appropriate part of the cerebral hemisphere for long-term storage and retrieving them when necessary. Hypothalamus - about the size of a pearl, this structure directs a multitude of important functions. It wakes you up in the morning, and gets the adrenaline flowing. The hypothalamus is also an ...
Brain_stemCh45
... A1/ A2 groups project to hypothalamus and controls cardiovascular and endocrine functions A5/A7 are located in the pons and mainly projects to the brain stem and spinal cord where they modulate autonomic reflexes and pain C1 neurons projects to hypothalamus where they modulate cardiovascular and end ...
... A1/ A2 groups project to hypothalamus and controls cardiovascular and endocrine functions A5/A7 are located in the pons and mainly projects to the brain stem and spinal cord where they modulate autonomic reflexes and pain C1 neurons projects to hypothalamus where they modulate cardiovascular and end ...
Slide 1
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
... thoughts and personality • Large memory storehouse. • Each portion of the nervous system performs specific functions, but it is the cortex that opens the world up for one’s mind. ...
Option E: Neurobiology and behaviour
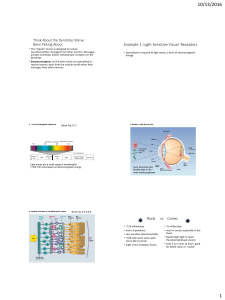
... E.2.1 Outline the diversity of stimuli that can be detected by human sensory receptors, including mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors and photoreceptors. E.2.2 Label a diagram of the structure of the human eye. E.2.3 Annotate a diagram of the retina to show the cell types and the direc ...
... E.2.1 Outline the diversity of stimuli that can be detected by human sensory receptors, including mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors and photoreceptors. E.2.2 Label a diagram of the structure of the human eye. E.2.3 Annotate a diagram of the retina to show the cell types and the direc ...
nitz - UCSD Cognitive Science
... medial entorhinal cortex contains grid cells, grid X head-direction cells, and head-direction cells – each cell type is also velocity sensitive, thus allowing for determination of position according to path integration (i.e., tracking of direction and speed over time) all within one structure ...
... medial entorhinal cortex contains grid cells, grid X head-direction cells, and head-direction cells – each cell type is also velocity sensitive, thus allowing for determination of position according to path integration (i.e., tracking of direction and speed over time) all within one structure ...
AP Psychology Test Review
... A four year old boy was involved in a terrible accident that damaged his brain. Though most of his left hemisphere was removed, three years later he was nearly normal. What term best explains the ability of the brain to recover from injury by rewiring itself? ...
... A four year old boy was involved in a terrible accident that damaged his brain. Though most of his left hemisphere was removed, three years later he was nearly normal. What term best explains the ability of the brain to recover from injury by rewiring itself? ...
L21-Cerebral Hemisph..
... Broadmann’s area 6. It lies immediately anterior to primary motor cortex. It is more extensive than primary motor cortex (about 6 times) Functions: It works with the help of basal ganglia, thalamus, primary motor cortex, posterior parietal cortex. It plays role in planning and anticipation of a spec ...
... Broadmann’s area 6. It lies immediately anterior to primary motor cortex. It is more extensive than primary motor cortex (about 6 times) Functions: It works with the help of basal ganglia, thalamus, primary motor cortex, posterior parietal cortex. It plays role in planning and anticipation of a spec ...
1. What different types of attention exist? Name and describe at least
... Endogenous / selective / top-down attention: attention deliberately directed by the brain to serve a behavioral goal, e.g., focusing of auditory attention to a specific speaker in at a social event. Sustained attention: attention devoted to a specific task for a prolonged period of time. Alternating ...
... Endogenous / selective / top-down attention: attention deliberately directed by the brain to serve a behavioral goal, e.g., focusing of auditory attention to a specific speaker in at a social event. Sustained attention: attention devoted to a specific task for a prolonged period of time. Alternating ...
File - firestone falcons
... candle 30 mi (48 km) away from us, if our eyes were used to the dark. If a person in front of you held up a candle and began backing up at the rate of one foot (30 cm) per second, that person would have to back up for 44 hours before the flame became invisible. ...
... candle 30 mi (48 km) away from us, if our eyes were used to the dark. If a person in front of you held up a candle and began backing up at the rate of one foot (30 cm) per second, that person would have to back up for 44 hours before the flame became invisible. ...
Towards natural stimulation in fMRI—Issues of data analysis
... about the locations of functional brain regions, such as the auditory cortex or the face-sensitive fusiform area, to monitor activations in these areas of interest. Such an approach was taken by Hasson et al. (2004) to demonstrate temporal similarities across subjects (“intersubject synchronization” ...
... about the locations of functional brain regions, such as the auditory cortex or the face-sensitive fusiform area, to monitor activations in these areas of interest. Such an approach was taken by Hasson et al. (2004) to demonstrate temporal similarities across subjects (“intersubject synchronization” ...
Brain Function and Organization via Imaging
... Outline of Topics 1. Imaging: postmortem and MRI 2. Brain Macro anatomy – lobes, tissues, ...
... Outline of Topics 1. Imaging: postmortem and MRI 2. Brain Macro anatomy – lobes, tissues, ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... a. controls general body arousal and the ability to focus our attention iii. Forebrain 1. controls thought and reason 2. thalamus a. receives sensory signals coming up the spinal cord and sends them to other forebrain areas 3. hypothalamus a. controls hunger, sexual arousal, thirst, and the endocrin ...
... a. controls general body arousal and the ability to focus our attention iii. Forebrain 1. controls thought and reason 2. thalamus a. receives sensory signals coming up the spinal cord and sends them to other forebrain areas 3. hypothalamus a. controls hunger, sexual arousal, thirst, and the endocrin ...
Dorsal Column * Medial Lemniscal System (DC-ML)
... Before she started copying, she was asked what she saw. She said, "A tree, a house, and a fence." After she believed that she had copied the entire picture, she was asked again what she saw in the original picture: "A tree and a house." Note not only the absence of figures from the left side of the ...
... Before she started copying, she was asked what she saw. She said, "A tree, a house, and a fence." After she believed that she had copied the entire picture, she was asked again what she saw in the original picture: "A tree and a house." Note not only the absence of figures from the left side of the ...
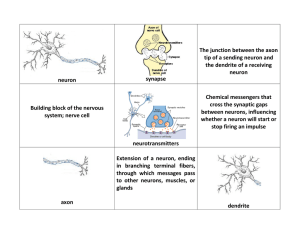
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
... linked to emotion; thought to determine whether we should emotionally react to sensory stimuli, especially with rage or fear; processes emotional memories ...
Unit 4: Neuroscience The Neuron Soma (cell body): Contains
... 1. When the action potential reaches the terminal buttons on the ends of the terminal branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. 2. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotran ...
... 1. When the action potential reaches the terminal buttons on the ends of the terminal branches, it causes the synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synapse. 2. The neurotransmitters then bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron (like a key fitting into a lock). Some neurotran ...
Myers AP - Unit 03B
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
Heroin - WordPress.com
... According to the Specification you need to be able to : Describe, with reference to heroin and nicotine 1. Mode of action 2. Effects 3. Tolerance 4. Physical / psychological dependencies 5. withdrawal ...
... According to the Specification you need to be able to : Describe, with reference to heroin and nicotine 1. Mode of action 2. Effects 3. Tolerance 4. Physical / psychological dependencies 5. withdrawal ...
Blair_Module08
... • Involved in language comprehension and expression; our ability to understand what is said to us • Usually in the left temporal lobe ...
... • Involved in language comprehension and expression; our ability to understand what is said to us • Usually in the left temporal lobe ...
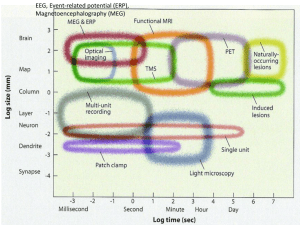
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.