Module 20 Basic Learning Concepts and Classical
... Acquisition: the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. Higher-order conditioning: a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutra ...
... Acquisition: the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. Higher-order conditioning: a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutra ...
Document
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
Document
... cortex. Some cortical neurons send their axons to the thalamus, while others receive input from ...
... cortex. Some cortical neurons send their axons to the thalamus, while others receive input from ...
Demonstrating the Implicit Processing of Visually Presented Words
... The present article investigates the implicit activation of language areas by engaging subjects in a nonlinguistic visual feature detection task with a button-press response while either words or nonwords were presented in the visual field. The task and the instructions to the subjects remained cons ...
... The present article investigates the implicit activation of language areas by engaging subjects in a nonlinguistic visual feature detection task with a button-press response while either words or nonwords were presented in the visual field. The task and the instructions to the subjects remained cons ...
Brain Research Methods - RevisionforPsy3
... o Can be used for mapping brain areas, pinpoint/diagnose brain damage and to track patients recovery ie. From a stroke o Repetitive TMS (rTMS) used in procedures involving repeated (not necessarily rapid) delivery of a pulse causing area of brain to be inactive without unwanted side effects – used t ...
... o Can be used for mapping brain areas, pinpoint/diagnose brain damage and to track patients recovery ie. From a stroke o Repetitive TMS (rTMS) used in procedures involving repeated (not necessarily rapid) delivery of a pulse causing area of brain to be inactive without unwanted side effects – used t ...
Opposing roles for dopamine and serotonin in the modulation of
... Spatial Working Memory Task Subjects were seated with sound-damping headphones and an adjustable chin-forehead rest with eyes 27 cm from a monochrome computer monitor. During each trial, subjects observed a central fixation point (a black ‘+’, 0.63° × 0.63°) on the monitor for 3 s. Next, a visual cu ...
... Spatial Working Memory Task Subjects were seated with sound-damping headphones and an adjustable chin-forehead rest with eyes 27 cm from a monochrome computer monitor. During each trial, subjects observed a central fixation point (a black ‘+’, 0.63° × 0.63°) on the monitor for 3 s. Next, a visual cu ...
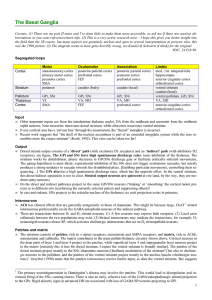
The Basal Ganglia
... • Unilateral 6-OHDA lesions cause an asymmetric posture (twisted to the side of the lesion) which recovers. At this point amphetamine-induced rotation will occur (towards the side of the lesion)3. Note that amphetamine releases DA presynaptically, so more on the intact side. Apomorphine (a direct DA ...
... • Unilateral 6-OHDA lesions cause an asymmetric posture (twisted to the side of the lesion) which recovers. At this point amphetamine-induced rotation will occur (towards the side of the lesion)3. Note that amphetamine releases DA presynaptically, so more on the intact side. Apomorphine (a direct DA ...
Psychology 312-1 - Northwestern University
... 2. Obvious clinical applications? (If you change a visual EP, do you change vision? We’ll come back to this. 3. OCNE uniquely can work out neural code/mechanisms of voluntary ...
... 2. Obvious clinical applications? (If you change a visual EP, do you change vision? We’ll come back to this. 3. OCNE uniquely can work out neural code/mechanisms of voluntary ...
The Brain and Addition
... a hot day—that's your limbic system at work. Because natural pleasures in our lives are necessary for survival, the limbic system creates an appetite that drives you to seek those things. ...
... a hot day—that's your limbic system at work. Because natural pleasures in our lives are necessary for survival, the limbic system creates an appetite that drives you to seek those things. ...
Itti: CS564 - Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence University
... so hippocampus seems to be the site neither of storage nor of retrieval. Mishkin 1982 proposes that the inferotemporal cortex (IT) is not only a site of higher-order visual processes but also the site of visual memories resulting from these processes. Not only are certain perceptual schemas instanti ...
... so hippocampus seems to be the site neither of storage nor of retrieval. Mishkin 1982 proposes that the inferotemporal cortex (IT) is not only a site of higher-order visual processes but also the site of visual memories resulting from these processes. Not only are certain perceptual schemas instanti ...
The neural subjective frame: from bodily signals to perceptual
... (ii) The subjective frame is necessary, but not sufficient, for subjective experience The neural subjective frame would bring in an important element: it would enable the ‘I’ by referring sensory information to the subject. The subjective frame is therefore necessary for any percept to be subjective ...
... (ii) The subjective frame is necessary, but not sufficient, for subjective experience The neural subjective frame would bring in an important element: it would enable the ‘I’ by referring sensory information to the subject. The subjective frame is therefore necessary for any percept to be subjective ...
Протокол
... the highest functional level of the nervous system and responsible for uniquely human characteristics, such as intricate hand movements, highly developed speech, symbolic thought, personality, conscience, and self-awareness. These qualities are known to depend on the cortex because, if certain areas ...
... the highest functional level of the nervous system and responsible for uniquely human characteristics, such as intricate hand movements, highly developed speech, symbolic thought, personality, conscience, and self-awareness. These qualities are known to depend on the cortex because, if certain areas ...
the neurobiology of emotion
... Nature vs. Nurture Fear behavior is essential for survival and much of its development appears to be innate. In humans, behavioral responses associated with fear are evident within the first months of life. However, it is not until sometime later that infants display fear reactions that are selectiv ...
... Nature vs. Nurture Fear behavior is essential for survival and much of its development appears to be innate. In humans, behavioral responses associated with fear are evident within the first months of life. However, it is not until sometime later that infants display fear reactions that are selectiv ...
chapt08_lecture
... a. Studies of people with amnesia reveal that areas of the temporal lobe, hippocampus, caudate nucleus, and dorsomedial thalamus are involved in memory. b. The amygdala is important in learning fear responses. c. The prefrontal cortex may be involved in complex problem solving and working memory– ve ...
... a. Studies of people with amnesia reveal that areas of the temporal lobe, hippocampus, caudate nucleus, and dorsomedial thalamus are involved in memory. b. The amygdala is important in learning fear responses. c. The prefrontal cortex may be involved in complex problem solving and working memory– ve ...
EN Sokolov`s Neural Model of Stimuli as Neuro
... Especially in the short term, increased familiarity with stimuli means that they are ignored. However, exposure to a stimulus on its first instance will elicite increased attention to it, and according to the above, familiarity with a stimulus implies that the perceiver possesses a neuronal model or ...
... Especially in the short term, increased familiarity with stimuli means that they are ignored. However, exposure to a stimulus on its first instance will elicite increased attention to it, and according to the above, familiarity with a stimulus implies that the perceiver possesses a neuronal model or ...
A5: Neuropharamcology (student) - Ms De Souza`s Super Awesome
... The secondary messengers can persist for days and cause what is known as long-term potentiation (LTP), allowing new synapses to form in the hippocampus and other areas of the brain. ...
... The secondary messengers can persist for days and cause what is known as long-term potentiation (LTP), allowing new synapses to form in the hippocampus and other areas of the brain. ...
The Mammalian Nervous System: Structure and
... Memories are transferred from shortto long-term. Hippocampal or limbic system damage may prevent this transfer. ...
... Memories are transferred from shortto long-term. Hippocampal or limbic system damage may prevent this transfer. ...
Time perception

Time perception is a field of study within psychology and neuroscience that refers to the subjective experience of time, which is measured by someone's own perception of the duration of the indefinite and continuous unfolding of events. The perceived time interval between two successive events is referred to as perceived duration. Another person's perception of time cannot be directly experienced or understood, but it can be objectively studied and inferred through a number of scientific experiments. Time perception is a construction of the brain that is manipulable and distortable under certain circumstances. These temporal illusions help to expose the underlying neural mechanisms of time perception.Pioneering work, emphasizing species-specific differences, was conducted by Karl Ernst von Baer. Experimental work began under the influence of the psycho-physical notions of Gustav Theodor Fechner with studies of the relationship between perceived and measured time.