Astro history notes 1
... Earth’s orbiting of the Sun The nearest stars are much farther away than the Greeks thought. So the parallax angles of the star are so small, that you need a telescope to observe them. ...
... Earth’s orbiting of the Sun The nearest stars are much farther away than the Greeks thought. So the parallax angles of the star are so small, that you need a telescope to observe them. ...
Spring `03 final exam study guide
... 2. Name the planets that are never seen very far from the Sun in the sky. 3. Why was Copernicus forced to use epicycles in his model? 4. Which criterion for a good model did Kepler’s model satisfy better than previous ones had? 5. The Earth is closer to the Sun in January than it is in July. During ...
... 2. Name the planets that are never seen very far from the Sun in the sky. 3. Why was Copernicus forced to use epicycles in his model? 4. Which criterion for a good model did Kepler’s model satisfy better than previous ones had? 5. The Earth is closer to the Sun in January than it is in July. During ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... "backward," westerly motion of a planet against the background stars is a consequence of • our view of a Sun-orbiting object from a constantly moving viewpoint, the orbiting Earth. • our view of the planet from a rotating object, the Earth. • the speeding up and slowing down of the planet as it move ...
... "backward," westerly motion of a planet against the background stars is a consequence of • our view of a Sun-orbiting object from a constantly moving viewpoint, the orbiting Earth. • our view of the planet from a rotating object, the Earth. • the speeding up and slowing down of the planet as it move ...
Early Astronomy
... Egyptian’s Observation of the Sun and Moon Motions. • Monitoring seasonal variation for agriculture Nile Flooded when sun rose near the star Sirius (the “Dog star”, in the Canis Major constellation; brightest star in the sky). • Link lunar and solar ‘birth’ and ‘death’ to religious festivals and an ...
... Egyptian’s Observation of the Sun and Moon Motions. • Monitoring seasonal variation for agriculture Nile Flooded when sun rose near the star Sirius (the “Dog star”, in the Canis Major constellation; brightest star in the sky). • Link lunar and solar ‘birth’ and ‘death’ to religious festivals and an ...
DOC
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) ...
... When our part of the Earth moves around so it is lit by the sun. The path an object takes around another object in space. A shape like a ball. A system of planets which revolve around a star (or sun) ...
Origin and Age of the Universe
... 36. When is the Earth closest to the Sun? This is called Perihelion. 37. When is the Earth farthest from the Sun? This is called Aphelion. 38. Define inertia: 39. ______________________ is the attractive force that exists between any two objects in the Universe. The gravitational force is proportion ...
... 36. When is the Earth closest to the Sun? This is called Perihelion. 37. When is the Earth farthest from the Sun? This is called Aphelion. 38. Define inertia: 39. ______________________ is the attractive force that exists between any two objects in the Universe. The gravitational force is proportion ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... a. Appreciate the scale of the universe and basic structure in relationship to the Big Bang theory. b. Give an historical perspective on the development of modern astronomy in conjunction with the development of Newtonian Mechanics and an understanding of gravity, as illustrated by the shift from a ...
... a. Appreciate the scale of the universe and basic structure in relationship to the Big Bang theory. b. Give an historical perspective on the development of modern astronomy in conjunction with the development of Newtonian Mechanics and an understanding of gravity, as illustrated by the shift from a ...
Homework #1 10 points Question #1 (2 pts) Even in ancient times
... Even in ancient times, astronomers knew that planets vary in brightness over the course of several months or even years. Explain, why this observation can not be used to rule out the geocentric model, in which all planets and the Sun orbit the Earth on circular orbits. Ignore the epicycles, i.e. ass ...
... Even in ancient times, astronomers knew that planets vary in brightness over the course of several months or even years. Explain, why this observation can not be used to rule out the geocentric model, in which all planets and the Sun orbit the Earth on circular orbits. Ignore the epicycles, i.e. ass ...
Solar System Unit Review - Parma City School District
... Chris wants to make a crosssection of an inner planet. Which characteristic should it have? • A. A large, solid core • B. A small, liquid core • C. A surface covered by liquid • D. A ball with a very large diameter ...
... Chris wants to make a crosssection of an inner planet. Which characteristic should it have? • A. A large, solid core • B. A small, liquid core • C. A surface covered by liquid • D. A ball with a very large diameter ...
Lecture 4, PPT version
... “Amazed, and as if astonished and stupefied, I stood still, gazing for a certain length of time with my eyes fixed intently upon it and noticing that same star placed close to the stars which antiquity attributed to Cassiopeia. When I had satisfied myself that no star of that kind had ever shone for ...
... “Amazed, and as if astonished and stupefied, I stood still, gazing for a certain length of time with my eyes fixed intently upon it and noticing that same star placed close to the stars which antiquity attributed to Cassiopeia. When I had satisfied myself that no star of that kind had ever shone for ...
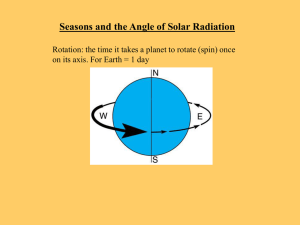
Seasons
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
... Billions of years ago, before there was life on Earth, a planet about the size of Mars smashed into us. It knocked the Earth over, so instead of rotating around an axis that is straight up and down, we are tilted by ...
Introduction Exploring the Heavens
... Massive objects actually orbit around their common center of mass; if one object is much more massive than the other, the center of mass is not far from the center of the more massive object. For objects more equal in mass, the center of mass is between the two. ...
... Massive objects actually orbit around their common center of mass; if one object is much more massive than the other, the center of mass is not far from the center of the more massive object. For objects more equal in mass, the center of mass is between the two. ...
3.2dl Apparent motion of stars
... The rotation of the Earth on its axis in an anticlockwise direction is the reason the stars track across the sky. As the axis passes close to Polaris, the Pole Star, this appears to stay in one place and the other stars move around the Pole Star. During the night, a constellation like Leo will rise ...
... The rotation of the Earth on its axis in an anticlockwise direction is the reason the stars track across the sky. As the axis passes close to Polaris, the Pole Star, this appears to stay in one place and the other stars move around the Pole Star. During the night, a constellation like Leo will rise ...
Astro history 1
... • With no street lights and no alarm clocks… • The Night sky was a great glowing question… • Who are we? (no answer yet?) • Why are we here (not clear on that one either…?) • Where are we? • Humans have been working on that one for a long time! ...
... • With no street lights and no alarm clocks… • The Night sky was a great glowing question… • Who are we? (no answer yet?) • Why are we here (not clear on that one either…?) • Where are we? • Humans have been working on that one for a long time! ...
Intro to Astronomy
... • Nicholas Copernicus with the help of Galileo proposed a model where the sun is the center of solar system. This model was not well received, but it did explain the retrograde motion better then Ptolemy’s model. • Johannes Kepler added to Copernicus’s by changing the orbital paths to elliptical ins ...
... • Nicholas Copernicus with the help of Galileo proposed a model where the sun is the center of solar system. This model was not well received, but it did explain the retrograde motion better then Ptolemy’s model. • Johannes Kepler added to Copernicus’s by changing the orbital paths to elliptical ins ...
Practice Questions: This is a series of practice tests that you should
... a. Astrology b. Geology c. Astronomy d. Cosmology 49. When scientists discus the “Big Bang’ theory of formation, they are talking about the a. Earth b. Universe c. Stars d. Galaxies 50. Which statement is today accepted as correct about the objects and their motion within the solar system? a. Aristo ...
... a. Astrology b. Geology c. Astronomy d. Cosmology 49. When scientists discus the “Big Bang’ theory of formation, they are talking about the a. Earth b. Universe c. Stars d. Galaxies 50. Which statement is today accepted as correct about the objects and their motion within the solar system? a. Aristo ...
Jeopardy - University of Nebraska–Lincoln
... of velocity by measuring the values of spectral lines (can be red-shifted or blue-shifted). ...
... of velocity by measuring the values of spectral lines (can be red-shifted or blue-shifted). ...
Celestial Mechanics
... conjunction - an elongation of 00 opposition - elongation of 1800; only superior planets quadrature - elongation of 900; only superior planets greatest elongation - only for inferior planets Model naturally explains occurrence of opposition, quadrature, and greatest elongation of various planets. Al ...
... conjunction - an elongation of 00 opposition - elongation of 1800; only superior planets quadrature - elongation of 900; only superior planets greatest elongation - only for inferior planets Model naturally explains occurrence of opposition, quadrature, and greatest elongation of various planets. Al ...
The History of Astronomy
... Overcoming the second objection (nature of motion): Galileo’s experiments showed that objects in air would stay with a moving Earth. • Aristotle thought that all objects naturally come to rest. • Galileo showed that objects will stay in motion unless a force acts to slow them down (Newton’s first l ...
... Overcoming the second objection (nature of motion): Galileo’s experiments showed that objects in air would stay with a moving Earth. • Aristotle thought that all objects naturally come to rest. • Galileo showed that objects will stay in motion unless a force acts to slow them down (Newton’s first l ...
Ancient Astronomy - Mrs. Petersen`s Earth Science
... speed of light, in mind. For example, a probe designed to land on Mars must be smart enough to handle problems in the flight on it's own without instructions from Earth. If a course change is needed during landing the probe would have to do it automatically. The delay caused by the probe requesting ...
... speed of light, in mind. For example, a probe designed to land on Mars must be smart enough to handle problems in the flight on it's own without instructions from Earth. If a course change is needed during landing the probe would have to do it automatically. The delay caused by the probe requesting ...
Do the planets orbit the Sun at constant speeds?
... theories. Scientific theories are accepted when they make testable predictions that can be verified using new observations and experiments. ...
... theories. Scientific theories are accepted when they make testable predictions that can be verified using new observations and experiments. ...
troy.edu - Center for Student Success / Student Support Services
... theories. Scientific theories are accepted when they make testable predictions that can be verified using new observations and experiments. ...
... theories. Scientific theories are accepted when they make testable predictions that can be verified using new observations and experiments. ...
Document
... theories. Scientific theories are accepted when they make testable predictions that can be verified using new observations and experiments. ...
... theories. Scientific theories are accepted when they make testable predictions that can be verified using new observations and experiments. ...
6.4 What can you see?
... small sphere to each celestial sphere to that each planet performed a loop during its circuit • Ptolemy’s model was accepted for thousands of years as it explained observations and fitted with their religious ...
... small sphere to each celestial sphere to that each planet performed a loop during its circuit • Ptolemy’s model was accepted for thousands of years as it explained observations and fitted with their religious ...
Models of the Solar System
... The Greek astronomer Aristarchus developed a heliocentric model, with the sun at the center. • His model was not accepted by most ancient Greeks. • The geocentric model could explain all observations ...
... The Greek astronomer Aristarchus developed a heliocentric model, with the sun at the center. • His model was not accepted by most ancient Greeks. • The geocentric model could explain all observations ...
Copernican heliocentrism

Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model departed from the Ptolemaic system that prevailed in Western culture for centuries, placing Earth at the center of the Universe, and is often regarded as the launching point to modern astronomy and the Scientific Revolution.Copernicus was aware that the ancient Greek Aristarchus had already proposed a heliocentric theory, and cited him as a proponent of it in a reference that was deleted before publication, but there is no evidence that Copernicus had knowledge of, or access to, the specific details of Aristarchus' theory. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so late in his life by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements causing the inaccuracies, such as the planets' circular orbits, epicycles, and uniform speeds, while at the same time re-introducing such innovations as,Earth is one of several planets revolving around a stationary Sun in a determined orderEarth has three motions: daily rotation, annual revolution, and annual tilting of its axisRetrograde motion of the planets is explained by Earth's motionDistance from Earth to the Sun is small compared to the distance to the stars.↑ 1.0 1.1 ↑