The basics of brain communication
... How do Drugs Affect Neural Communication Between Neurons? Many drugs, especially those that affect moods or behavior, work by interfering with normal functioning of neurotransmitters in the synapse. How this occurs depends on the drug, such as the following: 1. Drugs can mimic specific neurotransmit ...
... How do Drugs Affect Neural Communication Between Neurons? Many drugs, especially those that affect moods or behavior, work by interfering with normal functioning of neurotransmitters in the synapse. How this occurs depends on the drug, such as the following: 1. Drugs can mimic specific neurotransmit ...
Chp3 Weiten - Napa Valley College
... about one-third of the cerebral cortex. Contributes to certain types of decision making as some sort of “executive control system,” which is thought to monitor, organize, and direct thought ...
... about one-third of the cerebral cortex. Contributes to certain types of decision making as some sort of “executive control system,” which is thought to monitor, organize, and direct thought ...
Document
... Irregular contours, appendages (spines) Originates as thick, tapering process Ramifies by branching at acute angles Subdivides into smaller branches Confined to the vicinitiy of cell body Microtubules predominate in dendrites Conduct in a decremental fashion but may be capable of generating action p ...
... Irregular contours, appendages (spines) Originates as thick, tapering process Ramifies by branching at acute angles Subdivides into smaller branches Confined to the vicinitiy of cell body Microtubules predominate in dendrites Conduct in a decremental fashion but may be capable of generating action p ...
Notes0112
... signal such as the binding of a ligand to a receptor that forms part of the channel, eg, the acetylcholine receptor channel involved in neuromuscular transmission; and (iii) mechanically gated channels, in which the sensor is sensitive to mechanical deformation of the membrane, eg, stretch-activated ...
... signal such as the binding of a ligand to a receptor that forms part of the channel, eg, the acetylcholine receptor channel involved in neuromuscular transmission; and (iii) mechanically gated channels, in which the sensor is sensitive to mechanical deformation of the membrane, eg, stretch-activated ...
action potential
... postsynaptic cell A single neurotransmitter may have more than a dozen different receptors Acetylcholine is a common neurotransmitter in both invertebrates and vertebrates ...
... postsynaptic cell A single neurotransmitter may have more than a dozen different receptors Acetylcholine is a common neurotransmitter in both invertebrates and vertebrates ...
File
... -- an axon carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (lo ...
... -- an axon carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (lo ...
The Nervous System - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Reflexes are automatic, involuntary responses to changes occurring inside or outside the body. Can involve the brain (e.g. blinking) or not involve brain (e.g. withdraw hand from hot stove). • The Reflex arc is the main functional unit of the nervous system. It allows us to react to internal and ...
... • Reflexes are automatic, involuntary responses to changes occurring inside or outside the body. Can involve the brain (e.g. blinking) or not involve brain (e.g. withdraw hand from hot stove). • The Reflex arc is the main functional unit of the nervous system. It allows us to react to internal and ...
3-8_NeuronDiversity_SalmaA
... to the effector cells. Muscular output involves peripheral nervous system. ...
... to the effector cells. Muscular output involves peripheral nervous system. ...
Unit 3 - Mayfield City Schools
... - responds to input from the dendrites and soma -transmits a neural message down its length and then passes its information on to other cells -branch out from soma -receive input from other neurons through receptors on their surface -fatty coating surrounding the axon -insulation for the electrical ...
... - responds to input from the dendrites and soma -transmits a neural message down its length and then passes its information on to other cells -branch out from soma -receive input from other neurons through receptors on their surface -fatty coating surrounding the axon -insulation for the electrical ...
PDF
... The overall goal of this dissertation project was to characterize the impact of ulceration on propulsive motility in guinea pig tri-nitro benzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) colitis. The study was comprised of three aims: to determine how ulceration affects motility; to examine changes in neural control of ...
... The overall goal of this dissertation project was to characterize the impact of ulceration on propulsive motility in guinea pig tri-nitro benzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) colitis. The study was comprised of three aims: to determine how ulceration affects motility; to examine changes in neural control of ...
The Neuron - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... threshold of activation must be reached at the axon hillock Integration of IPSPs and EPSPs must result in a potential of about -65mV in order to generate an AP Page 67 ...
... threshold of activation must be reached at the axon hillock Integration of IPSPs and EPSPs must result in a potential of about -65mV in order to generate an AP Page 67 ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/nervous system tea
... 26. What is a Concussion? Occurs when the brain injury is slight. Although patient may be dizzy or briefly lose consciousness, the damage is not permanent. 27. What is a Stroke? Occurs when blood circulation to the brain area is blocked, as by a blood clot or a ruptured blood vessel and vital brain ...
... 26. What is a Concussion? Occurs when the brain injury is slight. Although patient may be dizzy or briefly lose consciousness, the damage is not permanent. 27. What is a Stroke? Occurs when blood circulation to the brain area is blocked, as by a blood clot or a ruptured blood vessel and vital brain ...
Drugs Hanson 4
... • Excitatory synapse initiates an impulse in the receiving neuron when stimulated, causing release of neurotransmitters or increasing activity in target cell. • Inhibitory synapse diminishes likelihood of an impulse in the receiving neuron or reduces the activity in other target cells. ...
... • Excitatory synapse initiates an impulse in the receiving neuron when stimulated, causing release of neurotransmitters or increasing activity in target cell. • Inhibitory synapse diminishes likelihood of an impulse in the receiving neuron or reduces the activity in other target cells. ...
Sensory Systems
... Pressure and Temperature: Mechanoreceptors in the skin make it possible to sense touch, ___________, and tension. For humans, touch receptors are concentrated in the face, tongue, and ________________. Body hair helps to sense touch because bending a hair stimulates mechanoreceptors at the base o ...
... Pressure and Temperature: Mechanoreceptors in the skin make it possible to sense touch, ___________, and tension. For humans, touch receptors are concentrated in the face, tongue, and ________________. Body hair helps to sense touch because bending a hair stimulates mechanoreceptors at the base o ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... • Afferent (Sensory) Neurons carry messages from tissues and sensory organs to the brain and spinal cord for ...
... • Afferent (Sensory) Neurons carry messages from tissues and sensory organs to the brain and spinal cord for ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... – Selectively permeable – gates do not allow sodium ions to pass through the cell membrane Step 2: Threshold – the minimum energy needed to generate an action potential (-55mv) ...
... – Selectively permeable – gates do not allow sodium ions to pass through the cell membrane Step 2: Threshold – the minimum energy needed to generate an action potential (-55mv) ...
BIOL 2121 Study Guide Test 4 Chapter 11: Nervous System List 3
... Understand and be able to explain the physiology behind the resting membrane potential o Know relative concentrations of ions on either side of the axolemma at rest Distinguish between polarize, depolarize, repolarize, and hyperpolarize o Understand what this translates to in terms of ion concen ...
... Understand and be able to explain the physiology behind the resting membrane potential o Know relative concentrations of ions on either side of the axolemma at rest Distinguish between polarize, depolarize, repolarize, and hyperpolarize o Understand what this translates to in terms of ion concen ...
1 - Hatboro
... sarcolemma but there was no sodium in the synaptic cleft, what would happen? no sodium in the cleft no diffusion of sodium into the muscle fiber no change in charge no calcium channels opening in the SR etc no contraction 13. What does sodium cause when it enters the muscle fiber? causes i ...
... sarcolemma but there was no sodium in the synaptic cleft, what would happen? no sodium in the cleft no diffusion of sodium into the muscle fiber no change in charge no calcium channels opening in the SR etc no contraction 13. What does sodium cause when it enters the muscle fiber? causes i ...
Disuse
... The onset of changes in the axon terminal depends on two things: the length of the distal stump of axon and the species of animal The onset of end-plate failure is also species dependent, being much later larger mammals. When degenerative changes have started, only 3-5 hours are required for com ...
... The onset of changes in the axon terminal depends on two things: the length of the distal stump of axon and the species of animal The onset of end-plate failure is also species dependent, being much later larger mammals. When degenerative changes have started, only 3-5 hours are required for com ...
Nervous System Notes Outline
... 13. Name 3 structurally different neurons. 1. _______________ – one input (dendrite), one output (axon); eyes, nose, ears 2. _______________ – one output with 2 branches (fused dendrites and axon); most ___________ neurons of ________ 3. _______________ – many inputs (dendrites), one output (axon); ...
... 13. Name 3 structurally different neurons. 1. _______________ – one input (dendrite), one output (axon); eyes, nose, ears 2. _______________ – one output with 2 branches (fused dendrites and axon); most ___________ neurons of ________ 3. _______________ – many inputs (dendrites), one output (axon); ...
Chapter 2: The synapse – regulating communication and
... are abnormal. We learned how information flow can be disrupted: Disorders of electrical signaling such as those that affect myelin, can directly affect the speed that the electrical signal is conveyed. Disorders of transport mechanisms, such as those that affect the nerve terminal, can directly ...
... are abnormal. We learned how information flow can be disrupted: Disorders of electrical signaling such as those that affect myelin, can directly affect the speed that the electrical signal is conveyed. Disorders of transport mechanisms, such as those that affect the nerve terminal, can directly ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
13-1 CHAPTER 13 SYNAPSES The nervous system consists of
... of voltage-gated Ca++ channels and the entry of Ca++ into the terminal. Once inside, Ca++ promotes fusion of the vesicles with the terminal membrane and release of the transmitter substance. The released transmitter substance diffuses across the cleft in a fraction of a millisecond and interacts wit ...
... of voltage-gated Ca++ channels and the entry of Ca++ into the terminal. Once inside, Ca++ promotes fusion of the vesicles with the terminal membrane and release of the transmitter substance. The released transmitter substance diffuses across the cleft in a fraction of a millisecond and interacts wit ...
nervous system worksheet
... 3. Match the descriptions in the table below with the terms in the list. A. Synapse B. Axon C. Myelin sheath D. Nerve impulse E. Sense receptor F. Response; G. Reflex H. Cell body I. Dendrite J. Nerve K. Neurotransmitter L. Axon terminal ...
... 3. Match the descriptions in the table below with the terms in the list. A. Synapse B. Axon C. Myelin sheath D. Nerve impulse E. Sense receptor F. Response; G. Reflex H. Cell body I. Dendrite J. Nerve K. Neurotransmitter L. Axon terminal ...
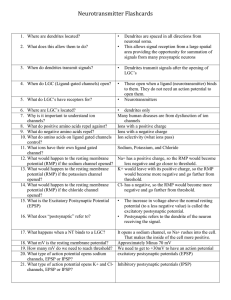
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... Many human diseases are from dysfunction of ion channels Ions with a positive charge Ions with a negative charge Ion selectivity (what ions pass) ...
... Many human diseases are from dysfunction of ion channels Ions with a positive charge Ions with a negative charge Ion selectivity (what ions pass) ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.