PDF version
... may mask the signal; or the neurons emitting the signals can die. To get around these problems, Joel Burdick and Richard Andersen at Caltech have developed a device in which the electrodes sense where the strongest signal is coming from, and move towards it. Their prototype, which is mounted on the ...
... may mask the signal; or the neurons emitting the signals can die. To get around these problems, Joel Burdick and Richard Andersen at Caltech have developed a device in which the electrodes sense where the strongest signal is coming from, and move towards it. Their prototype, which is mounted on the ...
Chapter 11- 14 Integration of Nervous System Functions
... – Alpha: Resting state with eyes closed – Beta: During intense mental activity – Theta: Occur in children but also in adults experiencing frustration or brain disorders – Delta: Occur in deep sleep, infancy, and severe brain disorders ...
... – Alpha: Resting state with eyes closed – Beta: During intense mental activity – Theta: Occur in children but also in adults experiencing frustration or brain disorders – Delta: Occur in deep sleep, infancy, and severe brain disorders ...
Biopsychology The Nervous System
... human sexual behavior is interpreted in terms of its survival value—the tendency for behaviors to be selected if they increase the likelihood of sending one’s genes into the future ...
... human sexual behavior is interpreted in terms of its survival value—the tendency for behaviors to be selected if they increase the likelihood of sending one’s genes into the future ...
Chapter 28
... action potential is a local event ii) this event must travel along neuron iii) Figure 28.5 (1) each action potential generates another next door (domino effect) (2) why do they only flow in one direction? (a)Na+ channels are inactivated while K+ is diffusing out (b) If they can’t open, there can’t b ...
... action potential is a local event ii) this event must travel along neuron iii) Figure 28.5 (1) each action potential generates another next door (domino effect) (2) why do they only flow in one direction? (a)Na+ channels are inactivated while K+ is diffusing out (b) If they can’t open, there can’t b ...
UNIT XI
... type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later life. – E.g. can recover after stroke (sensory and motor). ...
... type of cell dissolve • Nerves will not develop for a blocked eye. • 50% or more of original neurons in parts of cerebral cortex are eliminated. • This is a type of memory. • Plasticity continues to a lesser extent in later life. – E.g. can recover after stroke (sensory and motor). ...
Griggs Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... environment and consists of two parts The sympathetic nervous system is in control when we are very aroused and prepares us for defensive action (such as running away or fighting) The parasympathetic nervous system is in control when the aroused state ends to return our body to its normal restin ...
... environment and consists of two parts The sympathetic nervous system is in control when we are very aroused and prepares us for defensive action (such as running away or fighting) The parasympathetic nervous system is in control when the aroused state ends to return our body to its normal restin ...
On-center off surround ganglion cells
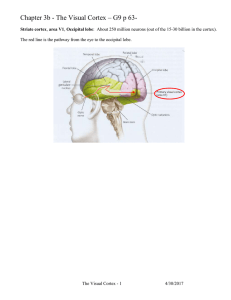
... Yes we can bypass retina and LGN and stimulate area V1. However, it seems impossible to recover full visual experience from higher visual areas bypassing primary visual cortex. ...
... Yes we can bypass retina and LGN and stimulate area V1. However, it seems impossible to recover full visual experience from higher visual areas bypassing primary visual cortex. ...
D. Brain
... 3. Dementia – general term for “losing your mind”….boxers who have received too many blows to the head a. Alzheimers – increasing loss of memory (forget to turn off stove after cooking or water after washing their hands). This progresses to infantile behavior….they will often talk about their “pas ...
... 3. Dementia – general term for “losing your mind”….boxers who have received too many blows to the head a. Alzheimers – increasing loss of memory (forget to turn off stove after cooking or water after washing their hands). This progresses to infantile behavior….they will often talk about their “pas ...
Neuroscience and Biopsychology
... Blindness - when reading Braille, the brain area dedicated to that finger expands as the sense of touch invades the visual cortex, which normally helps people see • Deafness - the auditory cortex receives no information from sound, so it expands to new functions like visual tasks, which is why deaf ...
... Blindness - when reading Braille, the brain area dedicated to that finger expands as the sense of touch invades the visual cortex, which normally helps people see • Deafness - the auditory cortex receives no information from sound, so it expands to new functions like visual tasks, which is why deaf ...
RHCh2 - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... With the corpus callosum severed, objects (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. ...
... With the corpus callosum severed, objects (apple) presented in the right visual field can be named. Objects (pencil) in the left visual field cannot. ...
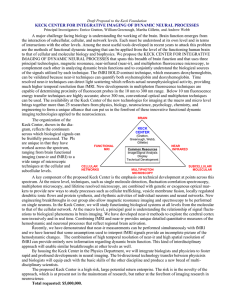
Draft Proposal to the Keck Foundation KECK CENTER FOR
... to that of the cellular network. At the macro level, a principal goal is understanding the relationship of signal fluctuations to biological phenomena in brain imaging. We have developed near-ir methods to explore the cerebral cortex non-invasively and in real time. Combining fMRI and near-ir provid ...
... to that of the cellular network. At the macro level, a principal goal is understanding the relationship of signal fluctuations to biological phenomena in brain imaging. We have developed near-ir methods to explore the cerebral cortex non-invasively and in real time. Combining fMRI and near-ir provid ...
Neuroscience and Behavior - Bremerton School District
... A functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
... A functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
Chapter 15 - Nervous System Brain & Cranial Nerves
... processes called tracts. There are three major types of tracts in the cerebral cortex: Commissural fibers – connect the gray matter between the two hemispheres. e.g. corpus callosum Association fibers – connect adjacent gyri in same hemisphere. e.g. visual and auditory association ...
... processes called tracts. There are three major types of tracts in the cerebral cortex: Commissural fibers – connect the gray matter between the two hemispheres. e.g. corpus callosum Association fibers – connect adjacent gyri in same hemisphere. e.g. visual and auditory association ...
The nervous system
... NERVOUS SYSTEM THAT RECEIVES AND TRANSMITS MESSAGES MADE UP OF 4 PARTS - DENDRITES - CELL BODY (which contains the nucleus) - AXON - AXON TERMINALS ...
... NERVOUS SYSTEM THAT RECEIVES AND TRANSMITS MESSAGES MADE UP OF 4 PARTS - DENDRITES - CELL BODY (which contains the nucleus) - AXON - AXON TERMINALS ...
brain
... • Changes in how much neurotransmitter a presynaptic neuron releases • Changes in neuron sensitivity to neurotransmitters • Creating new connections by growing new ...
... • Changes in how much neurotransmitter a presynaptic neuron releases • Changes in neuron sensitivity to neurotransmitters • Creating new connections by growing new ...
Revision material
... Describe briefly the optical factors that affect visual acuity. Write short notes on two of the following: visual agnosia; the pupil; bleaching adaptation. What kinds of neurotransmitters and neuropeptides occur in the central nervous system? What is the function of lateral inhibition? What purposes ...
... Describe briefly the optical factors that affect visual acuity. Write short notes on two of the following: visual agnosia; the pupil; bleaching adaptation. What kinds of neurotransmitters and neuropeptides occur in the central nervous system? What is the function of lateral inhibition? What purposes ...
brain
... • Changes in how much neurotransmitter a presynaptic neuron releases • Changes in neuron sensitivity to neurotransmitters • Creating new connections by growing new ...
... • Changes in how much neurotransmitter a presynaptic neuron releases • Changes in neuron sensitivity to neurotransmitters • Creating new connections by growing new ...
Jeopardy Bio Basis of Human Behavior
... digestion, adrenal gland releases adrenaline and noradrenaline (epinephrine and norepinephrine) ...
... digestion, adrenal gland releases adrenaline and noradrenaline (epinephrine and norepinephrine) ...
The Brain and The Nervous System
... difficulties with visual and spatial tasks such as reading maps. • Damage to left hemisphere often resulted in difficulties with language related tasks such as understanding speech, talking fluently reading and writing. • Damage to the right hemisphere often result in slower recognition of pictures. ...
... difficulties with visual and spatial tasks such as reading maps. • Damage to left hemisphere often resulted in difficulties with language related tasks such as understanding speech, talking fluently reading and writing. • Damage to the right hemisphere often result in slower recognition of pictures. ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... released into the water. If the platform is removed, the normal animal will spend most of his time searching in the quadrant where the platform should be. Learning of this sort of spatial map depends on the hippocampus. If a genetically altered rat with a malfunctioning hippocampus is given the same ...
... released into the water. If the platform is removed, the normal animal will spend most of his time searching in the quadrant where the platform should be. Learning of this sort of spatial map depends on the hippocampus. If a genetically altered rat with a malfunctioning hippocampus is given the same ...
Why light
... Evidence . . . Selective Adaptation Experiments Participants view a specific grating stimulus continuously. ...
... Evidence . . . Selective Adaptation Experiments Participants view a specific grating stimulus continuously. ...
Introductory chapter
... to record this activity. Indeed, the history of experiments on the electrical activity of nerves is intertwined with the history of electrical measurements more generally. The science of electricity as we understand it today began with Galvani and Volta in the 1700s (Pera 1986). Galvani observed tha ...
... to record this activity. Indeed, the history of experiments on the electrical activity of nerves is intertwined with the history of electrical measurements more generally. The science of electricity as we understand it today began with Galvani and Volta in the 1700s (Pera 1986). Galvani observed tha ...
Understanding Concepts through Songs and Poems
... Endocrine glands release (minute amounts of) tropic hormones They (glands) have no ducts and no tubes Target cells respond to these hormones ...
... Endocrine glands release (minute amounts of) tropic hormones They (glands) have no ducts and no tubes Target cells respond to these hormones ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.