Simulation of Stroke-related Damage in Cultured Human Nerve Cells
... ischaemia, the animal is allowed to recover for some time, then is sacrificed and the brain damage studied in detail. In such studies, the bioavailability of a potential drug, its pharmacokinetics, effects on blood pressure, body temperature and motor activity are also determined. ...
... ischaemia, the animal is allowed to recover for some time, then is sacrificed and the brain damage studied in detail. In such studies, the bioavailability of a potential drug, its pharmacokinetics, effects on blood pressure, body temperature and motor activity are also determined. ...
Artificial Eye.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... The human visual system is remarkable instrument. It features two mobile acquisition units each has formidable preprocessing circuitry placed at a remote location from the central processing system (brain). Its primary task include transmitting images with a viewing angle of at least 140deg and reso ...
... The human visual system is remarkable instrument. It features two mobile acquisition units each has formidable preprocessing circuitry placed at a remote location from the central processing system (brain). Its primary task include transmitting images with a viewing angle of at least 140deg and reso ...
Neurology, Neurons, and EEG
... to insulate one neuron from another; to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. There are many more glial cells than neurons. We do not fully understand the function of glial cells. Neurons are the basic “information processing” cells of the CNS. The information they process is carried in the for ...
... to insulate one neuron from another; to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. There are many more glial cells than neurons. We do not fully understand the function of glial cells. Neurons are the basic “information processing” cells of the CNS. The information they process is carried in the for ...
PNS Study Guide
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
Answers to What Did You Learn questions
... After an axon in the PNS is severed, the proximal portion of the severed end seals and begins to swell. The distal severed region degenerates and is phagocytized. The neurolemmocytes in the distal region survive and together with the remaining endoneurium form a regeneration tube. The axon regenerat ...
... After an axon in the PNS is severed, the proximal portion of the severed end seals and begins to swell. The distal severed region degenerates and is phagocytized. The neurolemmocytes in the distal region survive and together with the remaining endoneurium form a regeneration tube. The axon regenerat ...
Neuro 16 Neurotransmitters Student
... and putamen project to substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Reduced concentrations in patients with Huntington’s chorea: ...
... and putamen project to substantia nigra and globus pallidus. Reduced concentrations in patients with Huntington’s chorea: ...
Slide 1
... This was done by probing the brains of anesthetized owls with fine electrodes A remote-controlled sound speaker was moved to different locations around the owl's head along an imaginary sphere Firing of neurons in the vicinity of the electrodes was recorded. This was done over several months ...
... This was done by probing the brains of anesthetized owls with fine electrodes A remote-controlled sound speaker was moved to different locations around the owl's head along an imaginary sphere Firing of neurons in the vicinity of the electrodes was recorded. This was done over several months ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle or gland. (effectors) • 3.Interneurons: connect sensory &motor neurons within the brain and spinal cord ...
... • 1. Sensory neurons: carry impulses from the body to the spinal cord and brain (sense receptors) • 2. Motor neurons carry the response impulses away from the brain and spinal cord to a muscle or gland. (effectors) • 3.Interneurons: connect sensory &motor neurons within the brain and spinal cord ...
Lab 8: Muscle and Nervous Tissue
... images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply stained cell bodies of motor neurons (multipolar neurons) ...
... images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply stained cell bodies of motor neurons (multipolar neurons) ...
Slide ()
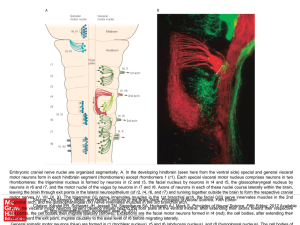
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
nervous system divisions cns, pns 1
... • It is a series of nerves by which the central nervous system is connected with the various tissues of the body. • PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the bloodbrain barrier, leaving it exposed to ...
... • It is a series of nerves by which the central nervous system is connected with the various tissues of the body. • PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the bloodbrain barrier, leaving it exposed to ...
The Nervous System
... Transmitting information… The impulse is called the action potential which is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon like a line of dominoes falling, each one tripping up the next This is real electricity as a handful of neurons produce enough power to light up a flashlight When e ...
... Transmitting information… The impulse is called the action potential which is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon like a line of dominoes falling, each one tripping up the next This is real electricity as a handful of neurons produce enough power to light up a flashlight When e ...
Document
... The impulse is called the action potential which is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon like a line of dominoes falling, each one tripping up the next This is real electricity as a handful of neurons produce enough power to light up a flashlight When electrical signals reach the ...
... The impulse is called the action potential which is a brief electrical charge that travels down the axon like a line of dominoes falling, each one tripping up the next This is real electricity as a handful of neurons produce enough power to light up a flashlight When electrical signals reach the ...
The Nervous System - Ridgewood High School
... circular area around it is the nucleus. The mottled dark areas found throughout the cytoplasm are the Nissl ...
... circular area around it is the nucleus. The mottled dark areas found throughout the cytoplasm are the Nissl ...
Slide 1
... potentials because their axons are short. Some neurons do not have a steady resting potential and are spontaneously active. Neurons differ in the types and combinations of ion channels in their cell membranes. Neurons differ in their neurotransmitters released and their receptors for transmitters. ...
... potentials because their axons are short. Some neurons do not have a steady resting potential and are spontaneously active. Neurons differ in the types and combinations of ion channels in their cell membranes. Neurons differ in their neurotransmitters released and their receptors for transmitters. ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... A. A synapse is a junction that mediates information transfer between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C ...
... A. A synapse is a junction that mediates information transfer between neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell (p. 406; Fig. 11.16). B. Neurons conducting impulses toward the synapse are presynaptic cells, and neurons carrying impulses away from the synapse are postsynaptic cells (p. 406). C ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it faster. just like wrapping tape around a leaky water hose ...
... neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it faster. just like wrapping tape around a leaky water hose ...
Neural Basis of the Ventriloquist
... ElectroEncephaloGraphy (EEG) Neurons use electrical potentials to communicate Multiple, aligned, synchronously-firing neurons produce enough voltage change to be read by electrodes on the scalp. ...
... ElectroEncephaloGraphy (EEG) Neurons use electrical potentials to communicate Multiple, aligned, synchronously-firing neurons produce enough voltage change to be read by electrodes on the scalp. ...
Module 3
... neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mix ...
... neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mix ...
Nueron - AP Psychology Community
... neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mix ...
... neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons at rest have a slightly negative charge). • The mix ...
Nerve Flash Cards
... Central Nervous System (CNS): brain and spinal cord. 1. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): nerves of the body 2. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): has parts of the CNS and PNS. Controls autonomic function (blood pressure, digestion, etc). a. Sympathetic division b. Parasympathetic division ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): brain and spinal cord. 1. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): nerves of the body 2. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): has parts of the CNS and PNS. Controls autonomic function (blood pressure, digestion, etc). a. Sympathetic division b. Parasympathetic division ...
Nerves Powerpoint
... • Neurons have three general structures: – Soma (cell body) – Axon (signal transmission) – Dendrite (signal reception) ...
... • Neurons have three general structures: – Soma (cell body) – Axon (signal transmission) – Dendrite (signal reception) ...
11)
... 4. ____________ support nervous tissue, whereas ____________ conduct the electrical impulses. a. leucocytes, erythrocytes b. axons, dendrites c. neuroglia, neurons d. proteins, lipids 5. Collagen fibers are proteins that are particularly abundant in a. epithelium b. muscle c. nervous tissue d. carti ...
... 4. ____________ support nervous tissue, whereas ____________ conduct the electrical impulses. a. leucocytes, erythrocytes b. axons, dendrites c. neuroglia, neurons d. proteins, lipids 5. Collagen fibers are proteins that are particularly abundant in a. epithelium b. muscle c. nervous tissue d. carti ...