Nerve cells - WordPress.com
... and are found in the Central Nervous System (CNS), that is in the tissues of the Brain and Spinal Cord. ...
... and are found in the Central Nervous System (CNS), that is in the tissues of the Brain and Spinal Cord. ...
The Nervous System
... towards the CNS Motor nerves – carry info from the CNS to muscles and organs ...
... towards the CNS Motor nerves – carry info from the CNS to muscles and organs ...
Lecture 6C
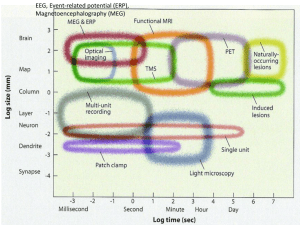
... – A series of X-rays is made from different angles; the images reflect the density of blood vessels in each area. – A computer combines the X-rays into a series of horizontal sections of the brain. ...
... – A series of X-rays is made from different angles; the images reflect the density of blood vessels in each area. – A computer combines the X-rays into a series of horizontal sections of the brain. ...
Nervous System
... Dementia - damaged brain cells caused by injury or disease (Alzheimer’s); memory loss and personality change. Drugs and the Nervous System ...
... Dementia - damaged brain cells caused by injury or disease (Alzheimer’s); memory loss and personality change. Drugs and the Nervous System ...
Module 3
... • Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from another neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons a ...
... • Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from another neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons a ...
Nueron - AP Psychology Community
... • Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from another neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons a ...
... • Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from another neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium) which mix with negative ions (Potassium) that is already inside the axon (thus Neurons a ...
Histology of Nerve the Nervous System
... Histology of Nerve the Nervous System human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons), assisted by many more glialcells. ...
... Histology of Nerve the Nervous System human body, is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons), assisted by many more glialcells. ...
Neurons
... Operate through electrical impulses Communicate with other neurons through chemical signals ...
... Operate through electrical impulses Communicate with other neurons through chemical signals ...
Name: Date: Period:
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
... types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Sensory neurons send information to the brain. Motor neurons carry out instructions from the brain. Interneurons carry the messages ‘in between’ the sensory and motor neurons. In today’s activity, we will be modeling how neurons work using ...
Neurons - Jordan High School
... Functional Divisions of PNS Afferent division Brings sensory info to CNS from receptors ...
... Functional Divisions of PNS Afferent division Brings sensory info to CNS from receptors ...
No Slide Title
... Receptors on Dendrites - Sensory (chemical reactions) - Chemicals from other neurons - Chemicals from endocrine glands - Chemicals from outside sources (e.g., Drugs) ...
... Receptors on Dendrites - Sensory (chemical reactions) - Chemicals from other neurons - Chemicals from endocrine glands - Chemicals from outside sources (e.g., Drugs) ...
Nervous System notes
... b. functional- based on the direction in which they transmit nerve impulses - sensory (afferent) – transmit form receptors in skin, sensory organs muscles, joints, and viscera to the brain and spinal cord - motor (efferent) – convey impulses from brain and spinal cord to effectors which may be muscl ...
... b. functional- based on the direction in which they transmit nerve impulses - sensory (afferent) – transmit form receptors in skin, sensory organs muscles, joints, and viscera to the brain and spinal cord - motor (efferent) – convey impulses from brain and spinal cord to effectors which may be muscl ...
Endocrine system: anatomy, Histology and Embryology
... Endocrine glands may be: • Unicellular (DNES = APUD) • Multicellular (thyroid, adrenal…..) ...
... Endocrine glands may be: • Unicellular (DNES = APUD) • Multicellular (thyroid, adrenal…..) ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
... Organization of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): – Brain and spinal cord – Command center – Interprets incoming sensory information – Make decisions based on past experiences ...
Nervous System
... and axons • Axons send information in the form of nerve impulses; each neuron has only one axon (usually) • Dendrites are numerous and receive the nerve impulses (electrochemical message) ...
... and axons • Axons send information in the form of nerve impulses; each neuron has only one axon (usually) • Dendrites are numerous and receive the nerve impulses (electrochemical message) ...
Breakdown of the Nervous System
... 1) bundles of subcortical gray matter deep within white matter 2) control large automatic skeletal muscle contractions and produce dopamine 2. Diencephalon – central core of brain; covered by cerebrum; 3 paired structures A) thalamus – connected by massa intermedia 1) relay station for sensory impul ...
... 1) bundles of subcortical gray matter deep within white matter 2) control large automatic skeletal muscle contractions and produce dopamine 2. Diencephalon – central core of brain; covered by cerebrum; 3 paired structures A) thalamus – connected by massa intermedia 1) relay station for sensory impul ...
Central Nervous System
... 1) bundles of subcortical gray matter deep within white matter 2) control large automatic skeletal muscle contractions and produce dopamine ...
... 1) bundles of subcortical gray matter deep within white matter 2) control large automatic skeletal muscle contractions and produce dopamine ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Age-related changes in hearing and vision can affect performance. Decline in sensory acuity affects: ...
... Age-related changes in hearing and vision can affect performance. Decline in sensory acuity affects: ...
Nervous System
... Function: To sense changes in their surroundings and respond by transmitting nerve impulses along cellular processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integ ...
... Function: To sense changes in their surroundings and respond by transmitting nerve impulses along cellular processes to other neurons or to muscles and glands. ◦ The complex patterns in which the neurons connect with each other and with muscle and gland cells they can coordinate, regulate, and integ ...
Quiz - psychm5
... Quiz CH 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
... Quiz CH 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
The Nervous System
... Ribosomes and rough ER (Nissl Substance)most active of any cell in the body Plasma membrane acts as part of the receptive surface Most located within the CNS (called nuclei) Cell body collections in the PNS are called ganglia ...
... Ribosomes and rough ER (Nissl Substance)most active of any cell in the body Plasma membrane acts as part of the receptive surface Most located within the CNS (called nuclei) Cell body collections in the PNS are called ganglia ...
3/26
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. CB 48.3 ...