Dark Matter Dark Energy The History of the Universe More of the
... luminosity of the supernovae which are used to get distances. All Type Ia Supernovae definitely come from white dwarfs but it is not known whether all involve accretion from a nearby star, merging with another white dwarf, or either/or! ...
... luminosity of the supernovae which are used to get distances. All Type Ia Supernovae definitely come from white dwarfs but it is not known whether all involve accretion from a nearby star, merging with another white dwarf, or either/or! ...
100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200
... luminosity of the supernovae which are used to get distances. All Type Ia Supernovae definitely come from white dwarfs but it is not known whether all involve accretion from a nearby star, merging with another white dwarf, or either/or! ...
... luminosity of the supernovae which are used to get distances. All Type Ia Supernovae definitely come from white dwarfs but it is not known whether all involve accretion from a nearby star, merging with another white dwarf, or either/or! ...
The New Cosmology: Our Expanding Universe
... on how big one made the circle and how many of them one invented to do the job. Copernicus realized that placing the sun in the center of the universe, and the planets orbiting this center, would both be simpler and would explain observable fact that before could not be explained. This is called the ...
... on how big one made the circle and how many of them one invented to do the job. Copernicus realized that placing the sun in the center of the universe, and the planets orbiting this center, would both be simpler and would explain observable fact that before could not be explained. This is called the ...
The New Cosmology: Our Expanding Universe
... on how big one made the circle and how many of them one invented to do the job. Copernicus realized that placing the sun in the center of the universe, and the planets orbiting this center, would both be simpler and would explain observable fact that before could not be explained. This is called the ...
... on how big one made the circle and how many of them one invented to do the job. Copernicus realized that placing the sun in the center of the universe, and the planets orbiting this center, would both be simpler and would explain observable fact that before could not be explained. This is called the ...
Star Groups and Big Bang Power Point
... All matter and energy in the early universe were compressed into a small volume at an extremely high temperature until the temperature cooled and all of the matter and energy were forced outward in all directions. ...
... All matter and energy in the early universe were compressed into a small volume at an extremely high temperature until the temperature cooled and all of the matter and energy were forced outward in all directions. ...
Unit 3 - Section 9.7 Stellar Spectra, Dark Matter0
... We seem to accept the hypothesis of the Big Bang as the start of the Universe some 14 billion years ago. From a singularity (…we shall leave it undefined…), all the energy and matter in the present Universe expanded. In other words, there is a finite amount of both matter and energy in the Universe. ...
... We seem to accept the hypothesis of the Big Bang as the start of the Universe some 14 billion years ago. From a singularity (…we shall leave it undefined…), all the energy and matter in the present Universe expanded. In other words, there is a finite amount of both matter and energy in the Universe. ...
PARTS OF THE UNIVERSE
... v Big Bang Theory: states that all matter and energy were once packed into a tiny particle smaller than a speck of dust. v The particle began to expand and matter and energy moved rapidly outward in all directions. v The matter cooled and collected to form stars, galaxies, nebulae, and planets ...
... v Big Bang Theory: states that all matter and energy were once packed into a tiny particle smaller than a speck of dust. v The particle began to expand and matter and energy moved rapidly outward in all directions. v The matter cooled and collected to form stars, galaxies, nebulae, and planets ...
Summer_Talk_new - University of Toronto, Particle Physics and
... has velocity c and has zero mass • In glass, a photon: has velocity < c , same as an effective mass Refractive Index • This is due to photon interacting with electromagnetic field in condensed matter • By analogy can understand masses of particles generated by Higgs Field in vacuum ...
... has velocity c and has zero mass • In glass, a photon: has velocity < c , same as an effective mass Refractive Index • This is due to photon interacting with electromagnetic field in condensed matter • By analogy can understand masses of particles generated by Higgs Field in vacuum ...
Studying Space Chapter 26 Notes
... 2d. Students know that stars differ in their life cycles, and visual, radio, and x-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
... 2d. Students know that stars differ in their life cycles, and visual, radio, and x-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... a. Appreciate the scale of the universe and basic structure in relationship to the Big Bang theory. b. Give an historical perspective on the development of modern astronomy in conjunction with the development of Newtonian Mechanics and an understanding of gravity, as illustrated by the shift from a ...
... a. Appreciate the scale of the universe and basic structure in relationship to the Big Bang theory. b. Give an historical perspective on the development of modern astronomy in conjunction with the development of Newtonian Mechanics and an understanding of gravity, as illustrated by the shift from a ...
Cosmology and Astrophysics II
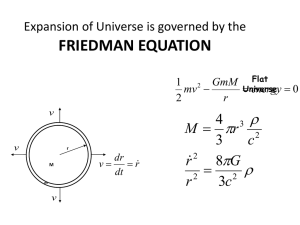
... universe was first derived using General Relativity but we have seen that they can be derived from Newton’s equations. ...
... universe was first derived using General Relativity but we have seen that they can be derived from Newton’s equations. ...
here
... is the laws of gravity which need revision. Under MOND, any object whose acceleration drops below some small threshold value receives an extra accelerative “kick” – this kick is tiny, a 1 part in 10 billion effect. An undetectable modification on Earth today, but its effect on the scale of galaxies ...
... is the laws of gravity which need revision. Under MOND, any object whose acceleration drops below some small threshold value receives an extra accelerative “kick” – this kick is tiny, a 1 part in 10 billion effect. An undetectable modification on Earth today, but its effect on the scale of galaxies ...
9. The very beginning - Mullard Space Science Laboratory
... 9. The beginning • This short lecture: • The hot big bang • Timeline –10-43 seconds to 380,000 years. ...
... 9. The beginning • This short lecture: • The hot big bang • Timeline –10-43 seconds to 380,000 years. ...
Age, EvoluFon, and Size of the Cosmos
... diameter (sphere defined by how far light has been able to travel since the beginning) ...
... diameter (sphere defined by how far light has been able to travel since the beginning) ...
Our Universe
... Nebulas are clouds of gas and dust in space. Gravity pulls the gas and dust particles closer and closer together until conditions are right for nuclear fusion to begin ...
... Nebulas are clouds of gas and dust in space. Gravity pulls the gas and dust particles closer and closer together until conditions are right for nuclear fusion to begin ...
Big Bang
... • There must have been a very slight excess of matter over antimatter • Like for every one billion antiprotons • There were one billion and one protons • So the billion antiprotons annihilated the billion ...
... • There must have been a very slight excess of matter over antimatter • Like for every one billion antiprotons • There were one billion and one protons • So the billion antiprotons annihilated the billion ...
Standard 1-1.A “The Big Bang Theory” Study Notes
... 7. Hubble’s discovery that there was red shift in the spectra of galaxies led to an understanding that the universe is expanding. 8. Astronomers believe that cosmic background radiation formed shortly after the big bang. 9. The event which began the universe was the big bang. 10. The two elements th ...
... 7. Hubble’s discovery that there was red shift in the spectra of galaxies led to an understanding that the universe is expanding. 8. Astronomers believe that cosmic background radiation formed shortly after the big bang. 9. The event which began the universe was the big bang. 10. The two elements th ...
Document
... extract around 10% of the source’s rest mass energy (same efficiency would give longer lifetime for a less luminous source) Is this realistic? Energy source believed to be gravitational infall (accretion) of matter onto a neutron star from a binary companion. Energy yield / unit mass ...
... extract around 10% of the source’s rest mass energy (same efficiency would give longer lifetime for a less luminous source) Is this realistic? Energy source believed to be gravitational infall (accretion) of matter onto a neutron star from a binary companion. Energy yield / unit mass ...
However the Big Bang theory had some competition…
... of a balloon, all galaxies are moving apart from each other, there is no centre!). Matter was thrown out in all directions forming stars and galaxies. Both Space and time were created in the Big Bang. However the Big Bang theory had some competition… ...
... of a balloon, all galaxies are moving apart from each other, there is no centre!). Matter was thrown out in all directions forming stars and galaxies. Both Space and time were created in the Big Bang. However the Big Bang theory had some competition… ...
Key Areas covered
... • Yes the Universe is expanding. We know this because of: 1. Stars / galaxies are moving away from us; 2. Cosmic microwave background radiation; and 3. The abundance of light elements • It is expanding in all directions with the space between each galaxy increasing as they move away from each other ...
... • Yes the Universe is expanding. We know this because of: 1. Stars / galaxies are moving away from us; 2. Cosmic microwave background radiation; and 3. The abundance of light elements • It is expanding in all directions with the space between each galaxy increasing as they move away from each other ...
Key Areas covered
... enough to light our sky at night. The only explanation that it is not is that the stars are moving away from us. An expanding universe must have started out infinitely small and agrees with the Big Bang Theory ...
... enough to light our sky at night. The only explanation that it is not is that the stars are moving away from us. An expanding universe must have started out infinitely small and agrees with the Big Bang Theory ...
Introduction of Astronomy Course No.: AST 1010 No. of Credit Hours
... The Core Learning Areas represent a common body of skills and knowledge to which all graduates with associate’s degrees should be exposed and for which the college may determine certain levels of competency which will be assessed through the general education curriculum. Scientific reasoning is the ...
... The Core Learning Areas represent a common body of skills and knowledge to which all graduates with associate’s degrees should be exposed and for which the college may determine certain levels of competency which will be assessed through the general education curriculum. Scientific reasoning is the ...
Galaxy Zoo: Pre and post‐workshop information
... Hubble showed there was a positive linear relationship between the velocity and distance of distant galaxies i.e. more distant galaxies are receding faster. The gradient of this graph is called H0 (Hubble’s constant), this gives the time since the Big Bang i.e. the age of the universe. The most accu ...
... Hubble showed there was a positive linear relationship between the velocity and distance of distant galaxies i.e. more distant galaxies are receding faster. The gradient of this graph is called H0 (Hubble’s constant), this gives the time since the Big Bang i.e. the age of the universe. The most accu ...
Flatness problem

The flatness problem (also known as the oldness problem) is a cosmological fine-tuning problem within the Big Bang model of the universe. Such problems arise from the observation that some of the initial conditions of the universe appear to be fine-tuned to very 'special' values, and that a small deviation from these values would have had massive effects on the nature of the universe at the current time.In the case of the flatness problem, the parameter which appears fine-tuned is the density of matter and energy in the universe. This value affects the curvature of space-time, with a very specific critical value being required for a flat universe. The current density of the universe is observed to be very close to this critical value. Since the total density departs rapidly from the critical value over cosmic time, the early universe must have had a density even closer to the critical density, departing from it by one part in 1062 or less. This leads cosmologists to question how the initial density came to be so closely fine-tuned to this 'special' value.The problem was first mentioned by Robert Dicke in 1969. The most commonly accepted solution among cosmologists is cosmic inflation, the idea that the universe went through a brief period of extremely rapid expansion in the first fraction of a second after the Big Bang; along with the monopole problem and the horizon problem, the flatness problem is one of the three primary motivations for inflationary theory.