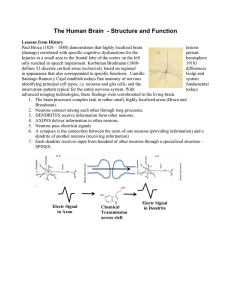
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal establish todays fine anatomy of nervous system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fundamental innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With toda ...
... in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal establish todays fine anatomy of nervous system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fundamental innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With toda ...
C! **D!**E!**F! - Amherst College
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
seminario - Instituto Cajal
... orthodromic responses in characterized dRPO and vRPO neurons. Accordingly, anatomical studies showed retrogradely-labeled neurons from both tegmental areas within the PeF, some of which contained Hcrt, and positive Hcrt synapses on dRPO and vRPO neurons. Hcrt-1 application in dRPO provoked an increa ...
... orthodromic responses in characterized dRPO and vRPO neurons. Accordingly, anatomical studies showed retrogradely-labeled neurons from both tegmental areas within the PeF, some of which contained Hcrt, and positive Hcrt synapses on dRPO and vRPO neurons. Hcrt-1 application in dRPO provoked an increa ...
METABOLIC-REDOX ADAPTATIONS OF NEURONS AND
... Energy and redox conservation in the brain requires metabolic cooperation between distinct cell types. We have identified mechanisms and factors that maintain cell specific programs to allow this metabolic-redox collaboration. Neurons show a high dependence on mitochondrial oxidative metabolism for ...
... Energy and redox conservation in the brain requires metabolic cooperation between distinct cell types. We have identified mechanisms and factors that maintain cell specific programs to allow this metabolic-redox collaboration. Neurons show a high dependence on mitochondrial oxidative metabolism for ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... located along the spinal cord; they derive during development from common progenitor cells which differentiate into many types of neurons that are mediating sensory information (touch, pain, heat, cold, and proprioception) from the body to the central nervous system. This differentiation process is ...
... located along the spinal cord; they derive during development from common progenitor cells which differentiate into many types of neurons that are mediating sensory information (touch, pain, heat, cold, and proprioception) from the body to the central nervous system. This differentiation process is ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage pulse that propagates along it (see arrow). ...
... (charged atoms) to flow into the cell from outside. This causes more channels farther along the axon to open, creating a voltage pulse that propagates along it (see arrow). ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
Neural Basis of the Oblique Effect
... and these cells exhibit a narrower tuning width at horizontal angles. – The slopes of the tuning curves are also steeper for horizontal orientations. ...
... and these cells exhibit a narrower tuning width at horizontal angles. – The slopes of the tuning curves are also steeper for horizontal orientations. ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... • About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
... • About 100 billion neurons (nerve cells) in the human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
File - SSHS AP Psychology
... cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. ...
... cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. ...
Levetiracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsy
... Brain scanning (CT scan, MRI) - to discover if the ...
... Brain scanning (CT scan, MRI) - to discover if the ...
Lecture 6C
... Macaque monkeys were trained to stare at a pattern (left panel) while injected with radioactive glucose. The radioactive glucose was absorbed and metabolized by active neurons to a much greater extent than by other neurons. After the experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioacti ...
... Macaque monkeys were trained to stare at a pattern (left panel) while injected with radioactive glucose. The radioactive glucose was absorbed and metabolized by active neurons to a much greater extent than by other neurons. After the experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioacti ...
Slide ()
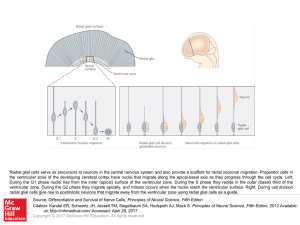
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
... Radial glial cells serve as precursors to neurons in the central nervous system and also provide a scaffold for radial neuronal migration. Progenitor cells in the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex have nuclei that migrate along the apical-basal axis as they progress through the cell ...
Lec17BioImProc
... Cones: Color sensitive, but poor light sensitivity 6.4E6, peak density in fovea ...
... Cones: Color sensitive, but poor light sensitivity 6.4E6, peak density in fovea ...
UNIT II: THE HUMAN BRAIN
... – Provide scaffolding to support both developing and mature neurons. – Wrap around neurons to form insulation from electrical signals – Releasing chemicals that influence neuron growth ...
... – Provide scaffolding to support both developing and mature neurons. – Wrap around neurons to form insulation from electrical signals – Releasing chemicals that influence neuron growth ...
myers Chapter 02 review game
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
... the cell body to receive information from other neurons are called: ...
Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... (space between neurons) – This is called a synaptic transmission ...
... (space between neurons) – This is called a synaptic transmission ...
Unit 3 Essential Vocabulary File - District 196 e
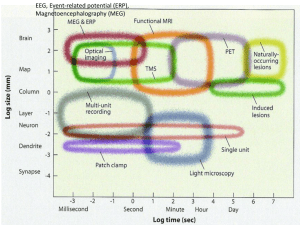
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.