Cosmic Evolution - University of Southern Maine
... and when we die we decay to ultimate disorder, thereby returning our elemental resources to Earth and the universe that gave us life. All things will eventually degenerate into chaotic, randomized, less ordered states. By utilizing energy, however, order can be achieved temporarily, or at least the ...
... and when we die we decay to ultimate disorder, thereby returning our elemental resources to Earth and the universe that gave us life. All things will eventually degenerate into chaotic, randomized, less ordered states. By utilizing energy, however, order can be achieved temporarily, or at least the ...
Alexander Polnarev QMUL, SPA 28 March 2014
... The expansion of the universe has caused that light to become dimmer and to shift to lower energies, but it can still be seen as microwave radiation - the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). ...
... The expansion of the universe has caused that light to become dimmer and to shift to lower energies, but it can still be seen as microwave radiation - the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). ...
Question 1
... Question 1 Based on galactic rotation curves and motions in clusters of galaxies, dark matter a) makes up about 90 percent of the matter in the universe. b) is best detected by the largest optical ...
... Question 1 Based on galactic rotation curves and motions in clusters of galaxies, dark matter a) makes up about 90 percent of the matter in the universe. b) is best detected by the largest optical ...
WORMHOLES AND SCIENCE FICTION According to the
... it reaches a maximum radius at the throat of r = 2M (maximum circumference of 4πM; maximum surface area of 16πM2). It then contracts and pinches off, leaving the two universes disconnected and containing singularities (r = 0) once again. The formation, expansion, and collapse of the bridge occur so ...
... it reaches a maximum radius at the throat of r = 2M (maximum circumference of 4πM; maximum surface area of 16πM2). It then contracts and pinches off, leaving the two universes disconnected and containing singularities (r = 0) once again. The formation, expansion, and collapse of the bridge occur so ...
A beam of antimatter could help to unravel the secrets of
... The supremacy of matter Why are we made of matter? This question does not have a commonly accepted answer yet. To answer this question one must go back in time to when the Universe was formed, to the Big Bang. A few moments after the Big Bang, around 14 billion years ago, the Universe was in a phase ...
... The supremacy of matter Why are we made of matter? This question does not have a commonly accepted answer yet. To answer this question one must go back in time to when the Universe was formed, to the Big Bang. A few moments after the Big Bang, around 14 billion years ago, the Universe was in a phase ...
threshold 1— the big bang
... • The Universe appears to emerge from nothing, but scientists cannot describe the moments before the Big Bang or the moment of the Big Bang itself. Major questions surround the origin of the Universe. • While four fundamental forces were created by the Big Bang, gravity has played the most influenti ...
... • The Universe appears to emerge from nothing, but scientists cannot describe the moments before the Big Bang or the moment of the Big Bang itself. Major questions surround the origin of the Universe. • While four fundamental forces were created by the Big Bang, gravity has played the most influenti ...
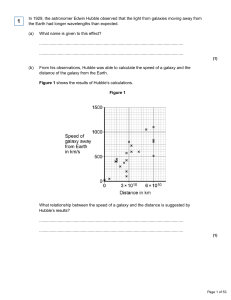
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from
... Why was the discovery of CMBR so important to the scientists believing the ‘Big Bang’ theory to be correct? ...
... Why was the discovery of CMBR so important to the scientists believing the ‘Big Bang’ theory to be correct? ...
a MS Word version.
... 2. What is "star gauging" and what did this technique tell us about the shape of our "galaxy"? This technique was used up until the early 20th century, name an 18th century astronomer and a 20th century astronomer who both used this technique. Where did this technique indicate the Sun was in the "g ...
... 2. What is "star gauging" and what did this technique tell us about the shape of our "galaxy"? This technique was used up until the early 20th century, name an 18th century astronomer and a 20th century astronomer who both used this technique. Where did this technique indicate the Sun was in the "g ...
FREE Sample Here
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
Chapter-by-Chapter Guide - We can offer most test bank and
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
FREE Sample Here
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
FREE Sample Here
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
... went far enough back in time, the universe would be compressed until everything were on top of everything else. This suggests that the universe may have been very tiny and dense at some point in the distant past and has been expanding ever since. This beginning is what we call the Big Bang. Based on ...
Problem 4.31 The circular disk of radius a shown in Fig. 4
... (a) Let V1 and V2 be the electric potentials across the upper and lower dielectrics, respectively. What are the corresponding electric fields E1 and E2 ? By applying the appropriate boundary condition at the interface between the two dielectrics, obtain explicit expressions for E1 and E2 in terms of ...
... (a) Let V1 and V2 be the electric potentials across the upper and lower dielectrics, respectively. What are the corresponding electric fields E1 and E2 ? By applying the appropriate boundary condition at the interface between the two dielectrics, obtain explicit expressions for E1 and E2 in terms of ...
Solutions for class #10 from Yosumism website Problem 1:
... The field is given as just B. The area of the loop is just , i.e., the cross-sectional area of the cylinder. As the cylinder is spun around, its flux changes at the rate of N rps. The change in flux is thus , and this is the magnitude of the potential difference in choice (C). (Also, one can drop ou ...
... The field is given as just B. The area of the loop is just , i.e., the cross-sectional area of the cylinder. As the cylinder is spun around, its flux changes at the rate of N rps. The change in flux is thus , and this is the magnitude of the potential difference in choice (C). (Also, one can drop ou ...
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field Project Overview
... at optical wavelengths, the emission you observe may have been emitted at much shorter (blue Visible or even UV) wavelengths. -Irregulars: Some galaxies can not be classified neatly as Spiral or Elliptical (or some variation thereof). These galaxies are then lumped into a catch-all morphological cla ...
... at optical wavelengths, the emission you observe may have been emitted at much shorter (blue Visible or even UV) wavelengths. -Irregulars: Some galaxies can not be classified neatly as Spiral or Elliptical (or some variation thereof). These galaxies are then lumped into a catch-all morphological cla ...
Exploring Space—The Universe: The Vast
... away from each other. What does it mean when scientists say they have detected a redshift in the color of the galaxies? Discuss answers from the video. (As wavelengths of light spread out, their color appears on the red end of the visible spectrum.) Does this mean that the universe is getting bigger ...
... away from each other. What does it mean when scientists say they have detected a redshift in the color of the galaxies? Discuss answers from the video. (As wavelengths of light spread out, their color appears on the red end of the visible spectrum.) Does this mean that the universe is getting bigger ...
The Universe
... generally the most massive, and also represent the endpoint in collisions between large spiral galaxies M87 is shown on the right ...
... generally the most massive, and also represent the endpoint in collisions between large spiral galaxies M87 is shown on the right ...
Homework-Current
... current is uniformly distributed over the outer surface of the wire (none is flowing through the "volume" of the wire; it's all surface charge), what is the surface current density K? B) Suppose that current does flow throughout the volume of the wire, in such a way that the volume current density J ...
... current is uniformly distributed over the outer surface of the wire (none is flowing through the "volume" of the wire; it's all surface charge), what is the surface current density K? B) Suppose that current does flow throughout the volume of the wire, in such a way that the volume current density J ...
Neutrinos and SN1987A
... (because although photons and neutrinos travel at relatively similar speeds, photons are not released until a shock wave reaches the surface of a star). The detection of a large amount of neutrinos from the core collapse of a star confirmed theories both about neutrinos and supernovae. If neutrinos ...
... (because although photons and neutrinos travel at relatively similar speeds, photons are not released until a shock wave reaches the surface of a star). The detection of a large amount of neutrinos from the core collapse of a star confirmed theories both about neutrinos and supernovae. If neutrinos ...
here are the solutions
... maximal. All of this energy is converted to K.E. and mgh = 0 right before the ball hits the ground. During the bounce, the ball gets compressed and all of the kinetic energy gets converted into elastic (deformation) energy. This gets converted back to kinetic energy at the end of the bounce, and all ...
... maximal. All of this energy is converted to K.E. and mgh = 0 right before the ball hits the ground. During the bounce, the ball gets compressed and all of the kinetic energy gets converted into elastic (deformation) energy. This gets converted back to kinetic energy at the end of the bounce, and all ...
SCIN 293-PL-New Course
... Topic Mastery: Based on the Hubble tuning fork compared the properties of the different classes of galaxies and their stellar populations. ...
... Topic Mastery: Based on the Hubble tuning fork compared the properties of the different classes of galaxies and their stellar populations. ...
The Electric Universe by Wallace Thornhill and David Talbott
... Raised in Portland, Oregon, David Talbott has remained in the area all his life. A graduate of Portland State University, where he majored in education and political science, he returned briefly for graduate work in urban studies. His college observations on the failure of modern education led him t ...
... Raised in Portland, Oregon, David Talbott has remained in the area all his life. A graduate of Portland State University, where he majored in education and political science, he returned briefly for graduate work in urban studies. His college observations on the failure of modern education led him t ...
English - Wise Observatory
... The ALFALFA survey detected 14 galaxies in a small region of the nearby Universe that are at about the same distance from us and whose optical images hint at their young age. The attention of the investigators was attracted by the appearance of the galaxies on the sky; they seemed to be arranged alo ...
... The ALFALFA survey detected 14 galaxies in a small region of the nearby Universe that are at about the same distance from us and whose optical images hint at their young age. The attention of the investigators was attracted by the appearance of the galaxies on the sky; they seemed to be arranged alo ...
Fields, particles and frontiers of physics - Specimen
... Describe the important properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation and how the standard model of the Universe explains these properties. Explain their significance as evidence for the past evolution of the Universe. ...
... Describe the important properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation and how the standard model of the Universe explains these properties. Explain their significance as evidence for the past evolution of the Universe. ...
Flatness problem

The flatness problem (also known as the oldness problem) is a cosmological fine-tuning problem within the Big Bang model of the universe. Such problems arise from the observation that some of the initial conditions of the universe appear to be fine-tuned to very 'special' values, and that a small deviation from these values would have had massive effects on the nature of the universe at the current time.In the case of the flatness problem, the parameter which appears fine-tuned is the density of matter and energy in the universe. This value affects the curvature of space-time, with a very specific critical value being required for a flat universe. The current density of the universe is observed to be very close to this critical value. Since the total density departs rapidly from the critical value over cosmic time, the early universe must have had a density even closer to the critical density, departing from it by one part in 1062 or less. This leads cosmologists to question how the initial density came to be so closely fine-tuned to this 'special' value.The problem was first mentioned by Robert Dicke in 1969. The most commonly accepted solution among cosmologists is cosmic inflation, the idea that the universe went through a brief period of extremely rapid expansion in the first fraction of a second after the Big Bang; along with the monopole problem and the horizon problem, the flatness problem is one of the three primary motivations for inflationary theory.