Know Your Neurons: How to Classify Different Types of Neurons in
... sensory organs—from the eyes, nose, tongue and skin, for example. Motor neurons carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles. Interneurons connect one neuron to another: the long axons of projection interneuons link distant brain regions; the shorter axons of local interneurons form small ...
... sensory organs—from the eyes, nose, tongue and skin, for example. Motor neurons carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles. Interneurons connect one neuron to another: the long axons of projection interneuons link distant brain regions; the shorter axons of local interneurons form small ...
“The Physiology of Excitable Cells”
... motion of 26 potassium ions and 26 chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive with respect to outside. The motion of each ion during each discrete time step is determined by, first, the net elec ...
... motion of 26 potassium ions and 26 chloride ions interacting through the intermolecular potential. Here we apply a potential difference across the channel such that inside is positive with respect to outside. The motion of each ion during each discrete time step is determined by, first, the net elec ...
Notes – Neurons and the nervous system
... At rest, the fluid inside a neuron has an excess of negatively charged ions. i.e. a negative resting potential When a neuron is in its resting state, sodium channels are blocked, thus keeping excess positive ions out of the cell. When a nearby neuron fires an action potential, this triggers so ...
... At rest, the fluid inside a neuron has an excess of negatively charged ions. i.e. a negative resting potential When a neuron is in its resting state, sodium channels are blocked, thus keeping excess positive ions out of the cell. When a nearby neuron fires an action potential, this triggers so ...
M.learning.hccs.edu
... introduced into the bloodstream cannot directly affect the neurons of the CNS because A) oligodendrocytes form a continuous myelin sheath around the axons. B) the endothelium of CNS capillaries forms a blood-brain barrier. C) the neurolemma is impermeable to most molecules. D) ependymal cells restri ...
... introduced into the bloodstream cannot directly affect the neurons of the CNS because A) oligodendrocytes form a continuous myelin sheath around the axons. B) the endothelium of CNS capillaries forms a blood-brain barrier. C) the neurolemma is impermeable to most molecules. D) ependymal cells restri ...
sensory overload - Saint Michael`s College
... that can lead to irreversible hearing loss after only a few minutes of exposure. Neurons can’t cope with this kind of excessive excitation. Unlike muscle tissue, they have no energy reserves or alternative energy resources. In many human-made environments, such as cinemas, rock concerts, or dance cl ...
... that can lead to irreversible hearing loss after only a few minutes of exposure. Neurons can’t cope with this kind of excessive excitation. Unlike muscle tissue, they have no energy reserves or alternative energy resources. In many human-made environments, such as cinemas, rock concerts, or dance cl ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... Membrane Potentials Act as Signals • Neurons use changes in their membrane potential as communication signals for receiving, integrating and sending information • A change in membrane potential can be caused by anything that: – Alters ion concentrations on the two sides of the membrane – Changes mem ...
... Membrane Potentials Act as Signals • Neurons use changes in their membrane potential as communication signals for receiving, integrating and sending information • A change in membrane potential can be caused by anything that: – Alters ion concentrations on the two sides of the membrane – Changes mem ...
Slide ()
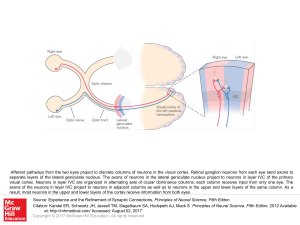
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
Unit 4 – Coordination Reflex Arc
... – Damage to developing oligodendrocytes usually during infancy – Mutations, lack of oxygen, interruption of blood flow – Treatment of symptoms, no cure ...
... – Damage to developing oligodendrocytes usually during infancy – Mutations, lack of oxygen, interruption of blood flow – Treatment of symptoms, no cure ...
At the crossroads of metabolism and reproduction in the brain
... powerful stimulatory effect on puberty (thus anatomically distinct from the satiety-inducing actions of leptin, which are relayed through other hypothalamic nuclei). The neuronal properties, network behaviour and transmitter identity of the reproduction-regulating PMv neurons remain elusive, however ...
... powerful stimulatory effect on puberty (thus anatomically distinct from the satiety-inducing actions of leptin, which are relayed through other hypothalamic nuclei). The neuronal properties, network behaviour and transmitter identity of the reproduction-regulating PMv neurons remain elusive, however ...
Candy Neurons Activity
... Lay out candy ahead of time along with computer paper to allow for a semi-clean surface. We all know that high school desks never really get washed. Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of ...
... Lay out candy ahead of time along with computer paper to allow for a semi-clean surface. We all know that high school desks never really get washed. Students work in pairs of two to create their candy neurons. They must be labeled and contain all key parts. Once they are done they must link of ...
Introduction to Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (and what it`s for).
... "organelles", as other cells in the body. •Nucleus - Contains genetic material (chromosomes) including information for cell development and synthesis of proteins necessary for cell maintenance and survival. Covered by a membrane. •Nucleolus - Produces ribosomes necessary for translation of genetic i ...
... "organelles", as other cells in the body. •Nucleus - Contains genetic material (chromosomes) including information for cell development and synthesis of proteins necessary for cell maintenance and survival. Covered by a membrane. •Nucleolus - Produces ribosomes necessary for translation of genetic i ...
VII. The Nervous System
... gates triggering depolarization c) Inhibitory postsynaptic Potential (IPSP) are caused by neurotransmitters which open K+ or Cl- gates causing hyperpolarization d) A single EPSP is rarely strong enough to trigger an action potential, although and additive effect, summation, from several terminals ca ...
... gates triggering depolarization c) Inhibitory postsynaptic Potential (IPSP) are caused by neurotransmitters which open K+ or Cl- gates causing hyperpolarization d) A single EPSP is rarely strong enough to trigger an action potential, although and additive effect, summation, from several terminals ca ...
Nervous System Part 1
... arising from cell bodies, commonly found in the CNS. 2. Bipolar neurons have a single axon and a single dendrite extending from opposite sides of the cell body, found only in eyes, nose, and ears 3. Unipolar neurons are found in ganglia outside the CNS and have one axon that divides; the peripheral ...
... arising from cell bodies, commonly found in the CNS. 2. Bipolar neurons have a single axon and a single dendrite extending from opposite sides of the cell body, found only in eyes, nose, and ears 3. Unipolar neurons are found in ganglia outside the CNS and have one axon that divides; the peripheral ...
Nervous tissues (NS)
... neurotransmitter. The neuron whose axon release the neurotransmitter is the presynaptic neuron, the neuron that receives the neurotransmitter is the postsynaptic neuron. Atypical synapse consist of the presynaptic knob of an axon separated from the postsynaptic region of adendrite or nerve cell body ...
... neurotransmitter. The neuron whose axon release the neurotransmitter is the presynaptic neuron, the neuron that receives the neurotransmitter is the postsynaptic neuron. Atypical synapse consist of the presynaptic knob of an axon separated from the postsynaptic region of adendrite or nerve cell body ...
Slide ()
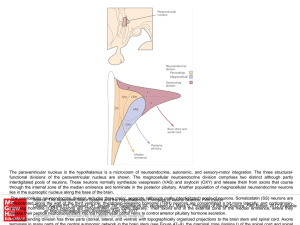
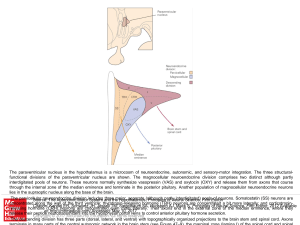
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Slide ()
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and ...
... dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and ...
PNS and Transmission
... • Sympathetic: most arise from the lower thoracic or lumbar region. Highly involved in the fight or flight reflex. • Parasympathetic: Craniosacral; promotes all the internal responses we associated with a relaxed state. • Commonalities: 1) they function automatically and usually involuntary, 2) they ...
... • Sympathetic: most arise from the lower thoracic or lumbar region. Highly involved in the fight or flight reflex. • Parasympathetic: Craniosacral; promotes all the internal responses we associated with a relaxed state. • Commonalities: 1) they function automatically and usually involuntary, 2) they ...
Module 04
... other nearby neurons for much the same reason that people live in cities—it is easier to have brief, quick interactions with other people when they are nearby. Learning occurs as feedback builds and strengthens these neural connections (neurons that fire together wire together). . . . information hi ...
... other nearby neurons for much the same reason that people live in cities—it is easier to have brief, quick interactions with other people when they are nearby. Learning occurs as feedback builds and strengthens these neural connections (neurons that fire together wire together). . . . information hi ...
Chapter 3
... • Guided by radial glial cells • Glycoproteins allow neurons to bind to other neurons or radial glial cells (a handhold). • Failures of the adequate production of glycoproteins may lead to behavioral deficits. • Cell migration dysfunction is implicated in schizophrenia where abnormal distributions o ...
... • Guided by radial glial cells • Glycoproteins allow neurons to bind to other neurons or radial glial cells (a handhold). • Failures of the adequate production of glycoproteins may lead to behavioral deficits. • Cell migration dysfunction is implicated in schizophrenia where abnormal distributions o ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 05 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System
... Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...
... Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...