Nervous system
... • Compared to other primates, newborns have very large heads relative to their body size. • Some researchers believe that humans have reached their maximum brain size. • Why??? ...
... • Compared to other primates, newborns have very large heads relative to their body size. • Some researchers believe that humans have reached their maximum brain size. • Why??? ...
`synapse`.
... released are recalled back into the axon terminal in a process called 'reuptake' so that they are available should the neuron need to fire again. ...
... released are recalled back into the axon terminal in a process called 'reuptake' so that they are available should the neuron need to fire again. ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... 16. Many tasks in the body are taken care of by the unconscious part of the brain, so that the brain’s owner doesn’t have to think about them. These tasks are performed by the A. Cerebrum B. Malpighian tubule C. Cortex D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the stru ...
... 16. Many tasks in the body are taken care of by the unconscious part of the brain, so that the brain’s owner doesn’t have to think about them. These tasks are performed by the A. Cerebrum B. Malpighian tubule C. Cortex D. Cerebellum _________ 17. Name three tasks that might be performed by the stru ...
nervous system ppt
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is pres ...
... In the normal communication process, dopamine is released by a neuron into the synapse, where it can bind to dopamine receptors on neighboring neurons. Normally, dopamine is then recycled back into the transmitting neuron by a specialized protein called the dopamine transporter. If cocaine is pres ...
49-1-2 Nervouse systems ppt
... • Ventricles of the brain are hollow, filled with cerebrospinal fluid • The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
... • Ventricles of the brain are hollow, filled with cerebrospinal fluid • The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes ...
File
... passed down to the cell body where the information is evaluated and on to the axon. Once the information is at axon it travel downs length of axon in form of electrical signal known as action potential. Once the electrical impulse has reached end of axon it must be transmitted to another neuron or c ...
... passed down to the cell body where the information is evaluated and on to the axon. Once the information is at axon it travel downs length of axon in form of electrical signal known as action potential. Once the electrical impulse has reached end of axon it must be transmitted to another neuron or c ...
Nervous System Note Packet
... c. Medulla Oblongata – d. Pons – e. Midbrain – f. Thalamus – g. Hypothalamus – - also controls pituitary gland which affects metabolism, sexual development, and emotions ...
... c. Medulla Oblongata – d. Pons – e. Midbrain – f. Thalamus – g. Hypothalamus – - also controls pituitary gland which affects metabolism, sexual development, and emotions ...
presentation
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...
... The cell body of one neuron is located in the spinal cord and brain and the second extends to a visceral effector. The Preganglionic fiber is the axon within the cell body that is located in the brain and spinal cord in which it travels through the CNS and synapse with the neurons within an autonomi ...
Do Now: Review the Human Spark
... Checking for Understanding Questions 1. What are the functions of the nervous system? 2. Describe 1 difference between the CNS and PNS. (do not say their names!) 3. List 4 structures of a neuron. ...
... Checking for Understanding Questions 1. What are the functions of the nervous system? 2. Describe 1 difference between the CNS and PNS. (do not say their names!) 3. List 4 structures of a neuron. ...
Chapter 6 - Sensory - Austin Community College
... Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons cell bodies are found in the terminal ganglia and their axons synapse with single visceral effectors. Sympathetic - “fight or flight” system, excites body in emergency or threatening situations Sympathetic preganglionic neurons have cell bodies in the lateral g ...
... Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons cell bodies are found in the terminal ganglia and their axons synapse with single visceral effectors. Sympathetic - “fight or flight” system, excites body in emergency or threatening situations Sympathetic preganglionic neurons have cell bodies in the lateral g ...
Autonomic Nervous System (Ch. 14)
... i. Heavily myelinated axons of the somatic motor neurons extend from CNS to the effector ii. Axons of the ANS are a two-neuron chain 1) Preganglionic (first) neuron has a lightly myelinated axon 2) Ganglionic (second) neuron extends to an effector organ 2. Neurotransmitter Effects a. Somatic motor n ...
... i. Heavily myelinated axons of the somatic motor neurons extend from CNS to the effector ii. Axons of the ANS are a two-neuron chain 1) Preganglionic (first) neuron has a lightly myelinated axon 2) Ganglionic (second) neuron extends to an effector organ 2. Neurotransmitter Effects a. Somatic motor n ...
nervous system development and histology
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards the CNS• most sensory neurons are unipolar, a few are bipolar• Motor (efferent) neurons – • transmit motor informa ...
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards the CNS• most sensory neurons are unipolar, a few are bipolar• Motor (efferent) neurons – • transmit motor informa ...
Chapter 6
... c. This amino acid neurotransmitter acts as excitatory signals, activating NMethyl-d–aspartate (NMDA) receptors which have been implicated in learning and memory. Overstimulation by this neurotransmitter of NMDA receptors, however, can cause nerve cell damage or cell death. d. This catecholamine neu ...
... c. This amino acid neurotransmitter acts as excitatory signals, activating NMethyl-d–aspartate (NMDA) receptors which have been implicated in learning and memory. Overstimulation by this neurotransmitter of NMDA receptors, however, can cause nerve cell damage or cell death. d. This catecholamine neu ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Swollen tips called synaptic end bulbs contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters ...
... • Swollen tips called synaptic end bulbs contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
File - BHS AP Psychology
... stubbed toe) that allows neural impulses to travel down an axon from node to node rather than more slowly along an axon that lacks this insulation. __________ Point 8: Neurotransmitter: Students should explain that neurotransmitters are released in response to an action potential and these neurotran ...
... stubbed toe) that allows neural impulses to travel down an axon from node to node rather than more slowly along an axon that lacks this insulation. __________ Point 8: Neurotransmitter: Students should explain that neurotransmitters are released in response to an action potential and these neurotran ...
Ch. 7 - The Nervous System
... E. Hypothalamus 1. Under the thalamus 2. Important autonomic nervous system center a. Helps regulate body temperature b. Controls water balance c. Regulates metabolism F. Hypothalamus (continued) 1. An important part of the limbic system (emotions) 2. The pituitary gland is attached to the hypothala ...
... E. Hypothalamus 1. Under the thalamus 2. Important autonomic nervous system center a. Helps regulate body temperature b. Controls water balance c. Regulates metabolism F. Hypothalamus (continued) 1. An important part of the limbic system (emotions) 2. The pituitary gland is attached to the hypothala ...
Autonomic nervous system
... 2) Modulated blood flow in the intestines 3) Regulates secretion from the intestinal glands ...
... 2) Modulated blood flow in the intestines 3) Regulates secretion from the intestinal glands ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... the body within a narrow range of physiological parameters, such as temperature, thirst, hunger, etc. Hypothalamus is important for homeostasis. Nuclei within the hypothalamus regulate homeostasis by comparing the body’s state with set points. ...
... the body within a narrow range of physiological parameters, such as temperature, thirst, hunger, etc. Hypothalamus is important for homeostasis. Nuclei within the hypothalamus regulate homeostasis by comparing the body’s state with set points. ...
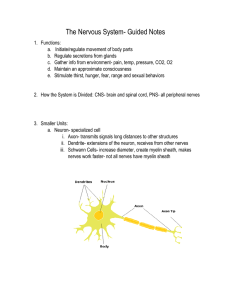
Nervous System Guided Notes
... Extends from base of the brain thru canal formed by vertebrae White matter-outer region, myelinated nerves Grey matter- inner portion, cell bodies 10. Sensory Somatic and Autonomic Systems: a. Autonomic: involuntary, controls internal environment of animal i. Two divisions: sympathetic and pa ...
... Extends from base of the brain thru canal formed by vertebrae White matter-outer region, myelinated nerves Grey matter- inner portion, cell bodies 10. Sensory Somatic and Autonomic Systems: a. Autonomic: involuntary, controls internal environment of animal i. Two divisions: sympathetic and pa ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Acetylcholine Acetylcholine is linked with learning and memory formation A lack of acetylcholine in the brain is thought to be partly responsible for the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. * See study by Martinez and Kesner, 1991, on lab mice ...
... Acetylcholine Acetylcholine is linked with learning and memory formation A lack of acetylcholine in the brain is thought to be partly responsible for the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. * See study by Martinez and Kesner, 1991, on lab mice ...
013368718X_CH31_483-498.indd
... Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system collects information about the body’s internal and external environment, processes that information, and responds to it. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves and supporting cells. It collects information about the body’s internal and ext ...
... Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system collects information about the body’s internal and external environment, processes that information, and responds to it. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves and supporting cells. It collects information about the body’s internal and ext ...