PPT Format of Slides
... Conservation of angular momentum says that product of radius and rotation rate must be constant ...
... Conservation of angular momentum says that product of radius and rotation rate must be constant ...
ph507-16-1exo3
... major axis < 0.07 AU have low e. This is similar to binary stars, and is likely due to tidal circularization. About 10% of the planets found so far have an eccentricity of nearly 0. About 15% have an eccentricity smaller than Earth's, and over 25% have an eccentricity smaller than Jupiter's. 45% are ...
... major axis < 0.07 AU have low e. This is similar to binary stars, and is likely due to tidal circularization. About 10% of the planets found so far have an eccentricity of nearly 0. About 15% have an eccentricity smaller than Earth's, and over 25% have an eccentricity smaller than Jupiter's. 45% are ...
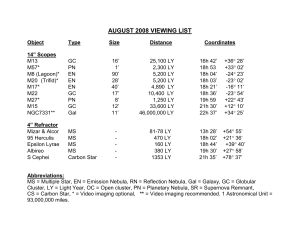
August
... Mizar & Alcor This pair in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh, MAY-jer) is a visual double. However, Mizar takes its place in the celestial hall of fame as the first known Binary Star, one that consists of a pair of gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. Found to be double in 1650, t ...
... Mizar & Alcor This pair in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh, MAY-jer) is a visual double. However, Mizar takes its place in the celestial hall of fame as the first known Binary Star, one that consists of a pair of gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. Found to be double in 1650, t ...
Why is there a main sequence?
... fly-ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). ...
... fly-ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). ...
Planetary Nebula
... Low Mass StarsIf a Star has a mass of less then 4 stellar masses, then the Star will become a Red Giant when it has used most of its Hydrogen in the process of nuclear fusion. This Red Giant will lose its mass by gently ejecting its outer layers to form a Planetary Nebula. There are between 20,000 ...
... Low Mass StarsIf a Star has a mass of less then 4 stellar masses, then the Star will become a Red Giant when it has used most of its Hydrogen in the process of nuclear fusion. This Red Giant will lose its mass by gently ejecting its outer layers to form a Planetary Nebula. There are between 20,000 ...
Synthetic color-magnitude diagrams: the ingredients
... at time t = 0, no metals were present; hence Z(0) = 0. – The galaxy did not contain any stars at the time of its birth, so that all baryonic matter was in the form of gas. – In addition, we consider the galaxy as a closed system out of which no matter can escape or be added later on by processes o ...
... at time t = 0, no metals were present; hence Z(0) = 0. – The galaxy did not contain any stars at the time of its birth, so that all baryonic matter was in the form of gas. – In addition, we consider the galaxy as a closed system out of which no matter can escape or be added later on by processes o ...
October 2011
... blowing off material at a rapid rate, perhaps one solar mass every 10,000 years. They are much more massive than the Sunlike stars that form planetary nebulae. During the middle of the night we looked at planets and one former planet. No, not that former planet. We looked at Ceres, ...
... blowing off material at a rapid rate, perhaps one solar mass every 10,000 years. They are much more massive than the Sunlike stars that form planetary nebulae. During the middle of the night we looked at planets and one former planet. No, not that former planet. We looked at Ceres, ...
The Formation and Evolution of the Milky Way
... The most metal-poor star ever observed in our galaxy is located in the halo. It is old and has a metallicity [Fe/H] of about -4.0, or about 10,000 times less than the Sun! That it happens to be an ancient star is not a coincidence. When it was born the stellar chemical factories were only just begin ...
... The most metal-poor star ever observed in our galaxy is located in the halo. It is old and has a metallicity [Fe/H] of about -4.0, or about 10,000 times less than the Sun! That it happens to be an ancient star is not a coincidence. When it was born the stellar chemical factories were only just begin ...
The Solar System
... galaxy. The Sun is a yellow dwarf star, which means it is a medium size star. It is believed to be over 4 billion years old. The Sun spins slowly on its axis as it moves around the galaxy. Because the Sun is so massive, it exerts a powerful gravitational pull on everything in our solar system. It is ...
... galaxy. The Sun is a yellow dwarf star, which means it is a medium size star. It is believed to be over 4 billion years old. The Sun spins slowly on its axis as it moves around the galaxy. Because the Sun is so massive, it exerts a powerful gravitational pull on everything in our solar system. It is ...
Star - Astrophysics
... around the forming star,potentially detectable as an infra-red source. We may also observe bipolar molecular outflows from young stellar objects (YSOs). Denser knots in these outflows are called Herbig-Haro objects. Once the surrounding gas and dust is burned off we see a T Tauri star. [Fig. 59:Infr ...
... around the forming star,potentially detectable as an infra-red source. We may also observe bipolar molecular outflows from young stellar objects (YSOs). Denser knots in these outflows are called Herbig-Haro objects. Once the surrounding gas and dust is burned off we see a T Tauri star. [Fig. 59:Infr ...
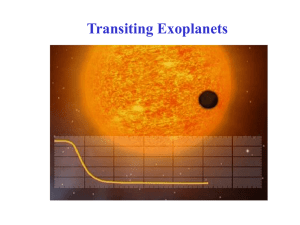
Timing Detection of Eclipsing Binary Planets and Transiting
... essentially independent of the inclination to the line-of-sight of the displacing moon's orbit. Conclusions Within the past decade over 100 extrasolar planetary systems have been discovered but, as of this date, none have been found in circum-binary orbits. The eclipsing binary timing method may be ...
... essentially independent of the inclination to the line-of-sight of the displacing moon's orbit. Conclusions Within the past decade over 100 extrasolar planetary systems have been discovered but, as of this date, none have been found in circum-binary orbits. The eclipsing binary timing method may be ...
The life cycle of the Sun – HR Diagram
... dense electrons become degenerate electron gas (no longer obey perfect gas law and pressure does not increase with temperature) . High thermal conductivity of degenerate electron gas allows burning to spread quickly through the core. The increase in temperature does not cause an increase in pressure ...
... dense electrons become degenerate electron gas (no longer obey perfect gas law and pressure does not increase with temperature) . High thermal conductivity of degenerate electron gas allows burning to spread quickly through the core. The increase in temperature does not cause an increase in pressure ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • There is an open house at the Observatory every Thursday when it’s clear. Students should check the observatory website before going since the times may change as the semester progresses and the telescope may be down for repairs at times. The website is ...
... • There is an open house at the Observatory every Thursday when it’s clear. Students should check the observatory website before going since the times may change as the semester progresses and the telescope may be down for repairs at times. The website is ...
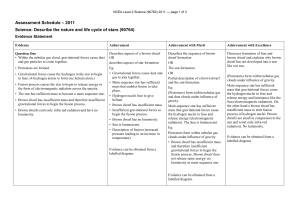
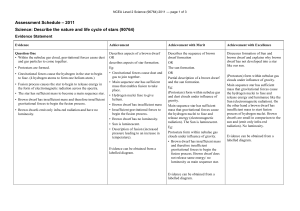
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... • Protostars are formed. • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to beco ...
... • Protostars are formed. • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to beco ...
Life on the Main Sequence + Expansion to Red Giant
... Guidepost Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main sequence and their old age as they swell to become giant stars. Here you will answer four essential questions: • Why is there ...
... Guidepost Stars form from the interstellar medium and reach stability fusing hydrogen in their cores. This chapter is about the long, stable middle age of stars on the main sequence and their old age as they swell to become giant stars. Here you will answer four essential questions: • Why is there ...
The Earth in Context: Universe and Solar System
... smallest white dwarfs = most massive, results from large gravitation field, resulting in collaps of star and nuclear compression into very small body i) i.e. the more mass the more gravity the more compression ...
... smallest white dwarfs = most massive, results from large gravitation field, resulting in collaps of star and nuclear compression into very small body i) i.e. the more mass the more gravity the more compression ...
Assessment Schedule
... • Protostars are formed. • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to beco ...
... • Protostars are formed. • Gravitational forces cause the hydrogen in the star to begin to fuse. (4 hydrogen atoms to form one helium atom.) • Fusion process causes the star to begin to release energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation across the spectra. • The star has sufficient mass to beco ...
TMSP Stellar Evolution & Life
... b. Cooler or less dense gas i. looking directly at the light source (produces a bright coloured line against a black background; this is called an emission spectrum) How does this happen? •Each of the absorption and emission spectra are produced by specific energies (wavelengths) of light interacti ...
... b. Cooler or less dense gas i. looking directly at the light source (produces a bright coloured line against a black background; this is called an emission spectrum) How does this happen? •Each of the absorption and emission spectra are produced by specific energies (wavelengths) of light interacti ...