astronomy notes2013
... 1600 - Tycho Brahe realized that if the Earth was moving about the Sun, then the relative positions of the stars should change as viewed from different parts of the Earth's orbit. But there was no evidence of this shift, called parallax. Tycho was not a Copernican, but proposed a system in which the ...
... 1600 - Tycho Brahe realized that if the Earth was moving about the Sun, then the relative positions of the stars should change as viewed from different parts of the Earth's orbit. But there was no evidence of this shift, called parallax. Tycho was not a Copernican, but proposed a system in which the ...
Day-7
... Cat: An animal that was once revered as a God by the Egyptians. Cats have not forgotten this. Orbit: The path of one body (e.g. a planet) around another (e.g. the Sun in our solar system). Orbital Period: The time it takes an orbit to occur. ...
... Cat: An animal that was once revered as a God by the Egyptians. Cats have not forgotten this. Orbit: The path of one body (e.g. a planet) around another (e.g. the Sun in our solar system). Orbital Period: The time it takes an orbit to occur. ...
Know wonder sunmoonearth
... Things besides planets orbit the sun. Pluto is now a dwarf planet Because they thought it was way too small. It’s not close enough to our solar system. It takes the earth 365 to go around the sun. A new planet X. Sun is a huge star. Made out of burning gasses. The earth is an Inner core outer core a ...
... Things besides planets orbit the sun. Pluto is now a dwarf planet Because they thought it was way too small. It’s not close enough to our solar system. It takes the earth 365 to go around the sun. A new planet X. Sun is a huge star. Made out of burning gasses. The earth is an Inner core outer core a ...
Science Curriculum Map
... (A) describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, and galaxies, and use models such as the Herztsprung-Russell diagram for classification; (B) recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times clo ...
... (A) describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, and galaxies, and use models such as the Herztsprung-Russell diagram for classification; (B) recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times clo ...
The Copernican Revolution
... • "If you have two theories which both explain the observed facts then you should use the simplest until more evidence comes along“ • "The simplest explanation for some phenomenon is more likely to be accurate than more complicated explanations.“ • KISS (instructor’s editorial comment) ...
... • "If you have two theories which both explain the observed facts then you should use the simplest until more evidence comes along“ • "The simplest explanation for some phenomenon is more likely to be accurate than more complicated explanations.“ • KISS (instructor’s editorial comment) ...
Planet Questions
... __________________1. The main component of the atmosphere of Venus is ? __________________2. The longest day is on the planet ? __________________3. The mean distance from the earth to the sun is called a ? __________________4. The longest year is on the planet ? __________________5. The largest pla ...
... __________________1. The main component of the atmosphere of Venus is ? __________________2. The longest day is on the planet ? __________________3. The mean distance from the earth to the sun is called a ? __________________4. The longest year is on the planet ? __________________5. The largest pla ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 5 - 9th Edition 2. Pluto is most
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
... snow line, these could remain frozen solid, allowing them to survive. This marks the difference between rock-and-metal objects (terrestrial planets and asteroids) and objects which have in addition volatile substances (giant planets and comet nuclei). 17. What if Earth had a highly elliptical orbit ...
exam_review_space
... 5. The ________________________ consists of our Sun and all the objects that travel around it. 6. Planets or moons that do not emit their own light are called _________________. 7. A _________________ is matter that emits huge amounts of energy. 8. A _____________________ is matter, generally spheri ...
... 5. The ________________________ consists of our Sun and all the objects that travel around it. 6. Planets or moons that do not emit their own light are called _________________. 7. A _________________ is matter that emits huge amounts of energy. 8. A _____________________ is matter, generally spheri ...
The Egyptians through the Romans
... …that the heavens are spherical and move spherically; …that the earth, in figure, is sensibly spherical also when taken as a whole …[that the earth] in position, lies right in the middle of the heavens, like a geometrical center; …[that the earth] in magnitude and distance, has the ratio of a point ...
... …that the heavens are spherical and move spherically; …that the earth, in figure, is sensibly spherical also when taken as a whole …[that the earth] in position, lies right in the middle of the heavens, like a geometrical center; …[that the earth] in magnitude and distance, has the ratio of a point ...
ScienceHelpNotes-UnitE1 - JA Williams High School
... Comets are also found travelling in the solar system. They are made up of dust and ice. The sun’s heat causes the ice to vaporize and leave a trail of visible gases. Halley’s comet orbits the sun; therefore, it has a predictable schedule and becomes visible every 76 years. ...
... Comets are also found travelling in the solar system. They are made up of dust and ice. The sun’s heat causes the ice to vaporize and leave a trail of visible gases. Halley’s comet orbits the sun; therefore, it has a predictable schedule and becomes visible every 76 years. ...
Chapter 1 Periods of Western Astronomy Prehistoric Astronomy
... • Through the use of models and observations, they were the first to use a careful and systematic manner to explain the workings of the heavens • Limited to naked-eye observations, their idea of using logic and mathematics as tools for investigating nature is still with us today • Their investigativ ...
... • Through the use of models and observations, they were the first to use a careful and systematic manner to explain the workings of the heavens • Limited to naked-eye observations, their idea of using logic and mathematics as tools for investigating nature is still with us today • Their investigativ ...
Apparent Motions of Celestial Objects
... Throughout human history, ancient civilizations and modern science have sought to explain the “apparent motions of celestial objects in the sky. The geocentric model places the Earth as a stationary body at the center of the universe – with most celestial objects revolving around it. ...
... Throughout human history, ancient civilizations and modern science have sought to explain the “apparent motions of celestial objects in the sky. The geocentric model places the Earth as a stationary body at the center of the universe – with most celestial objects revolving around it. ...
Only Thirty Questions To Go (150,000 points) 1.) If the distance
... comment in class about using the HST to find parallax of distance objects. ...
... comment in class about using the HST to find parallax of distance objects. ...
February 6
... of the Sun's apparent path (the ecliptic), that includes the apparent paths of the Moon and the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. ...
... of the Sun's apparent path (the ecliptic), that includes the apparent paths of the Moon and the planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. ...
Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015
... • Know and use the concepts of magnitude, parallax and proper motion in stellar astronomy • Describe the Galaxy as a collection of stars and their distribution in type and position • Describe the current state of planets and smaller bodies in our own Solar System, including internal structure, atmos ...
... • Know and use the concepts of magnitude, parallax and proper motion in stellar astronomy • Describe the Galaxy as a collection of stars and their distribution in type and position • Describe the current state of planets and smaller bodies in our own Solar System, including internal structure, atmos ...
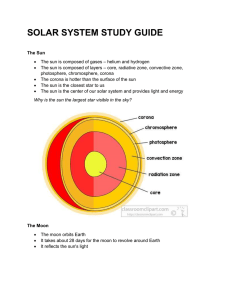
solar system study guide
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
... The sun is composed of layers – core, radiative zone, convective zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona The corona is hotter than the surface of the sun The sun is the closest star to us The sun is the center of our solar system and provides light and energy ...
Navigating by the Stars
... that the planets, Moon, and Sun all orbited around the Earth. Then in 1543, Nicolaus Copernicus proposed the idea that the planets and the Earth orbited around the Sun. However, Copernicus' new theory was no better at predicting the positions of the planets in the sky than the olderEarthcentered the ...
... that the planets, Moon, and Sun all orbited around the Earth. Then in 1543, Nicolaus Copernicus proposed the idea that the planets and the Earth orbited around the Sun. However, Copernicus' new theory was no better at predicting the positions of the planets in the sky than the olderEarthcentered the ...
Chapter 1 The Copernican Revolution
... motion, the period and relative distance to the Sun (In AU ) but it doesn’t tell us about the actual size of the orbit (in kilometers). How many kilometers is one AU? How we can determine that? The modern method to determine the actual distances in the solar system is RADAR (Acronym for RAdio Detect ...
... motion, the period and relative distance to the Sun (In AU ) but it doesn’t tell us about the actual size of the orbit (in kilometers). How many kilometers is one AU? How we can determine that? The modern method to determine the actual distances in the solar system is RADAR (Acronym for RAdio Detect ...
hw1
... What makes a theory “scientific?” Scientific theory starts off with a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a conjecture used to describe and predict some observable phenomenon. Extensive tests are carried out to measure the validity of any hypothesis. When the evidence in favor of the hypothesis is overwhelm ...
... What makes a theory “scientific?” Scientific theory starts off with a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a conjecture used to describe and predict some observable phenomenon. Extensive tests are carried out to measure the validity of any hypothesis. When the evidence in favor of the hypothesis is overwhelm ...
File - Miss S. Harvey
... Earth-centred; refers to the Earth-centred model of the universe, Geocentric which places a motionless Earth at the centre with all the planets and stars at fixed positions within eight concentric spheres that spin in circles called orbits Sun-centred; refers to the Sun-centred model of our solar sy ...
... Earth-centred; refers to the Earth-centred model of the universe, Geocentric which places a motionless Earth at the centre with all the planets and stars at fixed positions within eight concentric spheres that spin in circles called orbits Sun-centred; refers to the Sun-centred model of our solar sy ...
day04
... Once the telescope was used to observe Venus, the geocentric theory could not explain the phases of Venus. The heliocentric theory of Copernicus explained many of Galileo’s observations, but also used circular orbits. More accurate measurements did not agree with the simple theory of Copernicus (cir ...
... Once the telescope was used to observe Venus, the geocentric theory could not explain the phases of Venus. The heliocentric theory of Copernicus explained many of Galileo’s observations, but also used circular orbits. More accurate measurements did not agree with the simple theory of Copernicus (cir ...
Lecture on Planetary Configurations
... The angle between the Sun and an inferior planet as seen from Earth At Maximum Elongation, the planet reflects the most amount of sunlight, appears at its brightest ...
... The angle between the Sun and an inferior planet as seen from Earth At Maximum Elongation, the planet reflects the most amount of sunlight, appears at its brightest ...
Copernican heliocentrism

Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model departed from the Ptolemaic system that prevailed in Western culture for centuries, placing Earth at the center of the Universe, and is often regarded as the launching point to modern astronomy and the Scientific Revolution.Copernicus was aware that the ancient Greek Aristarchus had already proposed a heliocentric theory, and cited him as a proponent of it in a reference that was deleted before publication, but there is no evidence that Copernicus had knowledge of, or access to, the specific details of Aristarchus' theory. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so late in his life by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements causing the inaccuracies, such as the planets' circular orbits, epicycles, and uniform speeds, while at the same time re-introducing such innovations as,Earth is one of several planets revolving around a stationary Sun in a determined orderEarth has three motions: daily rotation, annual revolution, and annual tilting of its axisRetrograde motion of the planets is explained by Earth's motionDistance from Earth to the Sun is small compared to the distance to the stars.↑ 1.0 1.1 ↑














![Sun, Stars and Planets [Level 2] 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007097773_1-15996a23762c2249db404131f50612f3-300x300.png)