Nervous_System_PowerPoint
... Small masses of nervous tissue Located outside of the brain and spinal cord Closely associated with cranial/spinal nerves ...
... Small masses of nervous tissue Located outside of the brain and spinal cord Closely associated with cranial/spinal nerves ...
Ch.02 - Neuroscience
... Nerve cells Basic building blocks of the body’s information processing system. Made up of Dendrites Axons ...
... Nerve cells Basic building blocks of the body’s information processing system. Made up of Dendrites Axons ...
Guided Notes
... vi. pia mater:_____________________________ D. blood - brain barrier i. Function: ensures stable environment by endothelial tight junctions in blood capillaries ii. excludes some substances while allowing other substances to freely pass : List those that can pass through ____________________________ ...
... vi. pia mater:_____________________________ D. blood - brain barrier i. Function: ensures stable environment by endothelial tight junctions in blood capillaries ii. excludes some substances while allowing other substances to freely pass : List those that can pass through ____________________________ ...
here
... vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with muscles and control their contractions. ...
... vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with muscles and control their contractions. ...
The Nervous System: Overview The nervous system Divisions of the
... Two main divisions: 1. Central nervous system (CNS): The brain & spinal cord ...
... Two main divisions: 1. Central nervous system (CNS): The brain & spinal cord ...
Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1
... 2. oligodendrocytes - are responsible for formation of myelin in the CNS. 3. microglia - are phagocytic cells of the CNS. 4. astrocytes - help form part of the blood-brain barrier. 5. ependyma - cells that line the ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord. 6. satellite cells - provide str ...
... 2. oligodendrocytes - are responsible for formation of myelin in the CNS. 3. microglia - are phagocytic cells of the CNS. 4. astrocytes - help form part of the blood-brain barrier. 5. ependyma - cells that line the ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord. 6. satellite cells - provide str ...
Hormones
... Endocrine glands are ductless tissues surrounded by vascular tissue that produce and secrete chemical messengers (hormones) directly into the bloodstream, where they act upon specific target tissues ...
... Endocrine glands are ductless tissues surrounded by vascular tissue that produce and secrete chemical messengers (hormones) directly into the bloodstream, where they act upon specific target tissues ...
File
... movements of the muscles, like walking or swinging the arms. • This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don’t fall over when you turn around. • Cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learnin ...
... movements of the muscles, like walking or swinging the arms. • This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don’t fall over when you turn around. • Cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learnin ...
Chapter 3
... • Inside the neuron has a negative ionic charge • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurologi ...
... • Inside the neuron has a negative ionic charge • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurologi ...
Basic Neuroscience Series: Introduction and Series Overview
... being presented by clinicians • Pathology overview- We cannot do a whole overview of CNS/PNS pathology and also do what the Department has charged us with teaching you through this series, BUT we do have a few lectures sprinkled in ...
... being presented by clinicians • Pathology overview- We cannot do a whole overview of CNS/PNS pathology and also do what the Department has charged us with teaching you through this series, BUT we do have a few lectures sprinkled in ...
03. Neurons and Nerves
... • Two types of cells are found in the nervous system: 1. Glial cells – are non-conducting cells. They are important for structural support and metabolism of nerve cells. Schwann cell is a type of glial cell that surrounds axons. 2. Neurons – are functional units of the nervous system. They carry in ...
... • Two types of cells are found in the nervous system: 1. Glial cells – are non-conducting cells. They are important for structural support and metabolism of nerve cells. Schwann cell is a type of glial cell that surrounds axons. 2. Neurons – are functional units of the nervous system. They carry in ...
Slide ()
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
... Development of the cranial nuclei. A–D. Schematic section through the hind brain at three developmental time points (A–C) and maturity (D). The space within the sections is the fourth ventricle. During development the fourth ventricle, initially flattened dorsoventrally just like the spinal cord, ex ...
Reflex and autonomic nervous system
... Has sensory receptors that collect information form internal and external ...
... Has sensory receptors that collect information form internal and external ...
Chapter 9
... Name the 2 ____________ of the nervous system and list the __________________ of each Describe 3 _____________ of the nervous system Describe _______ types of _____________ cells Label all parts of a ___________ and explain the _________________ of each part Explain 6 _________________ of neurons De ...
... Name the 2 ____________ of the nervous system and list the __________________ of each Describe 3 _____________ of the nervous system Describe _______ types of _____________ cells Label all parts of a ___________ and explain the _________________ of each part Explain 6 _________________ of neurons De ...
LS Chapter 18: Control and Coordination The Nervous System
... o Different receptors allow for feeling _______________ _______________ (tickles) and ______________________________ (pokes or jabs) o There are more receptors in some areas than others ...
... o Different receptors allow for feeling _______________ _______________ (tickles) and ______________________________ (pokes or jabs) o There are more receptors in some areas than others ...
Internal Regulation I
... types project widely throughout the brain, including direct monosynaptic innervation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (where motor plans of action are formed). The systems are complementary, not redundant; for example, one may initiate a behavior whereas the other prolongs it. ...
... types project widely throughout the brain, including direct monosynaptic innervation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (where motor plans of action are formed). The systems are complementary, not redundant; for example, one may initiate a behavior whereas the other prolongs it. ...
Nervous System Notes
... Neurons are kept separate from blood borne substances Metabolic wastes like urea, toxins, and proteins are prevented from entering brain tissue. Nutrients (like glucose), anesthetics, water, alcohol, and nicotine all easily pass through the barrier. ...
... Neurons are kept separate from blood borne substances Metabolic wastes like urea, toxins, and proteins are prevented from entering brain tissue. Nutrients (like glucose), anesthetics, water, alcohol, and nicotine all easily pass through the barrier. ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage pulse that propagates along it (see arrow). ...
... (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage pulse that propagates along it (see arrow). ...
Control_Systems11
... in the potassium channels open, allowing potassium (K+) ions to flow OUT of the cell. This restores the negative potential ...
... in the potassium channels open, allowing potassium (K+) ions to flow OUT of the cell. This restores the negative potential ...
Slide ()
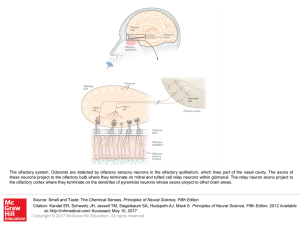
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Hypothalamus and Basic Needs
... In addition to the feed-back loops, the hypothalamus also has some intrinsic receptors, including thermoreceptors and osmoreceptors to monitor temperature and ionic balance, respectively. Once the hypothalamus is “aware” of a problem, how does it fix it? Essentially, there are two main outputs: 1. N ...
... In addition to the feed-back loops, the hypothalamus also has some intrinsic receptors, including thermoreceptors and osmoreceptors to monitor temperature and ionic balance, respectively. Once the hypothalamus is “aware” of a problem, how does it fix it? Essentially, there are two main outputs: 1. N ...
neurons
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
What is the structure of the neuron? (continued)
... than neurons. • Surround and support neurons, control the supply of nutrients to neurons, assist in the exchange of chemicals between neurons, destroy and remove damaged neurons. ...
... than neurons. • Surround and support neurons, control the supply of nutrients to neurons, assist in the exchange of chemicals between neurons, destroy and remove damaged neurons. ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... •Controls the function of internal organs. •The autonomic nervous system provides internal homeostasis. •Autonomic reflexes control blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, water balance, body temperature and other homeostatic functions. •Divided into two major subdivisions: the sympathetic and par ...
... •Controls the function of internal organs. •The autonomic nervous system provides internal homeostasis. •Autonomic reflexes control blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, water balance, body temperature and other homeostatic functions. •Divided into two major subdivisions: the sympathetic and par ...
The Nervous System
... It means to keep things in balance. Homeostasis keeps internal conditions relatively constant despite change to external environments. ...
... It means to keep things in balance. Homeostasis keeps internal conditions relatively constant despite change to external environments. ...