Chapter 14 Autonomic nervous system
... b. The axons of the corticospinal tracts, for example, do not become fully myelinated until the second year of life, explaining why infants and young children follow patterns of developmental activity. C. Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways involve the motor cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellu ...
... b. The axons of the corticospinal tracts, for example, do not become fully myelinated until the second year of life, explaining why infants and young children follow patterns of developmental activity. C. Indirect (extrapyramidal) pathways involve the motor cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus, cerebellu ...
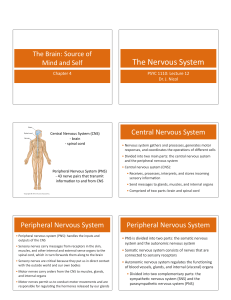
Central Nervous System
... Nervous System: coordinates and controls body activity. It detects and processes internal and external information and sends out an appropriate response. Major structures of nervous system: brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and sensory organs. Two major parts of the nervous system are: Centr ...
... Nervous System: coordinates and controls body activity. It detects and processes internal and external information and sends out an appropriate response. Major structures of nervous system: brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and sensory organs. Two major parts of the nervous system are: Centr ...
Organization of Nervous System
... As it turns out, there are also receptors on the bouton itself. These receptors modulate the release of neurotransmitters. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that acts on the presynaptic receptor. It inhibits the release of glutamate. ...
... As it turns out, there are also receptors on the bouton itself. These receptors modulate the release of neurotransmitters. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that acts on the presynaptic receptor. It inhibits the release of glutamate. ...
The matter of knowledge - America Saraswata Sangha
... What is soul (Atma), who is God and what is known as Universe? To learn these is discussion on knowledge and is necessary for salvation. Our primary duty is to study the scriptures about spiritual philosophy such that we can practice the learning process. The scripture of knowledge is nothing but th ...
... What is soul (Atma), who is God and what is known as Universe? To learn these is discussion on knowledge and is necessary for salvation. Our primary duty is to study the scriptures about spiritual philosophy such that we can practice the learning process. The scripture of knowledge is nothing but th ...
Document
... CNS Moderation of Reflexes • Upper CNS (brain) normally produces an inhibitory effect on the reflex arcs (muffled effect) • With injury, intact reflex arcs caudal to spinal cord trauma ...
... CNS Moderation of Reflexes • Upper CNS (brain) normally produces an inhibitory effect on the reflex arcs (muffled effect) • With injury, intact reflex arcs caudal to spinal cord trauma ...
Vision - Florida Atlantic University
... Associative visual agnosia refers to a disconnection between perceptions and verbal systems Person ...
... Associative visual agnosia refers to a disconnection between perceptions and verbal systems Person ...
brain and cranial nerves
... --Amount of oxygen brain uses varies with the degree of mental activity. Blood supply of the brain is from cerebral arterial circle( circle of Willis) at the base of the brain. ii. Interruption of oxygen supply to the brain can result in weakening, permanent damage or death of brain cells. iii. Th ...
... --Amount of oxygen brain uses varies with the degree of mental activity. Blood supply of the brain is from cerebral arterial circle( circle of Willis) at the base of the brain. ii. Interruption of oxygen supply to the brain can result in weakening, permanent damage or death of brain cells. iii. Th ...
Nervous System
... nervous system do? The nervous system picks up messages from in and out of the body and turns them ...
... nervous system do? The nervous system picks up messages from in and out of the body and turns them ...
Visual Perception: Objects and Scenes
... Besides the solid line between nodes and vertices, we can also find mutual excitatory links between pairs of node in the same subnetworks. This is when cooperation arises. As a result of these connections, activation in one node tends to increase activation in the other. That is, if one node of give ...
... Besides the solid line between nodes and vertices, we can also find mutual excitatory links between pairs of node in the same subnetworks. This is when cooperation arises. As a result of these connections, activation in one node tends to increase activation in the other. That is, if one node of give ...
The Nervous System
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS): handles the inputs and outputs of the CNS • Sensory nerves carry messages from receptors in the skin, muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spina ...
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS): handles the inputs and outputs of the CNS • Sensory nerves carry messages from receptors in the skin, muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spina ...
Interference to Neurotransmitter function
... • Levodopa (L-Dopa) can cross the blood-brain barrier and be converted into dopamine by the brain. • Dopamine agonists stimulate the dopamine receptors in the brain, mimicking the effect of dopamine in the brain. • Both drugs can alleviate symptoms of Parkinson’s, but are not a cure. The disease con ...
... • Levodopa (L-Dopa) can cross the blood-brain barrier and be converted into dopamine by the brain. • Dopamine agonists stimulate the dopamine receptors in the brain, mimicking the effect of dopamine in the brain. • Both drugs can alleviate symptoms of Parkinson’s, but are not a cure. The disease con ...
brain and spinal cord
... Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or ...
... Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or ...
neurology1ned2013 31.5 KB - d
... impulses. The SATII expects some detail about this. I will try to address as much as I can in class without compromising the detail of your knowledge on the physiology. The axon potentiates or pushes forward an electric message. (Gives) The dendrite receives an electric message. (Gets) The synapse ( ...
... impulses. The SATII expects some detail about this. I will try to address as much as I can in class without compromising the detail of your knowledge on the physiology. The axon potentiates or pushes forward an electric message. (Gives) The dendrite receives an electric message. (Gets) The synapse ( ...
Chapter 22 Thalamus
... Receptors; specialized cells which convert external stimulus energy into a signal that produces a neural response Each of the fundamental types of stimuli has a separate population of receptors selective for the particular form of energy Within a single sensory system are classes of receptors ...
... Receptors; specialized cells which convert external stimulus energy into a signal that produces a neural response Each of the fundamental types of stimuli has a separate population of receptors selective for the particular form of energy Within a single sensory system are classes of receptors ...
Danczi Csaba László - 2nd WORLD CONGRESS OF ARTS
... others. Two different sensory stimuli that originate from the same location in space (e.g. derived from the same event) will effect a pronounced enhancement of the neuron's response beyond that predicted by the sum of its activation when the two cues are presented individually. When one of the two c ...
... others. Two different sensory stimuli that originate from the same location in space (e.g. derived from the same event) will effect a pronounced enhancement of the neuron's response beyond that predicted by the sum of its activation when the two cues are presented individually. When one of the two c ...
Ch. 2 Practice
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
Document
... • Pathways of three neurons conduct sensory impulses upward to the appropriate brain regions • First-order neurons • Conduct impulses from the receptor level to the second-order neurons in the CNS ...
... • Pathways of three neurons conduct sensory impulses upward to the appropriate brain regions • First-order neurons • Conduct impulses from the receptor level to the second-order neurons in the CNS ...
Chapter 3 Section 2 - 6th
... aggression. If it is damaged, a person can recall old memories but can’t form new ones (50 First Dates) 4. Cerebrum- the part that thinks; it is uniquely human & accounts for 70% of brain weight cerebral cortex-outer layer of the brain, which deals with memory, language, emotions, complex motor func ...
... aggression. If it is damaged, a person can recall old memories but can’t form new ones (50 First Dates) 4. Cerebrum- the part that thinks; it is uniquely human & accounts for 70% of brain weight cerebral cortex-outer layer of the brain, which deals with memory, language, emotions, complex motor func ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
Ch05LifespanPPT
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
Neuroplasticity
... structure in response to abnormal input, the prevailing view that we are born with a hardwired system had to be wrong, therefore the brain had to be plastic. • Results: They realised that the hand map in the brain that was expected to be jumbled was nearly normal. Merzenich concluded that if the bra ...
... structure in response to abnormal input, the prevailing view that we are born with a hardwired system had to be wrong, therefore the brain had to be plastic. • Results: They realised that the hand map in the brain that was expected to be jumbled was nearly normal. Merzenich concluded that if the bra ...
Nervous System
... which the amygdala, uncus, hippocampal gyrus and anterior two-thirds of the hippocampus were removed, H.M. could not form long-term memories • The case of N.A.—a fencing foil poked into his right nostril damaged part of his thalamus and the medial temporal lobe on the right side as well as the mammi ...
... which the amygdala, uncus, hippocampal gyrus and anterior two-thirds of the hippocampus were removed, H.M. could not form long-term memories • The case of N.A.—a fencing foil poked into his right nostril damaged part of his thalamus and the medial temporal lobe on the right side as well as the mammi ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.