chapter38
... from the presynaptic neuron by exocytosis that can stimulate the postsynaptic neuron. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters. ...
... from the presynaptic neuron by exocytosis that can stimulate the postsynaptic neuron. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters. ...
Review - TheThinkSpot
... c. resting potentials into action potentials d. action potentials into resting potentials 11. If a neuron receives inhibitory signals, will it still fire? ...
... c. resting potentials into action potentials d. action potentials into resting potentials 11. If a neuron receives inhibitory signals, will it still fire? ...
Time representation in reinforcement learning models of
... In the bisection procedure, subjects are trained to respond differentially to short and long duration cues. Unreinforced probe trials with cue durations between these two extremes are occasionally presented. On these trials, typically, a psychometric curve is produced with greater selection of the ...
... In the bisection procedure, subjects are trained to respond differentially to short and long duration cues. Unreinforced probe trials with cue durations between these two extremes are occasionally presented. On these trials, typically, a psychometric curve is produced with greater selection of the ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
Chapter 10: Sensory Physiology
... are transducers → convert stimuli into graded potential (receptor potential) are of various complexity ...
... are transducers → convert stimuli into graded potential (receptor potential) are of various complexity ...
How Does the Brain Learn Through Music?
... – Facilitates learning and heightens memory – (Baroque Music with 40 – 60 beats per minuteAdagio) This music tends to slow down respiration, heart rate, and reduces stress. ...
... – Facilitates learning and heightens memory – (Baroque Music with 40 – 60 beats per minuteAdagio) This music tends to slow down respiration, heart rate, and reduces stress. ...
The Computational Brain
... brain into sections. The brain is made of highly specified areas, each able to communicate with other area specific parts of the brain, as well as the parts of the body it is to control. There are 6 distinct areas of the brain. Over the millions of years of evolution, nature is perfecting how the br ...
... brain into sections. The brain is made of highly specified areas, each able to communicate with other area specific parts of the brain, as well as the parts of the body it is to control. There are 6 distinct areas of the brain. Over the millions of years of evolution, nature is perfecting how the br ...
What can cognitive psychology and sensory evaluation learn from
... However, anatomically independent systems can be cognitively or psychologically integrated. This point is clearer if we take the example of vision which is the most studied and best known perceptual system. It comprises two main subsystems themselves made of several independent modules (see, e.g., O ...
... However, anatomically independent systems can be cognitively or psychologically integrated. This point is clearer if we take the example of vision which is the most studied and best known perceptual system. It comprises two main subsystems themselves made of several independent modules (see, e.g., O ...
Nervous system (Brain and Plexi)
... releases signaling molecules called hormones into bloodstream ex. pancreas secretes insulin testes secretes testosterone Cerebrum anterior larger upper part of brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action, divided by longitutional fissure Longitudional fissure divides cere ...
... releases signaling molecules called hormones into bloodstream ex. pancreas secretes insulin testes secretes testosterone Cerebrum anterior larger upper part of brain, associated with higher brain function such as thought and action, divided by longitutional fissure Longitudional fissure divides cere ...
Science of Addiction WebquestKEY
... 8. Explain why drug users develop a “tolerance” reduce the number of dopamine receptors 9. The faster a drug is delivered to the system the _more likely it will become addicting________. Look at the PET scan of a brain belonging to a previous cocaine user. 10. Do the affects on the brain from cocain ...
... 8. Explain why drug users develop a “tolerance” reduce the number of dopamine receptors 9. The faster a drug is delivered to the system the _more likely it will become addicting________. Look at the PET scan of a brain belonging to a previous cocaine user. 10. Do the affects on the brain from cocain ...
Midterm 1
... A. parietal lobe B. motor cortex C. prefrontal cortex *D. occipital lobe % Correct: 96.52% Notes: This is an identification question. It’s asking about the different lobes of the brain. Our back (posterior) region of our brain, contains a lobe that we call the occipital lobe. It has been linked to v ...
... A. parietal lobe B. motor cortex C. prefrontal cortex *D. occipital lobe % Correct: 96.52% Notes: This is an identification question. It’s asking about the different lobes of the brain. Our back (posterior) region of our brain, contains a lobe that we call the occipital lobe. It has been linked to v ...
Brain Info sheet
... is responsible for controlling a specific combination of activities within the body. An example of parts of the brain controlling at the same time would be the cerebrum and the cerebellum. The cerebrum controls processes that require conscious thought, sensation, and voluntary movement. The cerebell ...
... is responsible for controlling a specific combination of activities within the body. An example of parts of the brain controlling at the same time would be the cerebrum and the cerebellum. The cerebrum controls processes that require conscious thought, sensation, and voluntary movement. The cerebell ...
E.4.4 List three examples of excitatory and three examples of
... posterior lobe stores and releases hypothalamic hormones anterior lobe produces, stores, and secretes many hormones regulating many body functions ...
... posterior lobe stores and releases hypothalamic hormones anterior lobe produces, stores, and secretes many hormones regulating many body functions ...
The Nervous System
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes (simple, automatic response to sensory stimuli) ...
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes (simple, automatic response to sensory stimuli) ...
PowerPoint - Home (www2)
... Each has own lens & photoreceptor cells Very sensitive to motion 360o field of vision Multiple images integrated in brain Poor image resolution ...
... Each has own lens & photoreceptor cells Very sensitive to motion 360o field of vision Multiple images integrated in brain Poor image resolution ...
Brain and Consciousness - Oakton Community College
... The more neurons are exercised, the thicker the myelin tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
... The more neurons are exercised, the thicker the myelin tissue becomes. The thicker the myelin tissue, the faster the electric impulse can travel through the axon, up to 200 miles per hour. ...
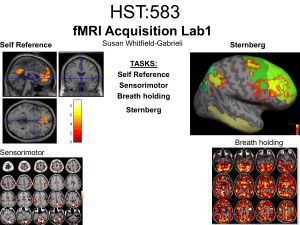
HST:583 fMRI Acquisition Lab1 Susan Whitfield
... acquires an image at 2 different echo times. This sequence generates 2 types of images, a magnitude image and a phase map. The phase map represents the phase differences of the spins which ultimately represent the local field inhomogeneities. You can display this map to see which regions are prone t ...
... acquires an image at 2 different echo times. This sequence generates 2 types of images, a magnitude image and a phase map. The phase map represents the phase differences of the spins which ultimately represent the local field inhomogeneities. You can display this map to see which regions are prone t ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... 12.2, a somatosensory and motor homunculus is drawn to explain which functions of the body take up more or less space on the cortex. Using that diagram, answer the following questions Which area(s) of the body is/are depicted as overly Why would these structures need greater space in large in the mo ...
... 12.2, a somatosensory and motor homunculus is drawn to explain which functions of the body take up more or less space on the cortex. Using that diagram, answer the following questions Which area(s) of the body is/are depicted as overly Why would these structures need greater space in large in the mo ...
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
... or skier is not conscious of all movements being made, even though these same movements were executed consciously while learning the skill. Sensing of motor action and motor feedback on sensory systems is important for smooth and accurate motor performance. For example, muscles, joints and tendons h ...
... or skier is not conscious of all movements being made, even though these same movements were executed consciously while learning the skill. Sensing of motor action and motor feedback on sensory systems is important for smooth and accurate motor performance. For example, muscles, joints and tendons h ...
Midterm 1
... Comments: When separating out our nervous system, there are a multitude of subsystems that neuropsychologists can study. The first split is typically between the central (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral (nerves extending throughout the body) nervous systems. The second split occurs within the ...
... Comments: When separating out our nervous system, there are a multitude of subsystems that neuropsychologists can study. The first split is typically between the central (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral (nerves extending throughout the body) nervous systems. The second split occurs within the ...
Document
... The medulla contains centers that control several automatic, homeostatic functions, including breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion. The pons also participates in some of these activities; for example, it regulates the breathing centers in the medulla. ...
... The medulla contains centers that control several automatic, homeostatic functions, including breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, and digestion. The pons also participates in some of these activities; for example, it regulates the breathing centers in the medulla. ...
BIOPSYCHOLOGY notes
... This significantly increases serotonin receptor binding (more serotonin in the synapse means a greater chance for some of them to bind to the receptors). This increased receptor activity leads to significant changes in the brain's electrical firing and is primarily responsible for the MDMA experienc ...
... This significantly increases serotonin receptor binding (more serotonin in the synapse means a greater chance for some of them to bind to the receptors). This increased receptor activity leads to significant changes in the brain's electrical firing and is primarily responsible for the MDMA experienc ...
638969476616MyersMod_LG_04
... 5. Discuss the capacity of the brain to reorganize following injury or illness. Research indicates that neural tissue can reorganize in response to injury or damage. When one brain area is damaged, others may in time take over some of its function. For example, if neurons are destroyed ...
... 5. Discuss the capacity of the brain to reorganize following injury or illness. Research indicates that neural tissue can reorganize in response to injury or damage. When one brain area is damaged, others may in time take over some of its function. For example, if neurons are destroyed ...
Decoding visual consciousness from human
... the one hand, a core NCC is necessary for a specific conscious experience (Box 1), and on the other hand, its activity patterns exhibit a consistent mapping to specific experiences that can be viewed as an ‘encoding’ of the experience in question. A key criterion for a core NCC is that it shows a ma ...
... the one hand, a core NCC is necessary for a specific conscious experience (Box 1), and on the other hand, its activity patterns exhibit a consistent mapping to specific experiences that can be viewed as an ‘encoding’ of the experience in question. A key criterion for a core NCC is that it shows a ma ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.