mean-field approach to magnetism
... calculate exactly the partition function, the natural way to work is to do some approximations. Several approximation methods are known between them the easiest one is the mean-field approximation. Other well-known approximations are the low and high temperature expansion, renormalization, scaling o ...
... calculate exactly the partition function, the natural way to work is to do some approximations. Several approximation methods are known between them the easiest one is the mean-field approximation. Other well-known approximations are the low and high temperature expansion, renormalization, scaling o ...
Particles and Waves Class Questions
... A particle can be represented by a symbol MA X where M represents the mass number, A the atomic number and X identifies the type of particle, for example a proton can be represented by 11 p . Give the symbols, in this form, for the following particles. (a) ...
... A particle can be represented by a symbol MA X where M represents the mass number, A the atomic number and X identifies the type of particle, for example a proton can be represented by 11 p . Give the symbols, in this form, for the following particles. (a) ...
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics • Dynamics • Two distinct parts:
... It gives t as a function of s. Rearrange to obtain s as a function of t to get the position coordinate. In all these cases, if integration is difficult, graphical, analytical, or computer methods can be utilized. ME101 - Division III ...
... It gives t as a function of s. Rearrange to obtain s as a function of t to get the position coordinate. In all these cases, if integration is difficult, graphical, analytical, or computer methods can be utilized. ME101 - Division III ...
Effective Field Theories, Reductionism and Scientific Explanation
... of the linearity of Maxwell’s equations (‘superposition principle’). In quantum electrodynamics, however, the superposition principle does not hold. Now, photons can interact and the elementary process, the discovery of which Euler attributes to Otto Halpern and Peter Debye, is this: the two photons ...
... of the linearity of Maxwell’s equations (‘superposition principle’). In quantum electrodynamics, however, the superposition principle does not hold. Now, photons can interact and the elementary process, the discovery of which Euler attributes to Otto Halpern and Peter Debye, is this: the two photons ...
Chemistry in Four Dimensions
... three quantum numbers. However, in order to account for atomic spectra, it is necessary to assume that the extranuclear electrons are not all concentrated at the lowest energy level, but distributed over several levels as stipulated by a fourth quantum number, postulated to represent a two-level spi ...
... three quantum numbers. However, in order to account for atomic spectra, it is necessary to assume that the extranuclear electrons are not all concentrated at the lowest energy level, but distributed over several levels as stipulated by a fourth quantum number, postulated to represent a two-level spi ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... (the drop method) – this of course also fixed the electron mass. The atomic nucleus Subsequently, different models of the atom were discussed, one of them being the model of Thomson. In this model, the electrons, and an equivalent number of positively charged particles are uniformly distributed thro ...
... (the drop method) – this of course also fixed the electron mass. The atomic nucleus Subsequently, different models of the atom were discussed, one of them being the model of Thomson. In this model, the electrons, and an equivalent number of positively charged particles are uniformly distributed thro ...
Abstracts - Texas Section AAPT
... a quantum particle (qp) in a dense Lennard-Jones 6-12 fluid having the thermodynamic properties of Xenon. Because of the difference in thermal wavelengths between the qp and the fluid molecules the fluid molecules can be treated classically. This combination of using quantum mechanics for the qp and ...
... a quantum particle (qp) in a dense Lennard-Jones 6-12 fluid having the thermodynamic properties of Xenon. Because of the difference in thermal wavelengths between the qp and the fluid molecules the fluid molecules can be treated classically. This combination of using quantum mechanics for the qp and ...
Notes for course on Physics of Particles and Fields, CMI, Autumn
... 10.11Magnetic moments from quark model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206 10.12QCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208 10.13Spontaneous global symmetry breaking ...
... 10.11Magnetic moments from quark model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206 10.12QCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208 10.13Spontaneous global symmetry breaking ...
Microscopic Theory of Superconductivity
... Leon N. Cooper, and J. Robert Schrieffer[1, 2]. It is among the most beautiful and successful theories in physics. The BCS-theory starts from an effective Hamiltonian of fermionic quasiparticle excitations that interact via a weak attractive interaction. It yields a ground-state many-body wave funct ...
... Leon N. Cooper, and J. Robert Schrieffer[1, 2]. It is among the most beautiful and successful theories in physics. The BCS-theory starts from an effective Hamiltonian of fermionic quasiparticle excitations that interact via a weak attractive interaction. It yields a ground-state many-body wave funct ...
The role of angular momentum conservation law in statistical
... As shown in [1,2] the statistical mechanics of charged particles gas in magnetic field can be formulated without paradoxes if the density of distribution (or the statistical operator in quantum theory) is considered to be also dependent on the angular momentum. The role of various motion integrals i ...
... As shown in [1,2] the statistical mechanics of charged particles gas in magnetic field can be formulated without paradoxes if the density of distribution (or the statistical operator in quantum theory) is considered to be also dependent on the angular momentum. The role of various motion integrals i ...
thin conducting wires or cables interacting with a surrounding
... In Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) methods, where a regular structured mesh is used, it is in fact possible to include the effect of conducting wires having a radius much smaller than the mesh size into a global 3D model [1]. A Telegrapher's equation is employed to solve for the wire current, t ...
... In Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) methods, where a regular structured mesh is used, it is in fact possible to include the effect of conducting wires having a radius much smaller than the mesh size into a global 3D model [1]. A Telegrapher's equation is employed to solve for the wire current, t ...
1. Mathematical Principles of Modern Natural Philosophy
... described by localizing the external forces in space and time and by considering the superposition of the corresponding special responses (method of the Green’s function). Furthermore, this can be used for computing nonlinear physical systems by iteration. (C) Planck’s constant: The smallest action ...
... described by localizing the external forces in space and time and by considering the superposition of the corresponding special responses (method of the Green’s function). Furthermore, this can be used for computing nonlinear physical systems by iteration. (C) Planck’s constant: The smallest action ...
幻灯片 1
... Michael Faraday (1791-1867) made one of the most important discoveries in the sciences of electricity and magnetism; namely, electromagnetic induction. James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) . His most important contribution was the extension and mathematical formulation of previous works on electricity ...
... Michael Faraday (1791-1867) made one of the most important discoveries in the sciences of electricity and magnetism; namely, electromagnetic induction. James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) . His most important contribution was the extension and mathematical formulation of previous works on electricity ...
MANUEL AGUILAR BENÍTEZ DE LUGO, 57 años
... 1997−2014. Joins the AMS−ISS (ALPHA Magnetic Spectrometer at the International Space Station) project, under the leadership of Prof. S.C.C. Ting, and organizes the participation of Spain (CIEMAT and IAC). CIEMAT builds the Avionic Box for the cryomagnet and is the leading Institute for the project o ...
... 1997−2014. Joins the AMS−ISS (ALPHA Magnetic Spectrometer at the International Space Station) project, under the leadership of Prof. S.C.C. Ting, and organizes the participation of Spain (CIEMAT and IAC). CIEMAT builds the Avionic Box for the cryomagnet and is the leading Institute for the project o ...
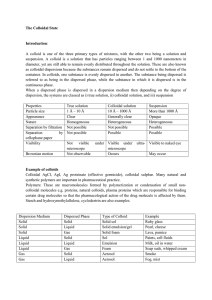
The Colloidal State Introduction: A colloid is one of the three primary
... Take a colloidal sol say AS2S3 sol in a U – tube. Place an electrolyte, having density less than that of solution (say distilled water). The electrolyte provides distinct boundary between electrolyte and colloidal sol. Place two platinum electrodes in two arms of U – tube such that they dip in the ...
... Take a colloidal sol say AS2S3 sol in a U – tube. Place an electrolyte, having density less than that of solution (say distilled water). The electrolyte provides distinct boundary between electrolyte and colloidal sol. Place two platinum electrodes in two arms of U – tube such that they dip in the ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.