doc 2.6M
... NOTE: The premise of this lesson is to provide ways to do the requirements with reference to only the internet. You need only have an inexpensive $50 plastic sextant. It is possible to do this requirement without a body of water nearby. See the explanation of artificial horizons. This explanation us ...
... NOTE: The premise of this lesson is to provide ways to do the requirements with reference to only the internet. You need only have an inexpensive $50 plastic sextant. It is possible to do this requirement without a body of water nearby. See the explanation of artificial horizons. This explanation us ...
MCWP 3-16.7 Chapter 7: Astronomy
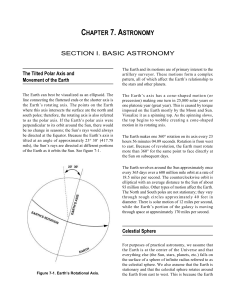
... hours 56 minutes 04.09 seconds. Rotation is from west to east. Because of revolution, the Earth must rotate more than 360° for the same point to face directly at the Sun on subsequent days. The Earth revolves around the Sun approximately once every 365 days over a 600 million mile orbit at a rate of ...
... hours 56 minutes 04.09 seconds. Rotation is from west to east. Because of revolution, the Earth must rotate more than 360° for the same point to face directly at the Sun on subsequent days. The Earth revolves around the Sun approximately once every 365 days over a 600 million mile orbit at a rate of ...
Basic Solar Positional Astronomy
... appear to move uniformly. So there is an imaginary Sun - the Mean Sun,- moving uniformly around the Equator which takes the place of the real Sun and tells such time. One cannot see an imaginary sun. But, since the Stars do appear to move uniformly around the Equator, they are used to measure Sidere ...
... appear to move uniformly. So there is an imaginary Sun - the Mean Sun,- moving uniformly around the Equator which takes the place of the real Sun and tells such time. One cannot see an imaginary sun. But, since the Stars do appear to move uniformly around the Equator, they are used to measure Sidere ...
Set 2 Astronomy questions
... Members of the “Key Project”, while working with the Hubble space telescope, are using observation primarily of what specific type of celestial object to calculate the Hubble constant? ANSWER: CEPHEIDS (ACCEPT: CEPHEID VARIABLES) BONUS 12) ASTRONOMY Short Answer Rounded to the first decimal place, h ...
... Members of the “Key Project”, while working with the Hubble space telescope, are using observation primarily of what specific type of celestial object to calculate the Hubble constant? ANSWER: CEPHEIDS (ACCEPT: CEPHEID VARIABLES) BONUS 12) ASTRONOMY Short Answer Rounded to the first decimal place, h ...
Chapter 2 CELESTIAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS
... To allow for greater precision, they decided to divide each arcminute into 60 equal parts called arcseconds, or seconds of arc. Hence, 1 arcsecond is 1/60th of an arcminute or 1/3600th of a degree. Such a system of measurement, based on the number 60, is called a sexagesimal system. We find a sexag ...
... To allow for greater precision, they decided to divide each arcminute into 60 equal parts called arcseconds, or seconds of arc. Hence, 1 arcsecond is 1/60th of an arcminute or 1/3600th of a degree. Such a system of measurement, based on the number 60, is called a sexagesimal system. We find a sexag ...
doc 2.6M
... NOTE: The premise of this lesson is to provide ways to do the requirements with reference to only the internet. You need only have an inexpensive $50 plastic sextant. It is possible to do this requirement without a body of water nearby. See the explanation of artificial horizons. This explanation us ...
... NOTE: The premise of this lesson is to provide ways to do the requirements with reference to only the internet. You need only have an inexpensive $50 plastic sextant. It is possible to do this requirement without a body of water nearby. See the explanation of artificial horizons. This explanation us ...
Founders of Modern Astronomy
... branches. Theoretical astronomy is concerned with the collection and analysis of data. To analyse the data basic principles of physics are used. Theoretical astronomy is concerned with the devel opment of computer or analytical models for describing astronomical objects and phenomena. The two branch ...
... branches. Theoretical astronomy is concerned with the collection and analysis of data. To analyse the data basic principles of physics are used. Theoretical astronomy is concerned with the devel opment of computer or analytical models for describing astronomical objects and phenomena. The two branch ...
Stars - Emera Astronomy Center
... State of Maine Learning Results Guiding Principles The lessons in this guide, in combination with Stars, will help students to work towards some of the Guiding Principles set forth by the State of Maine Learning Results. By the simple act of visiting the planetarium, students of all ages open an ave ...
... State of Maine Learning Results Guiding Principles The lessons in this guide, in combination with Stars, will help students to work towards some of the Guiding Principles set forth by the State of Maine Learning Results. By the simple act of visiting the planetarium, students of all ages open an ave ...
The-Cosmic-Perspective-Media-Update-with
... 18) Why do we have seasons on Earth? A) As Earth goes around the Sun and Earth's axis remains pointed toward Polaris, the Northern and Southern hemispheres alternately receive more and less direct sunlight. B) The tilt of Earth's axis constantly changes between 0 and 23 1/2°, giving us summer when ...
... 18) Why do we have seasons on Earth? A) As Earth goes around the Sun and Earth's axis remains pointed toward Polaris, the Northern and Southern hemispheres alternately receive more and less direct sunlight. B) The tilt of Earth's axis constantly changes between 0 and 23 1/2°, giving us summer when ...
Preview Sample 3
... varying Earth-Sun distance over the course of a year. What other fact does your friend likely know that completely contradicts this view of how the seasons are caused? Can you think of other examples of two beliefs that many people feel are both true but which completely contradict each other? How d ...
... varying Earth-Sun distance over the course of a year. What other fact does your friend likely know that completely contradicts this view of how the seasons are caused? Can you think of other examples of two beliefs that many people feel are both true but which completely contradict each other? How d ...
Sample
... varying Earth-Sun distance over the course of a year. What other fact does your friend likely know that completely contradicts this view of how the seasons are caused? Can you think of other examples of two beliefs that many people feel are both true but which completely contradict each other? How d ...
... varying Earth-Sun distance over the course of a year. What other fact does your friend likely know that completely contradicts this view of how the seasons are caused? Can you think of other examples of two beliefs that many people feel are both true but which completely contradict each other? How d ...
Scale the Universe - Crystal Ball Science
... • In colored groups - place these in order from smallest to largest. – Small on left, large on right. ...
... • In colored groups - place these in order from smallest to largest. – Small on left, large on right. ...
Ardua et Astra: On the Calculation of the Dates of the Rising and
... German mathematician and chronologist Ideler published an article comparing Ovid’s dates with those he calculated for Ovid’s time;6 he found that Ovid made a large number of errors in his dating, and since then criticism of this aspect of the poem has been common.7 More recently, however, some schol ...
... German mathematician and chronologist Ideler published an article comparing Ovid’s dates with those he calculated for Ovid’s time;6 he found that Ovid made a large number of errors in his dating, and since then criticism of this aspect of the poem has been common.7 More recently, however, some schol ...
Which planet has never been orbited or flown past by a
... Stars have a variety of obvious differences. Plus globular clusters might come in handy later this semester. Sure…I’ll start with this one, but how? Dr. C. Renee James NASA Top Stars 2010 ...
... Stars have a variety of obvious differences. Plus globular clusters might come in handy later this semester. Sure…I’ll start with this one, but how? Dr. C. Renee James NASA Top Stars 2010 ...
2Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... The Local Sky The celestial sphere provides a useful way of thinking about the appearance of the universe from Earth. But it is not what we actually see when we go outside. Instead, your local sky—the sky as seen from wherever you happen to be standing—appears to take the shape of a hemisphere or d ...
... The Local Sky The celestial sphere provides a useful way of thinking about the appearance of the universe from Earth. But it is not what we actually see when we go outside. Instead, your local sky—the sky as seen from wherever you happen to be standing—appears to take the shape of a hemisphere or d ...
Ch. 20 - Astro1010
... Once all the Galaxy is within an orbit, the Orbital Velocity should diminish with distance, as the dashed curve shows. It doesn’t; more than twice the mass of the Galaxy would have to be outside the visible part to reproduce the observed curve. This mass is called Dark Matter ...
... Once all the Galaxy is within an orbit, the Orbital Velocity should diminish with distance, as the dashed curve shows. It doesn’t; more than twice the mass of the Galaxy would have to be outside the visible part to reproduce the observed curve. This mass is called Dark Matter ...
lecture03_2013_sky_phases_eclipses
... • What is the cause of the seasons on Earth? • As the Earth orbits the sun, the tilt of the axis causes different portions of the Earth to receive more or less direct sunlight at different times of year. The two hemispheres have opposite seasons. The summer solstice is the time when the northern hem ...
... • What is the cause of the seasons on Earth? • As the Earth orbits the sun, the tilt of the axis causes different portions of the Earth to receive more or less direct sunlight at different times of year. The two hemispheres have opposite seasons. The summer solstice is the time when the northern hem ...
Proficiency Step #5--
... We tend to think of constellations as a group of related stars that form a pattern, when in fact, most of the constellations consist of stars that are not related—that is, they are varying distances from Earth and their relative positions are simply a coincidence. It might be convenient to note her ...
... We tend to think of constellations as a group of related stars that form a pattern, when in fact, most of the constellations consist of stars that are not related—that is, they are varying distances from Earth and their relative positions are simply a coincidence. It might be convenient to note her ...
r202 the new astronomy
... by Dr. Helmut Werner, completed and edited by Prof. Dr. Felix Schmeiller - Published in 1986 by “Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft” in Stuttgart - 510 pages - 21.3 x 30 cm 138.00 DM - ISBN 3-8047-0739-4 This book containing information about 2800 stars and 88 constellations is the result of an e ...
... by Dr. Helmut Werner, completed and edited by Prof. Dr. Felix Schmeiller - Published in 1986 by “Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft” in Stuttgart - 510 pages - 21.3 x 30 cm 138.00 DM - ISBN 3-8047-0739-4 This book containing information about 2800 stars and 88 constellations is the result of an e ...
The Pleiades in the Salle des Taureaux", Grotte de Lascaux
... The six stars and the Aurochs: markers of the start of spring 17300 years ago. It is highly probable that the Pleiades, Hyades and the Bull must have marked a special point at the ecliptic at the time when the cave paintings of Lascaux came into being. Such points could be the equinoxes and solstice ...
... The six stars and the Aurochs: markers of the start of spring 17300 years ago. It is highly probable that the Pleiades, Hyades and the Bull must have marked a special point at the ecliptic at the time when the cave paintings of Lascaux came into being. Such points could be the equinoxes and solstice ...
Astronomy 518 Astrometry Lecture
... • If the position of the celestial poles and equators are changing on the celestial sphere, then the celestial coordinates (α,δ ) of objects, which are defined by the reference of the celestial equator and celestial poles, are also constantly changing. • The effects are very noticeable (50.27) arc s ...
... • If the position of the celestial poles and equators are changing on the celestial sphere, then the celestial coordinates (α,δ ) of objects, which are defined by the reference of the celestial equator and celestial poles, are also constantly changing. • The effects are very noticeable (50.27) arc s ...
Archaeoastronomy

Archaeoastronomy (also spelled archeoastronomy) is the study of how people in the past ""have understood the phenomena in the sky, how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cultures."" Clive Ruggles argues it is misleading to consider archaeoastronomy to be the study of ancient astronomy, as modern astronomy is a scientific discipline, while archaeoastronomy considers symbolically rich cultural interpretations of phenomena in the sky by other cultures. It is often twinned with ethnoastronomy, the anthropological study of skywatching in contemporary societies. Archaeoastronomy is also closely associated with historical astronomy, the use of historical records of heavenly events to answer astronomical problems and the history of astronomy, which uses written records to evaluate past astronomical practice.Archaeoastronomy uses a variety of methods to uncover evidence of past practices including archaeology, anthropology, astronomy, statistics and probability, and history. Because these methods are diverse and use data from such different sources, integrating them into a coherent argument has been a long-term difficulty for archaeoastronomers. Archaeoastronomy fills complementary niches in landscape archaeology and cognitive archaeology. Material evidence and its connection to the sky can reveal how a wider landscape can be integrated into beliefs about the cycles of nature, such as Mayan astronomy and its relationship with agriculture. Other examples which have brought together ideas of cognition and landscape include studies of the cosmic order embedded in the roads of settlements.Archaeoastronomy can be applied to all cultures and all time periods. The meanings of the sky vary from culture to culture; nevertheless there are scientific methods which can be applied across cultures when examining ancient beliefs. It is perhaps the need to balance the social and scientific aspects of archaeoastronomy which led Clive Ruggles to describe it as: ""...[A] field with academic work of high quality at one end but uncontrolled speculation bordering on lunacy at the other.""