Key Facts
... In the hot Big Bang Theory, the observable universe began with an instantaneously expanding point, roughly ten to twenty billion years ago. Since then, the universe has continued to expand, gradually increasing the distance between our Galaxy and external galaxies. The expansion of the universe "str ...
... In the hot Big Bang Theory, the observable universe began with an instantaneously expanding point, roughly ten to twenty billion years ago. Since then, the universe has continued to expand, gradually increasing the distance between our Galaxy and external galaxies. The expansion of the universe "str ...
An Introduction - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to form low energy gammaray photons that can not reverse the process •As a result, matter and anti-matter content decreased, and radiation content increased •From 1 second to 380,000 years, the universe is ...
... •At about t = 1 second, temperature fell below 6 X 109 K, electrons and positions annihilated to form low energy gammaray photons that can not reverse the process •As a result, matter and anti-matter content decreased, and radiation content increased •From 1 second to 380,000 years, the universe is ...
Beverly`s writings on Nassim Haramein
... don’t know what it is, as they can’t see or measure it, so they named it “dark matter” and “dark energy” and believe it is some sort of as yet undiscovered particle.” That means our current understanding of the universe is based on just 4 percent of what we know is out there. That’s not a very good ...
... don’t know what it is, as they can’t see or measure it, so they named it “dark matter” and “dark energy” and believe it is some sort of as yet undiscovered particle.” That means our current understanding of the universe is based on just 4 percent of what we know is out there. That’s not a very good ...
The Universe
... galaxies. Many of them are surrounded by discs of material. As the discs swirl around them like a whirlpool, they become extremely hot and give off X-rays. Black holes come in many different sizes. Many of them are only a few times more massive than the Sun. ...
... galaxies. Many of them are surrounded by discs of material. As the discs swirl around them like a whirlpool, they become extremely hot and give off X-rays. Black holes come in many different sizes. Many of them are only a few times more massive than the Sun. ...
The Big Bang
... • It’s matter that’s not visible, but can only be detected by its gravitational effects – Best theory is that it is an exotic particle – If it is what we think it is, we might be close to finding it! ...
... • It’s matter that’s not visible, but can only be detected by its gravitational effects – Best theory is that it is an exotic particle – If it is what we think it is, we might be close to finding it! ...
2.5.4 astronomical distances Parallax and Distances to Stars
... is NOT a definition of time. It is the distance that light can travel through a vacuum in 1 year. If you work it out it is – 9.461 x 1015m When you consider the ridiculous distance involved in astronomy, it makes sense to have large units! ...
... is NOT a definition of time. It is the distance that light can travel through a vacuum in 1 year. If you work it out it is – 9.461 x 1015m When you consider the ridiculous distance involved in astronomy, it makes sense to have large units! ...
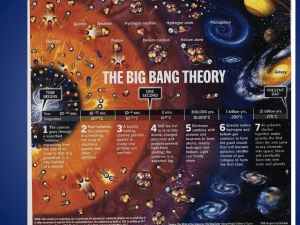
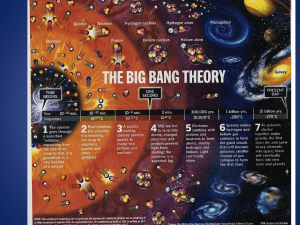
The Big Bang Theory
... Visible wavelengths emitted by objects moving away from us are shifted towards the red part of the visible spectrum The faster they move away from us, the more they are redshifted. Thus, redshift is a reasonable way to measure the speed of an object (this, by the way, is the principal by which radar ...
... Visible wavelengths emitted by objects moving away from us are shifted towards the red part of the visible spectrum The faster they move away from us, the more they are redshifted. Thus, redshift is a reasonable way to measure the speed of an object (this, by the way, is the principal by which radar ...
Week 2 (9/27) – Opinion Poll I am taking this class because:
... D. The nearest star to the Sun is about 4 light years away E. For many stars in our galaxy, astronomers have measured the “wobble” induced by the gravity of the orbiting planet ...
... D. The nearest star to the Sun is about 4 light years away E. For many stars in our galaxy, astronomers have measured the “wobble” induced by the gravity of the orbiting planet ...
The Big Bang
... exploded out of the big bang did not distribute itself evenly throughout the universe? What evidence supports this hypothesis? According to this theory, how old is the universe? ...
... exploded out of the big bang did not distribute itself evenly throughout the universe? What evidence supports this hypothesis? According to this theory, how old is the universe? ...
The Universe and Big Bang Theory Review Sheet
... 5. What does the red shift suggest? - It suggests the universe is expanding. 6. The farther the galaxy is from earth, the greater the red shift. 7. From where do stars originate from? -from clouds of gas and dust clouds. 8. How does gravity play a role in the forming of stars? - gravity causes the g ...
... 5. What does the red shift suggest? - It suggests the universe is expanding. 6. The farther the galaxy is from earth, the greater the red shift. 7. From where do stars originate from? -from clouds of gas and dust clouds. 8. How does gravity play a role in the forming of stars? - gravity causes the g ...
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s2 ...
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
... luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
ITB - In the Beginning
... The Hot Big Bang (the standard model) Developed in the late 1940’s by Gamow– named by Hoyle as an “insult” – it is the current basic model. Out of “nothingness”; the universe has a tiny, hot, beginning – then expands. As the energy-universe expands, it cools enough for matter to form (E=mc2), then ...
... The Hot Big Bang (the standard model) Developed in the late 1940’s by Gamow– named by Hoyle as an “insult” – it is the current basic model. Out of “nothingness”; the universe has a tiny, hot, beginning – then expands. As the energy-universe expands, it cools enough for matter to form (E=mc2), then ...
Describe essential ideas about the composition and structure of the
... Identify the accomplishments and contributions provided by selected past and present scientists in the field of astronomy. Identify and articulate space program efforts to investigate possibilities of living in space and on other planets. Explain essential ideas about the composition and structu ...
... Identify the accomplishments and contributions provided by selected past and present scientists in the field of astronomy. Identify and articulate space program efforts to investigate possibilities of living in space and on other planets. Explain essential ideas about the composition and structu ...
Document
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... • The H-R diagram shows the relationship of a star’s surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of stars in our galaxy are main sequence ...
... • The H-R diagram shows the relationship of a star’s surface temperature and its absolute magnitude. • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of stars in our galaxy are main sequence ...
notes_chapter1 - Auburn University
... He concluded that galaxies were moving away rapidly. No galaxies were found to be moving toward Earth. ...
... He concluded that galaxies were moving away rapidly. No galaxies were found to be moving toward Earth. ...
The Big Bang!
... Visible wavelengths emitted by objects moving away from us are shifted towards the red part of the visible spectrum The faster they move away from us, the more they are redshifted. Thus, redshift is a reasonable way to measure the speed of an object (this, by the way, is the principal by which radar ...
... Visible wavelengths emitted by objects moving away from us are shifted towards the red part of the visible spectrum The faster they move away from us, the more they are redshifted. Thus, redshift is a reasonable way to measure the speed of an object (this, by the way, is the principal by which radar ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... A. the star’s luminosity, or brightness B. the star’s color C. the star’s size D. All of these are possible characteristics. 7. Although they did not have telescopes, ancient people studied space. What did they observe? A. details on planets in far-away galaxies B. only the sun and the moon C. the c ...
... A. the star’s luminosity, or brightness B. the star’s color C. the star’s size D. All of these are possible characteristics. 7. Although they did not have telescopes, ancient people studied space. What did they observe? A. details on planets in far-away galaxies B. only the sun and the moon C. the c ...
Astronomy Introduction
... • Natural science that is the study of celestial objects, the physics, chemistry, mathematics and evolution of these objects and phenomena that originate outside/beyond the atmosphere of earth. Examples: supernovae, gamma ray bursts, black holes, neutron stars, pulsars, cosmic background radiation. ...
... • Natural science that is the study of celestial objects, the physics, chemistry, mathematics and evolution of these objects and phenomena that originate outside/beyond the atmosphere of earth. Examples: supernovae, gamma ray bursts, black holes, neutron stars, pulsars, cosmic background radiation. ...
Sample Writing Topics in Cosmology, Astro, and Particle Physics
... The HESS telescope: recent discovery of unanticipated sources of high-energy gamma rays, a new astronomy? From the Etvös experiment to LISA (via Ligo and Virgo): when will we detect the first gravity wave? ANTARES and IceCube: a neutrino window on active galactic nuclei? CDF and D0 at the Tevatron c ...
... The HESS telescope: recent discovery of unanticipated sources of high-energy gamma rays, a new astronomy? From the Etvös experiment to LISA (via Ligo and Virgo): when will we detect the first gravity wave? ANTARES and IceCube: a neutrino window on active galactic nuclei? CDF and D0 at the Tevatron c ...
Flatness problem

The flatness problem (also known as the oldness problem) is a cosmological fine-tuning problem within the Big Bang model of the universe. Such problems arise from the observation that some of the initial conditions of the universe appear to be fine-tuned to very 'special' values, and that a small deviation from these values would have had massive effects on the nature of the universe at the current time.In the case of the flatness problem, the parameter which appears fine-tuned is the density of matter and energy in the universe. This value affects the curvature of space-time, with a very specific critical value being required for a flat universe. The current density of the universe is observed to be very close to this critical value. Since the total density departs rapidly from the critical value over cosmic time, the early universe must have had a density even closer to the critical density, departing from it by one part in 1062 or less. This leads cosmologists to question how the initial density came to be so closely fine-tuned to this 'special' value.The problem was first mentioned by Robert Dicke in 1969. The most commonly accepted solution among cosmologists is cosmic inflation, the idea that the universe went through a brief period of extremely rapid expansion in the first fraction of a second after the Big Bang; along with the monopole problem and the horizon problem, the flatness problem is one of the three primary motivations for inflationary theory.