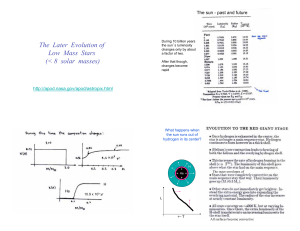
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
... The C-O core is degenerate and transports its radiation by conduction. ...
Chapter 4 Practice Questions
... a) a planet that once orbited the Sun but later was destroyed. b) ancient material from the formation of the solar system. c) a collision between Jupiter and one of its larger moons. d) comets that were trapped by Jupiter’s gravitational field. ...
... a) a planet that once orbited the Sun but later was destroyed. b) ancient material from the formation of the solar system. c) a collision between Jupiter and one of its larger moons. d) comets that were trapped by Jupiter’s gravitational field. ...
Question 1
... • Galileo Galilei found evidence that supported the ideas of Copernicus. • He observed that Venus went through phases like the Moon’s. • He also saw moons in orbit around Jupiter. ...
... • Galileo Galilei found evidence that supported the ideas of Copernicus. • He observed that Venus went through phases like the Moon’s. • He also saw moons in orbit around Jupiter. ...
The Lifecycle of the Stars
... *white dwarfs may only be the size of the earth, but it has the mass equal to half oh the sun. *it is the 6th stage in forming a star. Lifecycle of a star notes *also called a degenerate dwarf *it is a small star made up of electron-degenerate matter. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_dwarf ...
... *white dwarfs may only be the size of the earth, but it has the mass equal to half oh the sun. *it is the 6th stage in forming a star. Lifecycle of a star notes *also called a degenerate dwarf *it is a small star made up of electron-degenerate matter. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_dwarf ...
3/r -- this talks about the surface area vs the volume of a planet
... Light emitted from an object moving perpendicular to your line-ofsight will not change its wavelength. Change in wavelength / wavelength = V/C - doppler effect formula all planets orbit in the same direction around the sun and rotate in the same direction that they orbit. moons and satellites orbit ...
... Light emitted from an object moving perpendicular to your line-ofsight will not change its wavelength. Change in wavelength / wavelength = V/C - doppler effect formula all planets orbit in the same direction around the sun and rotate in the same direction that they orbit. moons and satellites orbit ...
Death of Stars notes
... • The SOFIA finding demonstrates that supernovas not only produce dust, but that the dust can survive the explosion to become raw material for the formation of other stars—and planets. • This result supports the notion that most of the dust observed in distant young galaxies may have been made by su ...
... • The SOFIA finding demonstrates that supernovas not only produce dust, but that the dust can survive the explosion to become raw material for the formation of other stars—and planets. • This result supports the notion that most of the dust observed in distant young galaxies may have been made by su ...
Chapter 12
... They emit line radiation (hot, low pressure gas) but in size they are much smaller than the emission nebulae (HII regions) ...
... They emit line radiation (hot, low pressure gas) but in size they are much smaller than the emission nebulae (HII regions) ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... Mass is the fundamental property of stars that determines their evolution because mass sets the central pressure, temperature and density that controls the fusion rates and fusion rates determine luminosity, and lifetime. 2. Why do massive stars last for a short time as main sequence stars but low-m ...
... Mass is the fundamental property of stars that determines their evolution because mass sets the central pressure, temperature and density that controls the fusion rates and fusion rates determine luminosity, and lifetime. 2. Why do massive stars last for a short time as main sequence stars but low-m ...
19. Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning
... associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or gas clouds against distance from the center of the galaxy. If most of the galaxy’s mass were concentrated toward the center, orbital speed would decline as distance from ...
... associated with our galaxy extends to large distances from the center. A rotation curve is a plot of the orbital speed of stars or gas clouds against distance from the center of the galaxy. If most of the galaxy’s mass were concentrated toward the center, orbital speed would decline as distance from ...
Lect15-3-23-11-stars..
... We are not sure where the star formation story ends on the low mass end of the scale. As very low mass protostars (say, below 0.08 solar masses) contract under gravity, we believe that a bizarre physical phenomenon h called ll d degeneracy d pressure would ld halt h lt the th collapse before efficie ...
... We are not sure where the star formation story ends on the low mass end of the scale. As very low mass protostars (say, below 0.08 solar masses) contract under gravity, we believe that a bizarre physical phenomenon h called ll d degeneracy d pressure would ld halt h lt the th collapse before efficie ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... low in metals and were thus formed when the Galaxy was young and less highly evolved. ...
... low in metals and were thus formed when the Galaxy was young and less highly evolved. ...
Ia 超新星的
... outer layers into space at the final stages of evolution. The mass of a remaining WD is always less than the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 Msun, above which a hydrostatic equilibrium of degenerate matter is impossible. ...
... outer layers into space at the final stages of evolution. The mass of a remaining WD is always less than the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 Msun, above which a hydrostatic equilibrium of degenerate matter is impossible. ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B PMS star
... is a fit to a Kurucz model (Kurucz 1979, 1993) based on an iterative procedure, with fixed parameters Teff = 13, 000 K, log g = 3.5, d = 1.98 kpc and RV = 3.3 (an effective value resulting from interstellar and local extinction). This yields independent best-fit values of AV = 6.1 ± 0.6 mag and R ? ...
... is a fit to a Kurucz model (Kurucz 1979, 1993) based on an iterative procedure, with fixed parameters Teff = 13, 000 K, log g = 3.5, d = 1.98 kpc and RV = 3.3 (an effective value resulting from interstellar and local extinction). This yields independent best-fit values of AV = 6.1 ± 0.6 mag and R ? ...
The Planetarium Fleischmann Planetarium
... LEFT: A visible-light image of a debris disk around the red dwarf star AU Microscopii. Planets may be forming, or might already exist, within it. The disk glows in starlight reflected by tiny grains of dust created by the collisions of asteroids and comets. Because it is composed of the pulverized r ...
... LEFT: A visible-light image of a debris disk around the red dwarf star AU Microscopii. Planets may be forming, or might already exist, within it. The disk glows in starlight reflected by tiny grains of dust created by the collisions of asteroids and comets. Because it is composed of the pulverized r ...
Workbook I
... months. Comets appear to be bright balls with fat tails. They do not fall rapidly in the sky; you would have to watch one for hours or days to see its movement. The center of a comet is a ball of frozen gas, dust, and water. Like planets or moons, comets orbit around the Sun. The comet that causes ...
... months. Comets appear to be bright balls with fat tails. They do not fall rapidly in the sky; you would have to watch one for hours or days to see its movement. The center of a comet is a ball of frozen gas, dust, and water. Like planets or moons, comets orbit around the Sun. The comet that causes ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
Life Histories Stars
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
... “histories” with the rest of the class. What do they notice about the life span of massive stars compared to the life spans of less massive stars? Since the age of the universe is about 15 billion years, what does this say about the kind of stars most likely to have remained from the beginnings of t ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... each other and fuse. So even though larger stars have more hydrogen reserves, they fuse hydrogen into helium at a much higher rate. This explains why large stars don’t spend much time as main sequence stars (compared to smaller stars). Finally, large stars have quick and explosive deaths compared to ...
... each other and fuse. So even though larger stars have more hydrogen reserves, they fuse hydrogen into helium at a much higher rate. This explains why large stars don’t spend much time as main sequence stars (compared to smaller stars). Finally, large stars have quick and explosive deaths compared to ...
Inner Solar System Material Discovered in the Oort Cloud
... migration, the giant planets scattered inner solar system material outward; during their outward migration they implanted a significant amount of icy planetesimals from 3.5-‐13 AU into the in ...
... migration, the giant planets scattered inner solar system material outward; during their outward migration they implanted a significant amount of icy planetesimals from 3.5-‐13 AU into the in ...
Secular Increase of the Astronomical Unit: a Possible Explanation in
... only in the inner-planets region, the decrease in the rotational angular momentum of the Sun has a sufficient contribution to the secular increase of the orbital radius. Then, as an answer to the question “why is AU increasing?”, we propose one possibility: namely “because the Sun is losing its angu ...
... only in the inner-planets region, the decrease in the rotational angular momentum of the Sun has a sufficient contribution to the secular increase of the orbital radius. Then, as an answer to the question “why is AU increasing?”, we propose one possibility: namely “because the Sun is losing its angu ...























