AAWM_abstract_short
... established over time out of compositional needs and musical practice. Equal-temperament was needed for music that began to include modulations and nowadays almost all western music relies on a welltempered, equidistant 12-tone organization. Non-western classical music often leans on a theoretical s ...
... established over time out of compositional needs and musical practice. Equal-temperament was needed for music that began to include modulations and nowadays almost all western music relies on a welltempered, equidistant 12-tone organization. Non-western classical music often leans on a theoretical s ...
A Periodicity-Based Approach on Harmony Perception Including
... triads, i.e. chords only. In this paper, we introduce an approach based on the notion of periodicity, providing a unified view on the perception of chords and scales. The method is psychophysically motivated: It applies the fact, that the just noticeable difference of human pitch perception is about ...
... triads, i.e. chords only. In this paper, we introduce an approach based on the notion of periodicity, providing a unified view on the perception of chords and scales. The method is psychophysically motivated: It applies the fact, that the just noticeable difference of human pitch perception is about ...
Music Notation 2
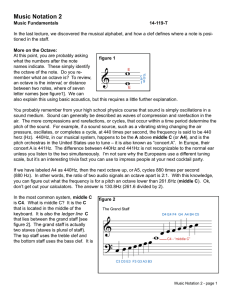
... You probably remember from your high school physics course that sound is simply oscillations in a sound medium. Sound can generally be described as waves of compression and rarefaction in the air. The more compressions and rarefactions, or cycles, that occur within a time period determine the pitch ...
... You probably remember from your high school physics course that sound is simply oscillations in a sound medium. Sound can generally be described as waves of compression and rarefaction in the air. The more compressions and rarefactions, or cycles, that occur within a time period determine the pitch ...
Basic Music Theory
... can be called D# or Eb, etc. That's a total of twelve notes, the letters A through G with a sharp or flat note between each pair of letters except between B and C and E and F. To find the twelve notes move up the neck one fret at a time. The distance from each note to the next at one-fret intervals ...
... can be called D# or Eb, etc. That's a total of twelve notes, the letters A through G with a sharp or flat note between each pair of letters except between B and C and E and F. To find the twelve notes move up the neck one fret at a time. The distance from each note to the next at one-fret intervals ...
GLOSSARY
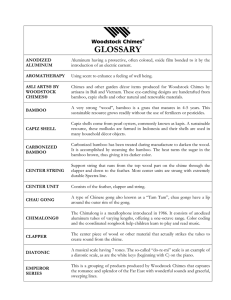
... For reasons of musical purity, we tune all of our products to an ancient system known as just intonation. Therefore, many of the notes used on Woodstock Chimes fall between the notes of the piano which is tuned to a modern system called equal temperament. This makes our products not only authentic w ...
... For reasons of musical purity, we tune all of our products to an ancient system known as just intonation. Therefore, many of the notes used on Woodstock Chimes fall between the notes of the piano which is tuned to a modern system called equal temperament. This makes our products not only authentic w ...
Popular Music Theory - The Academy Of Popular Music
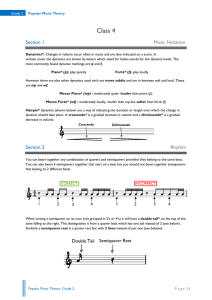
... Minor Triad*: Just the same as with a major triad, the 1st, 3rd, and 5th notes of a minor scale make up a minor triad. A minor triad is built by stacking the root, 3rd and 5th degrees of the major scale onto of each other. The root is once again the first note of the scale. As a result, the triad of ...
... Minor Triad*: Just the same as with a major triad, the 1st, 3rd, and 5th notes of a minor scale make up a minor triad. A minor triad is built by stacking the root, 3rd and 5th degrees of the major scale onto of each other. The root is once again the first note of the scale. As a result, the triad of ...
doc
... There’s a web app called Isle of Tune that you can download and play. It allows you to make songs by building a road and lining the road with different notes. The set of notes available is kind of weird—it seems to span a diatonic scale, but it’s missing two of the notes. In fact, this is a popular ...
... There’s a web app called Isle of Tune that you can download and play. It allows you to make songs by building a road and lining the road with different notes. The set of notes available is kind of weird—it seems to span a diatonic scale, but it’s missing two of the notes. In fact, this is a popular ...
1st GRADE MUSIC—NC LESSON PLANS From: (Th) Sept 26
... After reviewing the song, I’ll ask what happens with our voices and the motions as we sing the various sections of the song (each item is a higher pitch, the next sequence is a descending scale, the last two notes are a descending octave jump that the students will differentiate from stepwise motion ...
... After reviewing the song, I’ll ask what happens with our voices and the motions as we sing the various sections of the song (each item is a higher pitch, the next sequence is a descending scale, the last two notes are a descending octave jump that the students will differentiate from stepwise motion ...
The Structure of Plato`s Dialogues and Greek Music Theory: A
... But suppose we accept this very uneven set of twelve ratios as a potential “scale.” Even if we ignore the great variation in musical interval size, mapping this scale onto an equal twelve-fold division of dialogues, with each section being “harmonious” or “disharmonious” is still not straightforward ...
... But suppose we accept this very uneven set of twelve ratios as a potential “scale.” Even if we ignore the great variation in musical interval size, mapping this scale onto an equal twelve-fold division of dialogues, with each section being “harmonious” or “disharmonious” is still not straightforward ...
A Non-Pythagorean Musical Scale Based on Logarithms
... positions corresponding to logarithmic pitches marked on the fingerboards. Specially-constructed flutes, xylophones and marimbas, specially-tuned harps, and other acoustic instruments might also be utilized in performances. Certainly the natural harmonics of each instrument will interfere to some de ...
... positions corresponding to logarithmic pitches marked on the fingerboards. Specially-constructed flutes, xylophones and marimbas, specially-tuned harps, and other acoustic instruments might also be utilized in performances. Certainly the natural harmonics of each instrument will interfere to some de ...
Traditional composition techniques
... interval contraction smaller intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes interval expansion larger intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes inversion mirrored contour; e.g., subject and inversion in Bartok's Music for Strings, Percussion and Celeste, first movement isomelos same n ...
... interval contraction smaller intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes interval expansion larger intervals, same contour; e.g., Liszt's Les Preludes inversion mirrored contour; e.g., subject and inversion in Bartok's Music for Strings, Percussion and Celeste, first movement isomelos same n ...
NON-SERIAL ATONALITY ATONAL MUSIC
... ATONAL MUSIC: music without a tonal center; the free atonality of the 1920s led to a more structured method called serialism or 12-tone music. Characteristics of atonal music: lacks a tonal center unresolved dissonances mixed-interval chords pitch material derived from the chromatic scale very contr ...
... ATONAL MUSIC: music without a tonal center; the free atonality of the 1920s led to a more structured method called serialism or 12-tone music. Characteristics of atonal music: lacks a tonal center unresolved dissonances mixed-interval chords pitch material derived from the chromatic scale very contr ...
Sample Grade 4 Theory Paper
... Transpose this tune up an octave so that a double bass will be able to play it at the same pitch as the following notes. ...
... Transpose this tune up an octave so that a double bass will be able to play it at the same pitch as the following notes. ...
Major (our most common scale)
... When a pitch is sounded, many other “higher” sympathetic pitches also vibrate, called overtones. The strongest overtone of any pitch is the octave. Octaves are all pitches whose frequencies are related by powers of 2, meaning twice as fast or twice as slow, i.e. an “A” will sound with = 220, 440 or ...
... When a pitch is sounded, many other “higher” sympathetic pitches also vibrate, called overtones. The strongest overtone of any pitch is the octave. Octaves are all pitches whose frequencies are related by powers of 2, meaning twice as fast or twice as slow, i.e. an “A” will sound with = 220, 440 or ...
Intonation Variables in the Performance of Twelve
... (involving the Pythagorean comma) is discussed along with pitch adjustments (involving the syntonic comma, diaskhisma, diesis, etc.) sometimes required for harmonic reasons. Arguments by composers, performers and others concerning tempered versus untempered intonation are presented, followed by an a ...
... (involving the Pythagorean comma) is discussed along with pitch adjustments (involving the syntonic comma, diaskhisma, diesis, etc.) sometimes required for harmonic reasons. Arguments by composers, performers and others concerning tempered versus untempered intonation are presented, followed by an a ...
notes and equations
... An interval is a ratio between two frequencies. The interval between two musical tones is the ratio between their fundamental frequencies. A perfect interval is the ratio between two small integers (typically below 6). Commonly used perfect intervals are: name unison octave minor third major third f ...
... An interval is a ratio between two frequencies. The interval between two musical tones is the ratio between their fundamental frequencies. A perfect interval is the ratio between two small integers (typically below 6). Commonly used perfect intervals are: name unison octave minor third major third f ...
Middleton
... 1. Difference tones can train the ear to hear subtle pitch changes, and are useful for developing a feel for Just tuned (pure) intervals. 2. Difference tones sound something like a mosquito buzzing nearby and are easiest to hear when loud and high-pitched. Two piccolos are perfect to create some exa ...
... 1. Difference tones can train the ear to hear subtle pitch changes, and are useful for developing a feel for Just tuned (pure) intervals. 2. Difference tones sound something like a mosquito buzzing nearby and are easiest to hear when loud and high-pitched. Two piccolos are perfect to create some exa ...
Audio Explorer
... Chromatic Scale: in the scale of equal temperament, a scale in which the interval between the tones are all half-tones. Complex Tone: a sound sensation characterized by more than one pitch. Frequency: the number of recurrent waves or cycles which pass a certain observation point per second. Frequenc ...
... Chromatic Scale: in the scale of equal temperament, a scale in which the interval between the tones are all half-tones. Complex Tone: a sound sensation characterized by more than one pitch. Frequency: the number of recurrent waves or cycles which pass a certain observation point per second. Frequenc ...
Pitch Collections, Scales, and Major Keys
... from the given pitch up to and including the same pitch class an octave higher, i.e. from middle C to the next highest C. ...
... from the given pitch up to and including the same pitch class an octave higher, i.e. from middle C to the next highest C. ...
Music Vocabulary Lists Year 1
... the word “opus”. For example, Opus 28, No. 4. Orchestration - Arranging a piece of music for an orchestra. Also, the study of music. Ornaments - Tones used to embellish the principal melodic tone. Ostinato - A repeated phrase. Pentatonic Scale - A musical scale having five notes. For example: the fi ...
... the word “opus”. For example, Opus 28, No. 4. Orchestration - Arranging a piece of music for an orchestra. Also, the study of music. Ornaments - Tones used to embellish the principal melodic tone. Ostinato - A repeated phrase. Pentatonic Scale - A musical scale having five notes. For example: the fi ...
12_6_Deeper_Reading_Scales_and_Tuning
... key signature - consisting of a number of sharps or flats - in order to know which accidentals a particular major scale will have. An easy, but time consuming, way to do this would be to use the pattern of tone/tone/semitone/etc... given above. If we choose to write the scale of D-major, we know imm ...
... key signature - consisting of a number of sharps or flats - in order to know which accidentals a particular major scale will have. An easy, but time consuming, way to do this would be to use the pattern of tone/tone/semitone/etc... given above. If we choose to write the scale of D-major, we know imm ...
Musical Scales and Tuning
... key signature - consisting of a number of sharps or flats - in order to know which accidentals a particular major scale will have. An easy, but time consuming, way to do this would be to use the pattern of tone/tone/semitone/etc... given above. If we choose to write the scale of D-major, we know imm ...
... key signature - consisting of a number of sharps or flats - in order to know which accidentals a particular major scale will have. An easy, but time consuming, way to do this would be to use the pattern of tone/tone/semitone/etc... given above. If we choose to write the scale of D-major, we know imm ...
Just intonation

In music, just intonation (sometimes abbreviated as JI) or pure intonation is any musical tuning in which the frequencies of notes are related by ratios of small whole numbers. Any interval tuned in this way is called a pure or just interval. The two notes in any just interval are members of the same harmonic series. Frequency ratios involving large integers such as 1024:927 are not generally said to be justly tuned. ""Just intonation is the tuning system of the later ancient Greek modes as codified by Ptolemy; it was the aesthetic ideal of the Renaissance theorists; and it is the tuning practice of a great many musical cultures worldwide, both ancient and modern.""Just intonation can be contrasted and compared with equal temperament, which dominates Western instruments of fixed pitch (e.g., piano or organ) and default MIDI tuning on electronic keyboards. In equal temperament, all intervals are defined as multiples of the same basic interval, or more precisely, the intervals are ratios which are integer powers of the smallest step ratio, so two notes separated by the same number of steps always have exactly the same frequency ratio. However, except for doubling of frequencies (one or more octaves), no other intervals are exact ratios of small integers. Each just interval differs a different amount from its analogous, equally tempered interval.Justly tuned intervals can be written as either ratios, with a colon (for example, 3:2), or as fractions, with a solidus (3 ⁄ 2). For example, two tones, one at 300 Hertz (cycles per second), and the other at 200 hertz are both multiples of 100 Hz and as such members of the harmonic series built on 100 Hz. Thus 3/2, known as a perfect fifth, may be defined as the musical interval (the ratio) between the second and third harmonics of any fundamental pitch.