pdf, 181kb
... Pentatonic Scale: A scale consisting of five pitches. Often used as a scale omitting the fourth and seventh pitches of a major scale; or the second and fifth pitches of a minor scale. Phrasing: Dividing musical sentences or thoughts into melodic and/or rhythmic sections, similar to the effect of pu ...
... Pentatonic Scale: A scale consisting of five pitches. Often used as a scale omitting the fourth and seventh pitches of a major scale; or the second and fifth pitches of a minor scale. Phrasing: Dividing musical sentences or thoughts into melodic and/or rhythmic sections, similar to the effect of pu ...
Physics of Music PHY103 Worksheet #4 Setup for fretted monochord
... 2) Pitch measurement and calculating with cents. Pitches are commonly measured with respect to the frequencies of the tempered scale with a concert A of 440Hz. These frequencies are listed in the table below. Tuners usually give the nearest note on the tempered scale and the difference between this ...
... 2) Pitch measurement and calculating with cents. Pitches are commonly measured with respect to the frequencies of the tempered scale with a concert A of 440Hz. These frequencies are listed in the table below. Tuners usually give the nearest note on the tempered scale and the difference between this ...
HS Women's Choir
... play in musical expression. As these students mature emotionally and musically, they exhibit a higher level of confidence in their musical abilities and performance skills. If taken in Grades 9-12, this course satisfies the one-half credit for Fine Arts required for graduation. In this course, sight ...
... play in musical expression. As these students mature emotionally and musically, they exhibit a higher level of confidence in their musical abilities and performance skills. If taken in Grades 9-12, this course satisfies the one-half credit for Fine Arts required for graduation. In this course, sight ...
Lecture 6
... In music a key is the major or minor scale around which a piece of music revolves. A song in a major key is based on a major scale. A song in a minor key is based on a minor scale. A song played in the ‘key of C major’ revolves around the seven notes of the C major scale – C, D, E, F, G, A, and ...
... In music a key is the major or minor scale around which a piece of music revolves. A song in a major key is based on a major scale. A song in a minor key is based on a minor scale. A song played in the ‘key of C major’ revolves around the seven notes of the C major scale – C, D, E, F, G, A, and ...
music questions section i
... a. Typically 4 half steps apart 50. What are major and minor scales that begin and end on the same tonic pitch called? a. Parallel 51. How can you combine elements of both major and minor? a. A scale with blue inflections 52. What makes up a blues scale? a. Scale degrees 3 and 7 can be lowered 53. W ...
... a. Typically 4 half steps apart 50. What are major and minor scales that begin and end on the same tonic pitch called? a. Parallel 51. How can you combine elements of both major and minor? a. A scale with blue inflections 52. What makes up a blues scale? a. Scale degrees 3 and 7 can be lowered 53. W ...
Musical Terms - Rogers State University
... – moves in whole or half steps • Disjunct melody – many large skips and may sound “jagged” – moves in more than a whole step ...
... – moves in whole or half steps • Disjunct melody – many large skips and may sound “jagged” – moves in more than a whole step ...
chap3 hw Compute the Frequencies of the Notes of the C
... PROBLEM: We have seen that musical tones can be modeled mathematically by sinusoidal signals. If you read music or play the piano you are aware of the fact that the piano keyboard is divided into octaves, with the tones in each octave being twice the frequency of the corresponding tones in the next ...
... PROBLEM: We have seen that musical tones can be modeled mathematically by sinusoidal signals. If you read music or play the piano you are aware of the fact that the piano keyboard is divided into octaves, with the tones in each octave being twice the frequency of the corresponding tones in the next ...
AP Music Theory - Somerset Academy
... in pitch between two notes Harmonic Interval – performing the two notes at the same time Melodic Interval – performing the two notes successively ...
... in pitch between two notes Harmonic Interval – performing the two notes at the same time Melodic Interval – performing the two notes successively ...
File
... in pitch between two notes Harmonic Interval – performing the two notes at the same time Melodic Interval – performing the two notes successively ...
... in pitch between two notes Harmonic Interval – performing the two notes at the same time Melodic Interval – performing the two notes successively ...
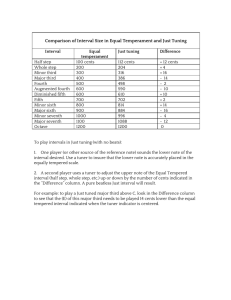
Comparison of Interval Size in Equal Temperament and Just Tuning
... 2. A second player uses a tuner to adjust the upper note of the Equal Tempered interval (half step, whole step, etc.) up or down by the number of cents indicated in the “Difference” column. A pure beatless Just interval will result. For example: to play a Just tuned major third above C, look in the ...
... 2. A second player uses a tuner to adjust the upper note of the Equal Tempered interval (half step, whole step, etc.) up or down by the number of cents indicated in the “Difference” column. A pure beatless Just interval will result. For example: to play a Just tuned major third above C, look in the ...
Experiencing Music - Petal School District
... rhythm, harmony, timbre, texture, and form. The more you know about these elements the easier it is to understand the music you hear. ...
... rhythm, harmony, timbre, texture, and form. The more you know about these elements the easier it is to understand the music you hear. ...
Minor Scales
... lower it. These last two can apply to any scale degree, but least commonly with the perfect intervals. ...
... lower it. These last two can apply to any scale degree, but least commonly with the perfect intervals. ...
Intervals and Dissonance in Human Evolution
... Many other composers pursued similar directions, among them Dane Rudhyer. In his view the inclusion of dissonance is “identifying opposites; metaphysically it is the power of relating spirit to matter.” Like Anthroposophy, his system also related the complication of musical intervals to the developm ...
... Many other composers pursued similar directions, among them Dane Rudhyer. In his view the inclusion of dissonance is “identifying opposites; metaphysically it is the power of relating spirit to matter.” Like Anthroposophy, his system also related the complication of musical intervals to the developm ...
Score Reading Vocabulary Key signature: The sharps or flats that
... Beat: Any pulsing unit of musical time Accidental: A marking used the raise and lower the indicated pitch; sharps raise the note a whole step, flats lower the note a half step, the naturals return the note to the original pitch Notation: The art of writing musical notes on paper Note: A symbol used ...
... Beat: Any pulsing unit of musical time Accidental: A marking used the raise and lower the indicated pitch; sharps raise the note a whole step, flats lower the note a half step, the naturals return the note to the original pitch Notation: The art of writing musical notes on paper Note: A symbol used ...
Bridges workshop worksheet
... The 3 : 2 and 2 : 1 ratios give us a way to find the frequencies of the 12 notes of the scale starting with one frequency. We’ll call tuning using just these intervals Pythagorean tuning. 2. Starting with any frequency you want (A=440 or 220 is canonical, but you can use anything you’d like), use A ...
... The 3 : 2 and 2 : 1 ratios give us a way to find the frequencies of the 12 notes of the scale starting with one frequency. We’ll call tuning using just these intervals Pythagorean tuning. 2. Starting with any frequency you want (A=440 or 220 is canonical, but you can use anything you’d like), use A ...
Document
... • Suggests a ladder of discrete pitches • Scale steps: specific notes of a scale (do, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti, do) ...
... • Suggests a ladder of discrete pitches • Scale steps: specific notes of a scale (do, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti, do) ...
16 באוקטובר, 2005
... 3. Adding an option of changing the scale of a musical sheet produced by the system. Background: Western music includes sounds which defer from each other by at least semitone. This gives rise to 12 basic different sounds, as seen here: ...
... 3. Adding an option of changing the scale of a musical sheet produced by the system. Background: Western music includes sounds which defer from each other by at least semitone. This gives rise to 12 basic different sounds, as seen here: ...
Minor Scales
... A scale is a series of notes dividing the octave, repeating each octave across the range of low to high pitches. According to the equal temperament tuning system, octaves are equally divided into twelve notes. A western scale is a series of notes selected among these twelve notes. Each of these note ...
... A scale is a series of notes dividing the octave, repeating each octave across the range of low to high pitches. According to the equal temperament tuning system, octaves are equally divided into twelve notes. A western scale is a series of notes selected among these twelve notes. Each of these note ...
Math and Music Worksheet - The Saga of Mathematics: A Brief History
... 7. The circle of fifths is generated by starting at a particular note and then going up an interval of a fifth (seven half-steps). For example, starting at middle A, a circle of fifths includes the notes A → E → B′ → F#′ → C#′′ → G#′′ → D#′′′ → A#′′′′→ F′′′′ → C′′′′′ → G′′′′′ → D′′′′′′ → A′′′′′′′, w ...
... 7. The circle of fifths is generated by starting at a particular note and then going up an interval of a fifth (seven half-steps). For example, starting at middle A, a circle of fifths includes the notes A → E → B′ → F#′ → C#′′ → G#′′ → D#′′′ → A#′′′′→ F′′′′ → C′′′′′ → G′′′′′ → D′′′′′′ → A′′′′′′′, w ...
Music Fundamentals Primer Lesson 4
... A triad is a group of three notes that sound at the same time. In much tonal music, chords are built by stacking thirds on top of each other, creating what is known as tertian harmony. A tertian triad is a chord with three notes that is built with thirds. Even when a chord is spread out over several ...
... A triad is a group of three notes that sound at the same time. In much tonal music, chords are built by stacking thirds on top of each other, creating what is known as tertian harmony. A tertian triad is a chord with three notes that is built with thirds. Even when a chord is spread out over several ...
Just intonation

In music, just intonation (sometimes abbreviated as JI) or pure intonation is any musical tuning in which the frequencies of notes are related by ratios of small whole numbers. Any interval tuned in this way is called a pure or just interval. The two notes in any just interval are members of the same harmonic series. Frequency ratios involving large integers such as 1024:927 are not generally said to be justly tuned. ""Just intonation is the tuning system of the later ancient Greek modes as codified by Ptolemy; it was the aesthetic ideal of the Renaissance theorists; and it is the tuning practice of a great many musical cultures worldwide, both ancient and modern.""Just intonation can be contrasted and compared with equal temperament, which dominates Western instruments of fixed pitch (e.g., piano or organ) and default MIDI tuning on electronic keyboards. In equal temperament, all intervals are defined as multiples of the same basic interval, or more precisely, the intervals are ratios which are integer powers of the smallest step ratio, so two notes separated by the same number of steps always have exactly the same frequency ratio. However, except for doubling of frequencies (one or more octaves), no other intervals are exact ratios of small integers. Each just interval differs a different amount from its analogous, equally tempered interval.Justly tuned intervals can be written as either ratios, with a colon (for example, 3:2), or as fractions, with a solidus (3 ⁄ 2). For example, two tones, one at 300 Hertz (cycles per second), and the other at 200 hertz are both multiples of 100 Hz and as such members of the harmonic series built on 100 Hz. Thus 3/2, known as a perfect fifth, may be defined as the musical interval (the ratio) between the second and third harmonics of any fundamental pitch.