Lesson Plan - ScienceA2Z.com
... The International Astronomical Union (IAU) divides the sky into 88 official constellations with exact boundaries, so that every direction or place in the sky belongs within one constellation. In the northern hemisphere, these are mostly based upon the constellations of the ancient Greek tradition, p ...
... The International Astronomical Union (IAU) divides the sky into 88 official constellations with exact boundaries, so that every direction or place in the sky belongs within one constellation. In the northern hemisphere, these are mostly based upon the constellations of the ancient Greek tradition, p ...
History of Astronomy
... historians, and for information about the Chinese we rely upon the researches of travellers and missionaries in comparatively recent times. The testimony of the Greek writers has fortunately been confirmed, and we now have in addition a mass of facts translated from the original sculptures, papyri, ...
... historians, and for information about the Chinese we rely upon the researches of travellers and missionaries in comparatively recent times. The testimony of the Greek writers has fortunately been confirmed, and we now have in addition a mass of facts translated from the original sculptures, papyri, ...
Venus
... Named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty, Venus. (Aphrodite in Greek) Venus is a terrestrial planet, basically it's known as Earth's "sister planet" because of the similiar size, mass, and density. It's atmosphere is 96% carbon dioxide. It is the 2nd brightest object in the night sky with a ...
... Named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty, Venus. (Aphrodite in Greek) Venus is a terrestrial planet, basically it's known as Earth's "sister planet" because of the similiar size, mass, and density. It's atmosphere is 96% carbon dioxide. It is the 2nd brightest object in the night sky with a ...
Astro Concepts: Learning Underlying Physics Principles in
... emission, reflection and dark nebulae plus examples of interstellar absorption, as an astronomy context in which to introduce students to the study of the reflection, transmission and emission of light, including the fundamentals of spectroscopy. In the first module (Nebulae A), which concentrates o ...
... emission, reflection and dark nebulae plus examples of interstellar absorption, as an astronomy context in which to introduce students to the study of the reflection, transmission and emission of light, including the fundamentals of spectroscopy. In the first module (Nebulae A), which concentrates o ...
Local Horizon View
... in the night sky. All the Solar System objects - the Sun, the Moon, the other planets, asteroids, and comets have their own motion across the background of stars, so for all these objects their sky position changes hourly or daily but can be mathematically predicted. ...
... in the night sky. All the Solar System objects - the Sun, the Moon, the other planets, asteroids, and comets have their own motion across the background of stars, so for all these objects their sky position changes hourly or daily but can be mathematically predicted. ...
18 Throughout history people around the world have looked up at
... PHOTOS COURTESY OF THE AUTHORS ...
... PHOTOS COURTESY OF THE AUTHORS ...
Solutions to End-of-Chapter Problems (Chapter 2)
... misconceptions. For example, some students might wonder if you could see the galaxy “sticking up” above our own galaxy’s disk—illustrating a misconception about how angular size declines with distance. They might also wonder if a telescope would make a difference, illustrating a misconception about ...
... misconceptions. For example, some students might wonder if you could see the galaxy “sticking up” above our own galaxy’s disk—illustrating a misconception about how angular size declines with distance. They might also wonder if a telescope would make a difference, illustrating a misconception about ...
FREE Sample Here
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
... This chapter focuses on the appearance of the night sky. Many of the concepts presented were common knowledge before time became quantified on clocks and city lights blocked our nightly view of the sky. Most people today no longer have an understanding of the basic appearance or motions of the sky. ...
Lecture02: Astronomical Distance
... Ex.4a: the size of the Moon: the angular diameter (or angular size) of the Moon is 0.5° or the Moon subtends an angle of 0.5°. Ex.4b: the angular diameter of the Sun as of 2014 August 25 is about 1900”. How does it compare with the Moon? Ex.4c: the angular size of the Moon is approximately the same ...
... Ex.4a: the size of the Moon: the angular diameter (or angular size) of the Moon is 0.5° or the Moon subtends an angle of 0.5°. Ex.4b: the angular diameter of the Sun as of 2014 August 25 is about 1900”. How does it compare with the Moon? Ex.4c: the angular size of the Moon is approximately the same ...
NAME: SECTION: Mon Tue Wed Thu ASTRONOMY LAB Stellarium
... toward the South cardinal point (labeled “S”), with stars visible in the sky above the horizon. Some stars may be labeled with their common names (e.g., “Betelgeuse” is an example of such a name, but it is very unlikely that Betelgeuse will be visible in the initial view you see). Notice the status ...
... toward the South cardinal point (labeled “S”), with stars visible in the sky above the horizon. Some stars may be labeled with their common names (e.g., “Betelgeuse” is an example of such a name, but it is very unlikely that Betelgeuse will be visible in the initial view you see). Notice the status ...
ASTRONOMICAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS AND FRAMES
... obvious necessity of two others, describing the motion of a conventionally chosen intermediary axis with respect to both systems; P This axis must be naturally chosen so that: ‚ it is close to instantaneous axis of rotation, ‚ its motion in terrestrial and celestial systems is ...
... obvious necessity of two others, describing the motion of a conventionally chosen intermediary axis with respect to both systems; P This axis must be naturally chosen so that: ‚ it is close to instantaneous axis of rotation, ‚ its motion in terrestrial and celestial systems is ...
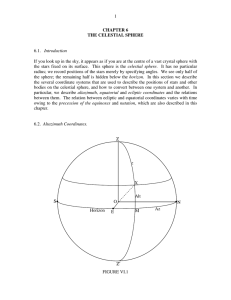
CHAPTER 6 THE CELESTIAL SPHERE
... You might possibly have noticed that, in section 2, I had not properly defined the north point of the horizon other than by saying that it was the point marked N in figure VI.1. We see now that the north and south points of the horizon are the points where the vertical circle that passes through the ...
... You might possibly have noticed that, in section 2, I had not properly defined the north point of the horizon other than by saying that it was the point marked N in figure VI.1. We see now that the north and south points of the horizon are the points where the vertical circle that passes through the ...
ASTRONOMY IN MODERN TURKEY Akdeniz University Space
... Gökmen’s work later became more astronomically oriented and continued to be so until today. Other departments, such as solar physics, radio astronomy, time measurement, seismology and geo-magnetism were developed in the years after 1925. After the Turkish Republic was founded in 1923, Fatin Gökmen ...
... Gökmen’s work later became more astronomically oriented and continued to be so until today. Other departments, such as solar physics, radio astronomy, time measurement, seismology and geo-magnetism were developed in the years after 1925. After the Turkish Republic was founded in 1923, Fatin Gökmen ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... However, he could not explain this possible relationship. Was it that of cause and effect between the two, or was there something else involved that “… gave origin to both the change of weather and the meteors?” (Olmsted 1834a, p. 402). The meteors were at their most striking in frequency and brilli ...
... However, he could not explain this possible relationship. Was it that of cause and effect between the two, or was there something else involved that “… gave origin to both the change of weather and the meteors?” (Olmsted 1834a, p. 402). The meteors were at their most striking in frequency and brilli ...
View Diary of Astronomical Events - Astronomical Society of Singapore
... meteors this year, but the Perseids are so bright and numerous that it should still be a good show. Best viewing will be from a dark location after midnight. Meteors will radiate from the constellation Perseus, but can appear anywhere in the sky. ***August 18 - Conjunction of Venus and Jupiter. Conj ...
... meteors this year, but the Perseids are so bright and numerous that it should still be a good show. Best viewing will be from a dark location after midnight. Meteors will radiate from the constellation Perseus, but can appear anywhere in the sky. ***August 18 - Conjunction of Venus and Jupiter. Conj ...
November 2015 - Denver Astronomical Society
... NASA Space Place. . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 about 14° above the horizon, and slightly closer; at ...
... NASA Space Place. . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 about 14° above the horizon, and slightly closer; at ...
Make Up Lab: Phases of Venus
... type in “Pisa,” and select Pisa, Italy as your location. However, do not set this as your default location, since you can return to ...
... type in “Pisa,” and select Pisa, Italy as your location. However, do not set this as your default location, since you can return to ...
Venus has no ozone layer
... It has a different surface then the different to the other planets Venus is very slow Venus has a molten core Venus is earths sister ...
... It has a different surface then the different to the other planets Venus is very slow Venus has a molten core Venus is earths sister ...
EarthScience_Topic 3
... Sometimes called Third Quarter. The left half of the Moon appears lighted, and the right side of the Moon appears dark. During the time between the Full Moon and the Last Quarter Moon, the part of the Moon that appears lighted gets smaller and smaller every day. It will continue to shrink until the ...
... Sometimes called Third Quarter. The left half of the Moon appears lighted, and the right side of the Moon appears dark. During the time between the Full Moon and the Last Quarter Moon, the part of the Moon that appears lighted gets smaller and smaller every day. It will continue to shrink until the ...
Stellar Evolution
... O- and B-type stars can lose a tenth of their total mass this way in only a million years These stellar winds hollow out cavities in the interstellar medium surrounding giant stars ...
... O- and B-type stars can lose a tenth of their total mass this way in only a million years These stellar winds hollow out cavities in the interstellar medium surrounding giant stars ...
April 2015 - Southern Astronomical Society
... we have long sought to unravel,” NASA spokesman John Grunsfeld said. “With the combined capabilities of these great observatories, both in extended mission, we are ever closer to understanding this cosmic phenomenon.” To determine how substantial dark matter may be, astronomers have been analysing t ...
... we have long sought to unravel,” NASA spokesman John Grunsfeld said. “With the combined capabilities of these great observatories, both in extended mission, we are ever closer to understanding this cosmic phenomenon.” To determine how substantial dark matter may be, astronomers have been analysing t ...
Damian and Jack 7K
... Core of the sun The core of the sun has a density one hundred and fifty times the density of the water on earth. The core has a temperate of 15.7 million kelvin (k) (or about 15,700,000 degrees Celsius). The inner core of the sun is basically the engine of the star and fuels the star. In the core o ...
... Core of the sun The core of the sun has a density one hundred and fifty times the density of the water on earth. The core has a temperate of 15.7 million kelvin (k) (or about 15,700,000 degrees Celsius). The inner core of the sun is basically the engine of the star and fuels the star. In the core o ...
calendars from around the world
... - Introduction All human societies have developed ways to determine the length of the year, when the year should begin, and how to divide the year into manageable units of time, such as months, weeks and days. Many systems for doing this – calendars – have been adopted throughout history. About 40 ...
... - Introduction All human societies have developed ways to determine the length of the year, when the year should begin, and how to divide the year into manageable units of time, such as months, weeks and days. Many systems for doing this – calendars – have been adopted throughout history. About 40 ...
Archaeoastronomy

Archaeoastronomy (also spelled archeoastronomy) is the study of how people in the past ""have understood the phenomena in the sky, how they used these phenomena and what role the sky played in their cultures."" Clive Ruggles argues it is misleading to consider archaeoastronomy to be the study of ancient astronomy, as modern astronomy is a scientific discipline, while archaeoastronomy considers symbolically rich cultural interpretations of phenomena in the sky by other cultures. It is often twinned with ethnoastronomy, the anthropological study of skywatching in contemporary societies. Archaeoastronomy is also closely associated with historical astronomy, the use of historical records of heavenly events to answer astronomical problems and the history of astronomy, which uses written records to evaluate past astronomical practice.Archaeoastronomy uses a variety of methods to uncover evidence of past practices including archaeology, anthropology, astronomy, statistics and probability, and history. Because these methods are diverse and use data from such different sources, integrating them into a coherent argument has been a long-term difficulty for archaeoastronomers. Archaeoastronomy fills complementary niches in landscape archaeology and cognitive archaeology. Material evidence and its connection to the sky can reveal how a wider landscape can be integrated into beliefs about the cycles of nature, such as Mayan astronomy and its relationship with agriculture. Other examples which have brought together ideas of cognition and landscape include studies of the cosmic order embedded in the roads of settlements.Archaeoastronomy can be applied to all cultures and all time periods. The meanings of the sky vary from culture to culture; nevertheless there are scientific methods which can be applied across cultures when examining ancient beliefs. It is perhaps the need to balance the social and scientific aspects of archaeoastronomy which led Clive Ruggles to describe it as: ""...[A] field with academic work of high quality at one end but uncontrolled speculation bordering on lunacy at the other.""