Renaissance
... historian who wrote of the rebirth of art in Italy during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. The concept of the Renaissance was then applied more broadly to describe a dramatic rebirth of civilization in Western Europe. This view of the Renaissance involves two erroneous concepts. First, there i ...
... historian who wrote of the rebirth of art in Italy during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. The concept of the Renaissance was then applied more broadly to describe a dramatic rebirth of civilization in Western Europe. This view of the Renaissance involves two erroneous concepts. First, there i ...
A. “Re-birth” - Marshall Public Schools
... a) City-States, Communes, and Republics - each city state of Italy was ...
... a) City-States, Communes, and Republics - each city state of Italy was ...
The Italian Renaissance - Manasquan Public Schools
... rebirth of ancient Greek and Roman worlds Characteristics Secular Urban Society (City-States) Age or Recovery New view of human ability and worth ...
... rebirth of ancient Greek and Roman worlds Characteristics Secular Urban Society (City-States) Age or Recovery New view of human ability and worth ...
Italian Renaissance Art
... Therefore, the consumption of art was used as a form of competition for social & political status! ...
... Therefore, the consumption of art was used as a form of competition for social & political status! ...
HUMAN FIGURES IN SCULPTURES Changes of the human figure
... However, Raphael is mainly remembered for the beauty of his human figures, expressed to near-perfection in paintings such as ‘The Madonna del Granduca’ and ‘The Nymph Galatea’. Unlike his predecessors, Raphael painted to an ideal of beauty, rather than a realistic copying of ...
... However, Raphael is mainly remembered for the beauty of his human figures, expressed to near-perfection in paintings such as ‘The Madonna del Granduca’ and ‘The Nymph Galatea’. Unlike his predecessors, Raphael painted to an ideal of beauty, rather than a realistic copying of ...
CH35 A New Way of Thinking
... It took several years to set all the letters to make the first printed Bible, but once the pages were set, Gutenberg and twenty helpers printed out 450 Bibles in one year. If twenty monks had to write them by hand, it would have taken them 90 years each. ...
... It took several years to set all the letters to make the first printed Bible, but once the pages were set, Gutenberg and twenty helpers printed out 450 Bibles in one year. If twenty monks had to write them by hand, it would have taken them 90 years each. ...
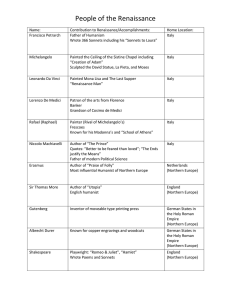
People of the Renaissance Graphic Organizer Key (1)
... Author of “The Prince” Quotes: “Better to be feared than loved”; “The Ends justify the Means” Father of modern Political Science ...
... Author of “The Prince” Quotes: “Better to be feared than loved”; “The Ends justify the Means” Father of modern Political Science ...
Brief Introduction to European Culture---
... as Plato and Aristotle (center);it is considered a masterpiece in the portrayal of the artistic ideals of the Renaissance. It also illustrates the importance of classical studies to literary and cultural achievements of the era. ...
... as Plato and Aristotle (center);it is considered a masterpiece in the portrayal of the artistic ideals of the Renaissance. It also illustrates the importance of classical studies to literary and cultural achievements of the era. ...
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
... into harmony w/Christian doctrine Italian scholars = studied the ancient world to explore its great achievements Stressed the study of grammar, rhetoric, history, & poetry (“humanities”) --- “Humanists” ...
... into harmony w/Christian doctrine Italian scholars = studied the ancient world to explore its great achievements Stressed the study of grammar, rhetoric, history, & poetry (“humanities”) --- “Humanists” ...
The Art of the Italian Renaissance
... During the Middle Ages Italy was made up of many independent city-states in northern and central Italy that played an important role in Italian politics and art during the Renaissance. Milan One of the richest cities, it controls trade through the Alps. Venice Sitting on the Adriatic, it attracts tr ...
... During the Middle Ages Italy was made up of many independent city-states in northern and central Italy that played an important role in Italian politics and art during the Renaissance. Milan One of the richest cities, it controls trade through the Alps. Venice Sitting on the Adriatic, it attracts tr ...
New Values Shaped the Renaissance: 1. Love of classical learning
... – A variety of knowledge is the ideal ...
... – A variety of knowledge is the ideal ...
Chapter 11, Lesson 2 New Ideas and Art
... • Scholars could read each others’ work and ideas spread quickly • Gutenberg’s Bible printed in 1455 • More books printed in next 50 years than in all of history to that point ...
... • Scholars could read each others’ work and ideas spread quickly • Gutenberg’s Bible printed in 1455 • More books printed in next 50 years than in all of history to that point ...
Causes of the Renaissance
... Rome • analyzed use of power, force, & Deception • How to book for future leaders Niccolo Machiavelli • Including... ...
... Rome • analyzed use of power, force, & Deception • How to book for future leaders Niccolo Machiavelli • Including... ...
Renaissance Artists
... The Natural World Renaissance painters began to pay attention to the natural world. Most medieval art had been made for churches. ...
... The Natural World Renaissance painters began to pay attention to the natural world. Most medieval art had been made for churches. ...
Renaissance - Cherokee County Schools
... art but not create it Isabella d-Este, patron of artists, wields power in Mantua ...
... art but not create it Isabella d-Este, patron of artists, wields power in Mantua ...
Machiavelli, Leonardo, Michelangelo, and Raphael
... 3. The 13-foot marble nude figure of David is beautiful without being idealized. 4. Much of David’s power and charm are derived from its ambiguity. 5. Michelangelo’s greatest vehicle of expression was the human body, a fact that conflicted with his personal religious values. 6. Michelangelo’s works ...
... 3. The 13-foot marble nude figure of David is beautiful without being idealized. 4. Much of David’s power and charm are derived from its ambiguity. 5. Michelangelo’s greatest vehicle of expression was the human body, a fact that conflicted with his personal religious values. 6. Michelangelo’s works ...
Document
... traveling between Florence and Rome, depending on who is in power and who can afford to pay him to work ...
... traveling between Florence and Rome, depending on who is in power and who can afford to pay him to work ...
Leonardo da Vinci
... Impact of the printing press: In the Middle Ages, books had been costly and education rare; only the clergy had been regular readers and owners of books. Most books had been written in Latin, considered the language of scholarship. In the Renaissance, the educated middle classes, who could now affor ...
... Impact of the printing press: In the Middle Ages, books had been costly and education rare; only the clergy had been regular readers and owners of books. Most books had been written in Latin, considered the language of scholarship. In the Renaissance, the educated middle classes, who could now affor ...
The Renaissance c. 1350-1600
... Painted the Mona Lisa & The Last Supper. Discovered how bones & muscles worked. Drew plans for early flying machines & submarines. Interested in science, engineering, music, architecture, etc. This was way ahead of his time. He was the True Renaissance Man. ...
... Painted the Mona Lisa & The Last Supper. Discovered how bones & muscles worked. Drew plans for early flying machines & submarines. Interested in science, engineering, music, architecture, etc. This was way ahead of his time. He was the True Renaissance Man. ...
Italian Renaissance
... • center of trade routes • attachment to classical (Roman) traditions • prosperous city-states • Florence, Venice, Rome ...
... • center of trade routes • attachment to classical (Roman) traditions • prosperous city-states • Florence, Venice, Rome ...
Italian Renaissance
... • center of trade routes • attachment to classical (Roman) traditions • prosperous city-states • Florence, Venice, Rome ...
... • center of trade routes • attachment to classical (Roman) traditions • prosperous city-states • Florence, Venice, Rome ...
renaissance and italy - sccoesocialstudiesresources
... courage ever royal and magnanimous; and the fame of his name so increased, that not only in his lifetime was he held in esteem, but his reputation became even greater among posterity after his death.” ...
... courage ever royal and magnanimous; and the fame of his name so increased, that not only in his lifetime was he held in esteem, but his reputation became even greater among posterity after his death.” ...
Renaissance
... you their blood, their goods, their life, and their children , as I have before said, when the necessity is remote; but when it approaches, they revolt. And the prince who has relied solely on their words, without making preparations is ruined” ...
... you their blood, their goods, their life, and their children , as I have before said, when the necessity is remote; but when it approaches, they revolt. And the prince who has relied solely on their words, without making preparations is ruined” ...
Mannerism

Mannerism is a period of European art that emerged from the later years of the Italian High Renaissance around 1520. It lasted until about 1580 in Italy, when the Baroque style began to replace it, but Northern Mannerism continued into the early 17th century.Stylistically, Mannerism encompasses a variety of approaches influenced by, and reacting to, the harmonious ideals associated with artists such as Leonardo da Vinci, Raphael, and early Michelangelo. While High Renaissance explored harmonious ideals, Mannerism wanted to go a step further. Mannerism is notable for its intellectual sophistication as well as its artificial (as opposed to naturalistic) qualities. Mannerism favours compositional tension and instability rather than the balance and clarity of earlier Renaissance painting. Mannerism in literature and music is notable for its highly florid style and intellectual sophistication.The definition of Mannerism, and the phases within it, continues to be the subject of debate among art historians. For example, some scholars have applied the label to certain early modern forms of literature (especially poetry) and music of the 16th and 17th centuries. The term is also used to refer to some late Gothic painters working in northern Europe from about 1500 to 1530, especially the Antwerp Mannerists—a group unrelated to the Italian movement. Mannerism also has been applied by analogy to the Silver Age of Latin literature.