Quiz - Web Adventures
... 1) Which scientist won a Nobel Prize for discovering how nerve cells communicate? a) Friedrich Serturner b) Hippocrates c) Linnaeus d) Otto Loewi 2) The part of a neuron where the receptors are located is the: a) Axon b) Cell body c) Dendrite d) Myelin 3) Synapses are: a) Gaps between neurons b) Ele ...
... 1) Which scientist won a Nobel Prize for discovering how nerve cells communicate? a) Friedrich Serturner b) Hippocrates c) Linnaeus d) Otto Loewi 2) The part of a neuron where the receptors are located is the: a) Axon b) Cell body c) Dendrite d) Myelin 3) Synapses are: a) Gaps between neurons b) Ele ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... cerebrum, medulla oblongata, pons, thalamus, hypothalamus. Know the location and main function of each component. What would be the effect of damage individually to each of these components? (11.8) 36. The cerebral cortex is involved in many complex functions of the brain that require coordination o ...
... cerebrum, medulla oblongata, pons, thalamus, hypothalamus. Know the location and main function of each component. What would be the effect of damage individually to each of these components? (11.8) 36. The cerebral cortex is involved in many complex functions of the brain that require coordination o ...
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
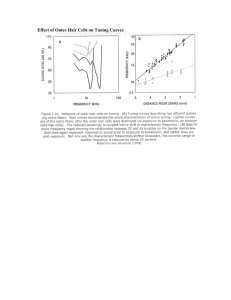
... waves elicit maximal responses at the basal end of the membrane, near the stapes, whereas lowfrequency sounds induce maxima at the other end, near the apex of the cochlea. The membrane has been "uncoiled" in this illustration to show the sensory hair cells, each studded with stiff rods called stereo ...
... waves elicit maximal responses at the basal end of the membrane, near the stapes, whereas lowfrequency sounds induce maxima at the other end, near the apex of the cochlea. The membrane has been "uncoiled" in this illustration to show the sensory hair cells, each studded with stiff rods called stereo ...
A1987F573800001
... H-thymidine, I found that in the rhesus monkey, granule cells have their last mitotic division during the late gestational and early neonatal period. How do postmitotic cells find their way through neural tissue that, at this age, is already densely packed with synapses? ...
... H-thymidine, I found that in the rhesus monkey, granule cells have their last mitotic division during the late gestational and early neonatal period. How do postmitotic cells find their way through neural tissue that, at this age, is already densely packed with synapses? ...
The Brain
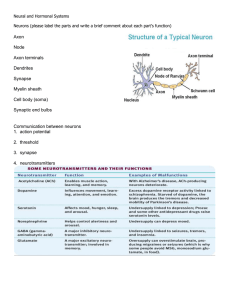
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
NATURAL PRODUCT EXTRACTS TO PROTECT
... rotenone (relevant to Parkinson’s disease) and thapsigargin (which increases cellular calcium content that causes death to neurons relevant to most neurological injuries). These results invite the promise of new ...
... rotenone (relevant to Parkinson’s disease) and thapsigargin (which increases cellular calcium content that causes death to neurons relevant to most neurological injuries). These results invite the promise of new ...
Slide ()
... Different neural mechanisms underlie long-term potentiation at each of the three synapses in the trisynaptic pathway in the hippocampus. Long-term potentiation (LTP) is present at synapses throughout the hippocampus but depends to differing degrees on activation of NMDA-type glutamate receptors. A. ...
... Different neural mechanisms underlie long-term potentiation at each of the three synapses in the trisynaptic pathway in the hippocampus. Long-term potentiation (LTP) is present at synapses throughout the hippocampus but depends to differing degrees on activation of NMDA-type glutamate receptors. A. ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... CELL MEMBRANE: thin, porous outer covering of a neuron or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
... CELL MEMBRANE: thin, porous outer covering of a neuron or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
SM 11.04.12 - Premio principe asturias
... The jury for this prestigious award recently announced in Oviedo, Spain that this year the prize for Technical and Scientific Research would be awarded to three distinguished researchers in the field of neuroscience: Giacomo Rizzolati of Italy, Joseph Altman of the U.S., and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla Ro ...
... The jury for this prestigious award recently announced in Oviedo, Spain that this year the prize for Technical and Scientific Research would be awarded to three distinguished researchers in the field of neuroscience: Giacomo Rizzolati of Italy, Joseph Altman of the U.S., and Arturo Alvarez-Buylla Ro ...
Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other
... Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other somatic cells By Balogh Olivér ...
... Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other somatic cells By Balogh Olivér ...
Exercise 17 - Harford Community College
... Neurons specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body ...
... Neurons specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body ...
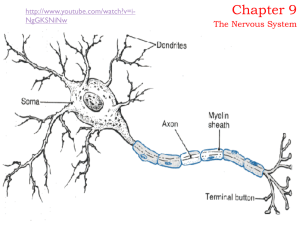
The Nervous System
... Anatomy of a Neuron Each neuron contains: - Cell body with nucleus - Dendrites : fibers that receive messages from other neurons - Axons : fibers that send messages to other neurons ...
... Anatomy of a Neuron Each neuron contains: - Cell body with nucleus - Dendrites : fibers that receive messages from other neurons - Axons : fibers that send messages to other neurons ...
Slide ()
... Neurons are classified as unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar according to the number of processes that originate from the cell body. A. Unipolar cells have a single process emanating from the cell. Different segments serve as receptive surfaces or releasing terminals. Unipolar cells are characteristic ...
... Neurons are classified as unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar according to the number of processes that originate from the cell body. A. Unipolar cells have a single process emanating from the cell. Different segments serve as receptive surfaces or releasing terminals. Unipolar cells are characteristic ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
neurophilosophical foundations 2 levels of organization cell theory
... performance of cognitive activities, the neuronal level is generally regarded as too low a level of organization to make sense of cognition • Populations of neurons seem to be involved in an cognitive task • Challenge: can one distinguish brain structures at a higher level of organization, one that ...
... performance of cognitive activities, the neuronal level is generally regarded as too low a level of organization to make sense of cognition • Populations of neurons seem to be involved in an cognitive task • Challenge: can one distinguish brain structures at a higher level of organization, one that ...
Neuron-target interaction 1. Synapse formation between presynaptic
... Act on Trk receptors and p75(low affinity) receptor Retrograde transport Differential effects ...
... Act on Trk receptors and p75(low affinity) receptor Retrograde transport Differential effects ...
Chapter 9 Nerves
... Sensory functions employ receptors that detect internal and external changes ...
... Sensory functions employ receptors that detect internal and external changes ...
Perception, learning and memory - Max-Planck
... Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in combination rather than in isolation, and experimental techniques traditionally used to study individual elements need to evolve towards this. One new approach involves light-activated genetic switches that control the activity of sp ...
... Networks, neurons and molecular constituents need to be studied in combination rather than in isolation, and experimental techniques traditionally used to study individual elements need to evolve towards this. One new approach involves light-activated genetic switches that control the activity of sp ...
1050927abstract
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
APPLIED MATHEMATICS SEMINAR - Arlington
... Without conscious thought, we breath over and over again reliably throughout most of our lives, adjusting automatically to changes in metabolic and environmental demands. This remarkable capability requires the generation of a robust, tunable rhythm by a network of neurons in the brain stem, as well ...
... Without conscious thought, we breath over and over again reliably throughout most of our lives, adjusting automatically to changes in metabolic and environmental demands. This remarkable capability requires the generation of a robust, tunable rhythm by a network of neurons in the brain stem, as well ...
Hippocampus+and+Neurons+Final+Draft
... brains of vertebrates, situated at the base of the forebrain that are connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other areas. ...
... brains of vertebrates, situated at the base of the forebrain that are connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other areas. ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... Action potentials are electrical signals carried along neurons. ...
... Action potentials are electrical signals carried along neurons. ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.