atomic number
... generated, creating a glowing patch where they strike the glass at the opposite end of the tube. Through experimentation, Thomson discovered that the rays could be deflected by an electric field (in addition to magnetic fields, which was already known). He concluded that these rays, rather than bein ...
... generated, creating a glowing patch where they strike the glass at the opposite end of the tube. Through experimentation, Thomson discovered that the rays could be deflected by an electric field (in addition to magnetic fields, which was already known). He concluded that these rays, rather than bein ...
"Strange nuclear materials"()
... are not emitted from nuclei in beta decay, but are created, along with neutrinos. The idea that particles can be created was one consequence of combining quantum mechanics with Einstein’s special theory of relativity, a feat achieved by Paul Dirac. Combining relativity and quantum mechanics had anot ...
... are not emitted from nuclei in beta decay, but are created, along with neutrinos. The idea that particles can be created was one consequence of combining quantum mechanics with Einstein’s special theory of relativity, a feat achieved by Paul Dirac. Combining relativity and quantum mechanics had anot ...
Spring Semester 2009
... B. In the circuit diagram above, draw in an ammeter to measure the current from the battery. C. Determine what the ammeter would read for this circuit. D. In the circuit diagram above, draw in a voltmeter to measure the voltage across the 15 Ω resistor. Determine what the voltmeter would read for th ...
... B. In the circuit diagram above, draw in an ammeter to measure the current from the battery. C. Determine what the ammeter would read for this circuit. D. In the circuit diagram above, draw in a voltmeter to measure the voltage across the 15 Ω resistor. Determine what the voltmeter would read for th ...
File
... 11. describe, predict, explain, and perform experiments that demonstrate the effect of: - a uniform magnetic field on a moving charge , - a uniform magnetic field on a current-carrying conductor, -two current carrying wires side-by-side - a moving conductor (eg. a wire) in an external magnetic fiel ...
... 11. describe, predict, explain, and perform experiments that demonstrate the effect of: - a uniform magnetic field on a moving charge , - a uniform magnetic field on a current-carrying conductor, -two current carrying wires side-by-side - a moving conductor (eg. a wire) in an external magnetic fiel ...
The Alternative to the Standard Model The Nuclear Forces
... nature of nuclear forces would remain an enigma. The reader should remember that this whole approach concerning the charge and mass distribution in the proton and neutron, with known values of energy, mass and magnetic moments, is supported by an irrefutable fact: all this lead us to a binding energ ...
... nature of nuclear forces would remain an enigma. The reader should remember that this whole approach concerning the charge and mass distribution in the proton and neutron, with known values of energy, mass and magnetic moments, is supported by an irrefutable fact: all this lead us to a binding energ ...
Matter Waves - Common Sense Science
... corresponding electromagnetic fields) arranged in a geometry that is able to produce the properties of a particle and/or a wave in experiments (the position of Parson, Iida, Bostick, and Common Sense Science). Charged Ring Model. The ring electron is composed purely of electrostatic charge, the esse ...
... corresponding electromagnetic fields) arranged in a geometry that is able to produce the properties of a particle and/or a wave in experiments (the position of Parson, Iida, Bostick, and Common Sense Science). Charged Ring Model. The ring electron is composed purely of electrostatic charge, the esse ...
physical world
... theory (Quantum Mechanics) to deal with atomic and molecular phenomena. Just as a new experiment may suggest an alternative theoretical model, a theoretical advance may suggest what to look for in some experiments. The result of experiment of scattering of alpha particles by gold foil, in 1911 by Er ...
... theory (Quantum Mechanics) to deal with atomic and molecular phenomena. Just as a new experiment may suggest an alternative theoretical model, a theoretical advance may suggest what to look for in some experiments. The result of experiment of scattering of alpha particles by gold foil, in 1911 by Er ...
Scaling investigation for the dynamics of charged particles in an
... As an attempt to explain the origin of high energy cosmic rays, Fermi proposed a simple model1 where charged particles interact with time dependent magnetic fields. Such interaction triggered a mechanism leading them to exhibit an enormous energy growth. The phenomena of unlimited energy gain, also ...
... As an attempt to explain the origin of high energy cosmic rays, Fermi proposed a simple model1 where charged particles interact with time dependent magnetic fields. Such interaction triggered a mechanism leading them to exhibit an enormous energy growth. The phenomena of unlimited energy gain, also ...
Electrospray Operation Using Nitrogen in Place of Air Application
... To prevent these phenomena, the gas or gas mixture used in an electrospray must be electrically insulating. That is, the gas molecules can remove electrons freed during ionization by attaching to the electrons during collisions. N2 is a non-electron-attaching gas, due to its electronic structure, an ...
... To prevent these phenomena, the gas or gas mixture used in an electrospray must be electrically insulating. That is, the gas molecules can remove electrons freed during ionization by attaching to the electrons during collisions. N2 is a non-electron-attaching gas, due to its electronic structure, an ...
Note 2e - Decay Processes
... It turns out that the linear momentum & angular momentum are also violated, and a third particle is needed in order for both momenta to be balanced before & after the decay ...
... It turns out that the linear momentum & angular momentum are also violated, and a third particle is needed in order for both momenta to be balanced before & after the decay ...
PowerPoint Transparencies
... Typically, the brane realization is useful in a regime of parameter space different from the one in which the gauge theory is valid. For protected quantities related to the vacuum structure this should not matter, but the possible existence and properties of metastable states might ...
... Typically, the brane realization is useful in a regime of parameter space different from the one in which the gauge theory is valid. For protected quantities related to the vacuum structure this should not matter, but the possible existence and properties of metastable states might ...
why do physicists think that there are extra dimensions
... an extra dimension of space just means new degrees of freedom of a certain type (Kaluza-Klein modes). but we already have discovered examples in string theory (e.g. AdS/CFT) where new degrees of freedom can be interpreted either as an extra dimension or as new dynamics without an extra dimension! ...
... an extra dimension of space just means new degrees of freedom of a certain type (Kaluza-Klein modes). but we already have discovered examples in string theory (e.g. AdS/CFT) where new degrees of freedom can be interpreted either as an extra dimension or as new dynamics without an extra dimension! ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... (46%), silicate particles (17%) and particles made of a lower density material (37%). At larger size (>10 m) most meteoroids are expected to be silicate particles, with an average density of 2.5 g/cm3. On the other hand, orbital debris consists of fragments of various size left in the space env ...
... (46%), silicate particles (17%) and particles made of a lower density material (37%). At larger size (>10 m) most meteoroids are expected to be silicate particles, with an average density of 2.5 g/cm3. On the other hand, orbital debris consists of fragments of various size left in the space env ...
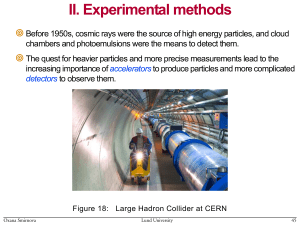
Accelerators - Particle Physics, Lund University
... “generator” at CERN: accelerates particles by an electrostatic field Oxana Smirnova ...
... “generator” at CERN: accelerates particles by an electrostatic field Oxana Smirnova ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.