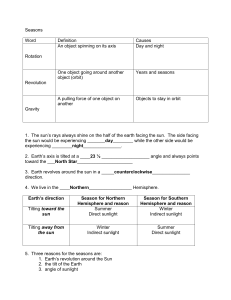
Level 6 Stars and Constellations
... If you observe a planet, say Mars, for one complete revolution, you will see that it passes successively through 12 constellations. All planets (except Pluto at certain times) can be observed only in these 12 constellations, which form the so-called zodiac, and the Sun also moves through the zodiaca ...
... If you observe a planet, say Mars, for one complete revolution, you will see that it passes successively through 12 constellations. All planets (except Pluto at certain times) can be observed only in these 12 constellations, which form the so-called zodiac, and the Sun also moves through the zodiaca ...
Homework #1 10 points Question #1 (2 pts) Even in ancient times
... Even in ancient times, astronomers knew that planets vary in brightness over the course of several months or even years. Explain, why this observation can not be used to rule out the geocentric model, in which all planets and the Sun orbit the Earth on circular orbits. Ignore the epicycles, i.e. ass ...
... Even in ancient times, astronomers knew that planets vary in brightness over the course of several months or even years. Explain, why this observation can not be used to rule out the geocentric model, in which all planets and the Sun orbit the Earth on circular orbits. Ignore the epicycles, i.e. ass ...
File
... Our universe is an amazing place. Since prehistoric days, inquisitive minds have been wondering about the celestial objects that surround our planet, and today scientists and astronauts continue that exploration. This study of celestial objects-such as the planets, stars, and moons-is called Astrono ...
... Our universe is an amazing place. Since prehistoric days, inquisitive minds have been wondering about the celestial objects that surround our planet, and today scientists and astronauts continue that exploration. This study of celestial objects-such as the planets, stars, and moons-is called Astrono ...
AstroLesson4Slides
... Can you understand why Ptolemy saw the Earth as the center of the Universe based on what you can see of the Sun, the Moon, and the stars? What major shift occurred with the Copernican view of the Universe? ...
... Can you understand why Ptolemy saw the Earth as the center of the Universe based on what you can see of the Sun, the Moon, and the stars? What major shift occurred with the Copernican view of the Universe? ...
File
... Four celestial spheres, A, B, C, and D, are depicted above. Each sphere represents a different location. Which sphere depicts the apparent motion of the sun on June 21st in New Zealand? Please explain. ...
... Four celestial spheres, A, B, C, and D, are depicted above. Each sphere represents a different location. Which sphere depicts the apparent motion of the sun on June 21st in New Zealand? Please explain. ...
Star or planet, or what?
... there was one for wandering stars (planets?), another for hairy stars (comets) and finally two lonely cages for the Sun (which was not yet recognized as a star) and the Moon (which had clear bodily markings). Modern knowledge inflation now decrees that today’s potential occupants of the planetary ca ...
... there was one for wandering stars (planets?), another for hairy stars (comets) and finally two lonely cages for the Sun (which was not yet recognized as a star) and the Moon (which had clear bodily markings). Modern knowledge inflation now decrees that today’s potential occupants of the planetary ca ...
The Egyptians through the Romans
... …that the heavens are spherical and move spherically; …that the earth, in figure, is sensibly spherical also when taken as a whole …[that the earth] in position, lies right in the middle of the heavens, like a geometrical center; …[that the earth] in magnitude and distance, has the ratio of a point ...
... …that the heavens are spherical and move spherically; …that the earth, in figure, is sensibly spherical also when taken as a whole …[that the earth] in position, lies right in the middle of the heavens, like a geometrical center; …[that the earth] in magnitude and distance, has the ratio of a point ...
The night sky - Mr. Champion
... • Chances are, at some point you have looked up during a clear night and noticed patterns and changes. • Humans have for many years speculated at what was above us. • This is the study of astronomy – what is beyond Earth. • The first would likely be the most numerous object we see – stars. ...
... • Chances are, at some point you have looked up during a clear night and noticed patterns and changes. • Humans have for many years speculated at what was above us. • This is the study of astronomy – what is beyond Earth. • The first would likely be the most numerous object we see – stars. ...
Time - Academic Computer Center
... West to East the Sun, Moon and stars all appear to move from East to West. • The Sun appears to rise in the East and set in the West because the Earth spins. • The Moon however also orbits the Earth traveling from West to East but it takes much longer than 24 hours to orbit the Earth. However from n ...
... West to East the Sun, Moon and stars all appear to move from East to West. • The Sun appears to rise in the East and set in the West because the Earth spins. • The Moon however also orbits the Earth traveling from West to East but it takes much longer than 24 hours to orbit the Earth. However from n ...
29.1 Models of the Solar System
... Cycle of Lunar Phases Takes 29.53 days This is because when moon gets back to its original position in 27.3 days, the earth has moved 1°/day or about 27°. The moon moving at l3°/day takes about 2 days to catch up with Earth and align with it and the sun in a new moon phase. ...
... Cycle of Lunar Phases Takes 29.53 days This is because when moon gets back to its original position in 27.3 days, the earth has moved 1°/day or about 27°. The moon moving at l3°/day takes about 2 days to catch up with Earth and align with it and the sun in a new moon phase. ...
The Roots of Astronomy
... explain Retrograde Motion. • Ptolemy suggests that planets orbit the Earth in a large circular orbits but also follow a small circular orbit around an imaginary point. • These small orbits were known as Epicycles ...
... explain Retrograde Motion. • Ptolemy suggests that planets orbit the Earth in a large circular orbits but also follow a small circular orbit around an imaginary point. • These small orbits were known as Epicycles ...
Georgia Travels
... • Click the yellow button below for your first word. Then, select the correct definition for the word at the top of the page. ...
... • Click the yellow button below for your first word. Then, select the correct definition for the word at the top of the page. ...
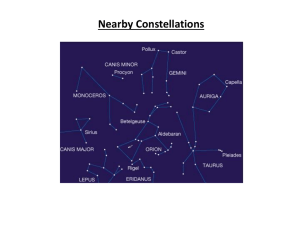
Nearby Constellations
... “Precession” of Earth’s Axis, and the temporary nature of the “North Star” . . . ...
... “Precession” of Earth’s Axis, and the temporary nature of the “North Star” . . . ...
AST 101 Lecture 8 Astronomy in the 17th and 18th Centuries
... Right Ascension within each constellation. We still use these Flamsteed designations today. (The Royal Greenwich Observatory was closed in 1998 for lack of funds, and is now a museum.) ...
... Right Ascension within each constellation. We still use these Flamsteed designations today. (The Royal Greenwich Observatory was closed in 1998 for lack of funds, and is now a museum.) ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... to explain natural phenomena, however they also relied on observations of the night sky. ...
... to explain natural phenomena, however they also relied on observations of the night sky. ...
17 th and 18 th Century Astronomy
... Right Ascension within each constellation. We still use these Flamsteed designations today. (The Royal Greenwich Observatory was closed in 1998 for lack of funds, and is now a museum.) ...
... Right Ascension within each constellation. We still use these Flamsteed designations today. (The Royal Greenwich Observatory was closed in 1998 for lack of funds, and is now a museum.) ...
02 - University of New Mexico
... Newtonian mechanics tells us that the force keeping the planets in orbit around the Sun is the gravitational force due to the masses of the planet and Sun. This allows us to calculate the mass of the Sun, knowing the orbit of the Earth: ...
... Newtonian mechanics tells us that the force keeping the planets in orbit around the Sun is the gravitational force due to the masses of the planet and Sun. This allows us to calculate the mass of the Sun, knowing the orbit of the Earth: ...
Astronomy Test Review
... 8. Why can we see some stars all year round, but others only during certain seasons? 9. Draw what the moon looks like in each of the following phases: a. Waxing crescent b. Waning gibbous c. First quarter 10. Why is it that we can see Jupiter, Mars and Saturn very well during some nights, but Venus ...
... 8. Why can we see some stars all year round, but others only during certain seasons? 9. Draw what the moon looks like in each of the following phases: a. Waxing crescent b. Waning gibbous c. First quarter 10. Why is it that we can see Jupiter, Mars and Saturn very well during some nights, but Venus ...
ASTR 1010 – Spring 2016 – Study Notes Dr. Magnani
... the Greeks were intrigued by the problem of the motions of the visible planets. The word planet in classical Greek means “wanderer” because the planets change their position with respect to the star ...
... the Greeks were intrigued by the problem of the motions of the visible planets. The word planet in classical Greek means “wanderer” because the planets change their position with respect to the star ...
Terms - HULK SCIENCE
... Full Moon New Moon Tides Inner Planets Outer Planets gravity Terrestrial Gas Giants ...
... Full Moon New Moon Tides Inner Planets Outer Planets gravity Terrestrial Gas Giants ...
Some facts and concepts to have at your fingertips.
... • Mean Earth-Sun distance (1 Astronomical Unit) = 92.9 million miles • Speed of light ≈ 300,000 km/sec ≈ 186,000 miles/sec • 1 light-year = distance light travels in a vacuum in one year • 1 parsec (“parallax of a second of arc”) = 3.26 light-years = 206265 Astronomical Units • Nearest star (after t ...
... • Mean Earth-Sun distance (1 Astronomical Unit) = 92.9 million miles • Speed of light ≈ 300,000 km/sec ≈ 186,000 miles/sec • 1 light-year = distance light travels in a vacuum in one year • 1 parsec (“parallax of a second of arc”) = 3.26 light-years = 206265 Astronomical Units • Nearest star (after t ...
Sky Science Review for Test Part A
... S.O. 1 – Recognize that the Sun and stars emit the light by which they are seen, and that most other bodies in space, including Earth’s moon, other planets and their moons, comets and asteroids, are seen by reflected light. Bodies in space that emit (give off) light- ...
... S.O. 1 – Recognize that the Sun and stars emit the light by which they are seen, and that most other bodies in space, including Earth’s moon, other planets and their moons, comets and asteroids, are seen by reflected light. Bodies in space that emit (give off) light- ...